Ready to leave?
Oops ! Condition name you have entered is invalid.
You are now leaving Aposbook.com and going to an external site managed by another organization.
Please confirm your email address and try to login again.
This account has been deleted. do you want to restore it?

Validate your email
A verification link will be sent to within the next 2 minutes. Please click it to validate your e mail.
*If you didn't get the link, please check your spam folder
Welcome to Aposbook,
As a registered user, you can benefit from the various free tools and services that we provide.
All you need to do is log in to start discussing with others, interacting, asking questions, and sharing your point of view about the various topics.
You can also write reviews and testimonials about any natural solution you have tried and share your experience. Your feedback can be very helpful.
If you are a health expert, you can add information about any topic or suggest text edit. You can also publish content, including articles and videos, about any topic from the related library section.
Together we can help.
The Aposbook Team
Forgot Password?
A validation link will be sent to you by email. Please confirm your address to log in
*If you didn't get the link, please check your spam folder
Please log in to use this feature
Your account has been suspended because you have violated our code of conduct. If you think this was a mistake, you can contact us by email at: support@aposbook.com "Contact us" form.
Success! Thank you for your feedback. Your contribution can make a difference. Together we can help each other.


Diseases and conditions
GERD (Acid Reflux)
Acid Reflux (GERD): Causes, Prevention, Natural Treatments
Complete Guide to GERD (Acid Reflux)
What is GERD (Gastroesophageal Reflux Disease)
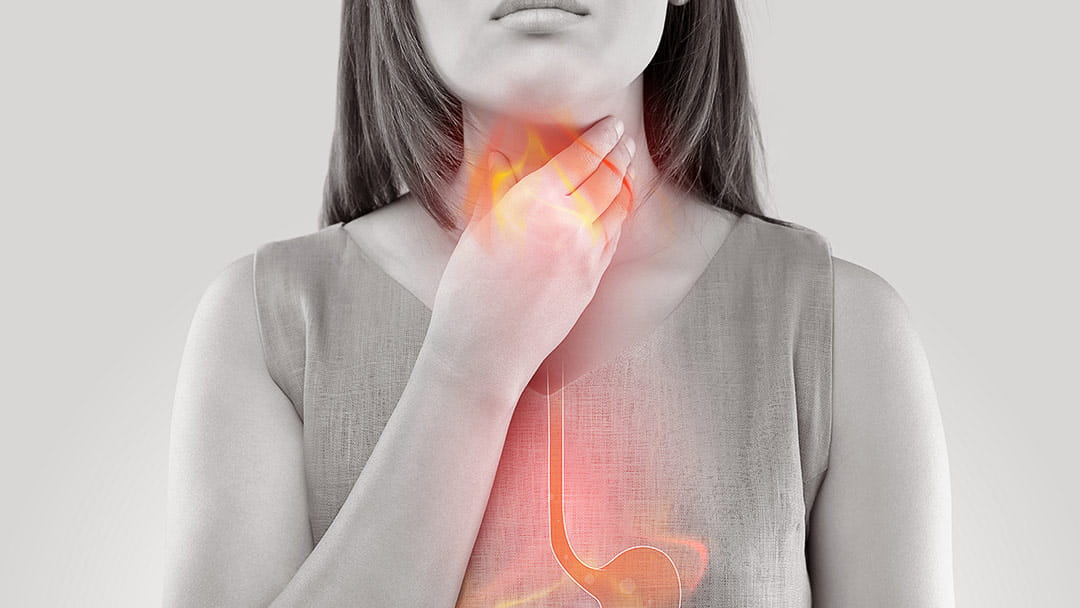
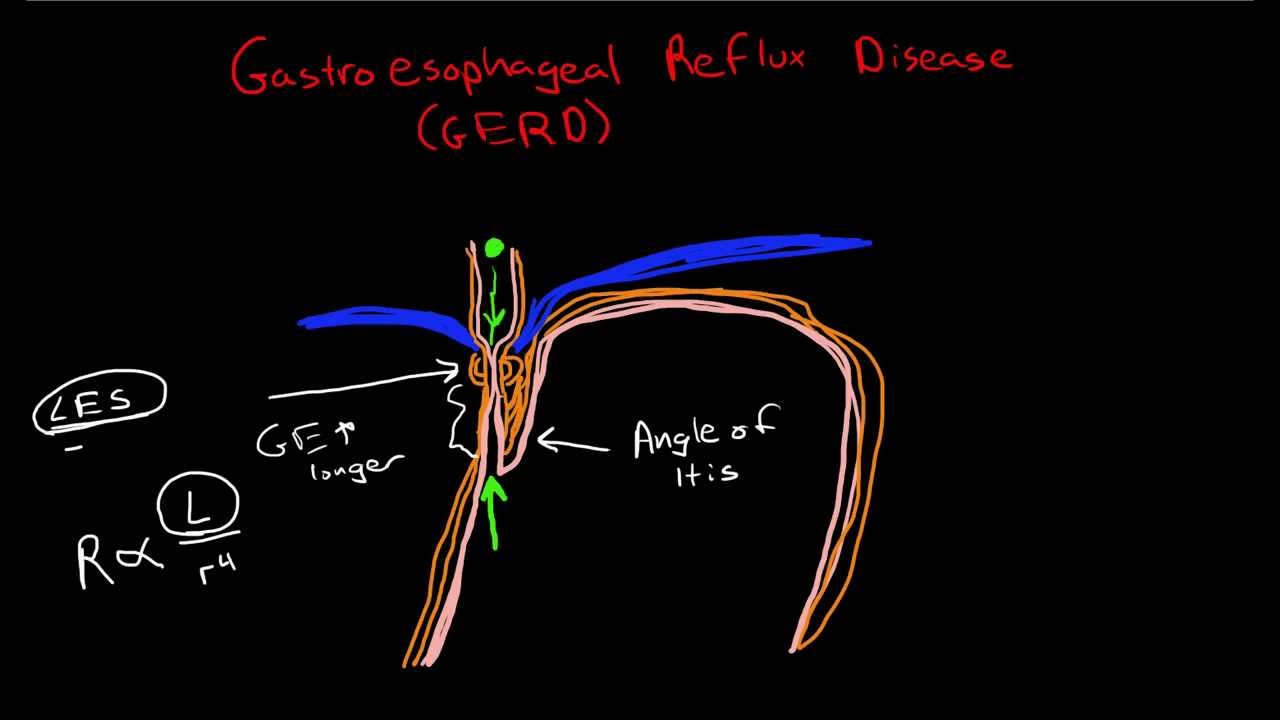
Gastroesophageal reflux disease (GERD) is a digestive disorder that affects the lower esophageal sphincter (LES) causing the reflux of gastric content.
GERD occurs when stomach acid flows back into the esophagus which is the tube that runs through the throat connecting the mouth and the stomach.
The esophagus is a muscular tube about 8 inches long. At the very end of this tube is a valve called the lower esophageal sphincter (LES) which closes ...
What is GERD (Gastroesophageal Reflux Disease)
Gastroesophageal reflux disease (GERD) is a digestive disorder that affects the lower esophageal sphincter (LES) causing the reflux of gastric content.
GERD occurs when stomach acid flows back into the esophagus which is the tube that runs through the throat connecting the mouth and the stomach.
The esophagus is a muscular tube about 8 inches long. At the very end of this tube is a valve called the lower esophageal sphincter (LES) which closes the entrance to the stomach and keeps the food we eat inside it.
Normally, the LES closes after the food passes through it. However, in someone suffering from GERD, the sphincter does not function properly.
This causes the food and stomach acid to move back into the esophagus. Gastric content can even reach the throat and mouth. This produces a feeling of discomfort and causes various symptoms, such as a burning sensation in the chest, called heartburn, and an acidic taste in the throat and mouth.
GERD could be due to the lower esophageal sphincter’s weak muscles or to a hiatal hernia at the entrance of the stomach. A hiatal hernia occurs when the upper part of the stomach pushes through an opening in the diaphragm and into the chest. The diaphragm is the muscle that separates the chest and the stomach. It helps keep stomach acid and food inside the stomach.
GERD symptoms can be easily controlled if people watch over their diet, change their lifestyle and eating habits, or take natural over-the-counter medicine. However, sometimes GERD cases can be more complicated and require further medical attention.
Types of GERD
There are two primary types of GERD (Gastroesophageal Reflux Disease), each with distinct characteristics and symptoms:
Erosive GERD (Erosive Esophagitis): This form occurs when the stomach acid damages the esophageal lining, leading to visible inflammation and erosion in the esophagus. Symptoms include heartburn, chest pain, difficulty swallowing, and sometimes bleeding or ulcers. Erosive GERD is often diagnosed through an endoscopy, where the damage to the esophagus lining can be seen.
Non-Erosive Reflux Disease (NERD): In this type of GERD, patients experience typical reflux symptoms like heartburn and regurgitation, but there is no visible damage to the esophagus lining during an endoscopy. Although the esophagus appears normal, the acid reflux still causes discomfort. NERD is common, and the symptoms may be less severe than erosive GERD, but can still impact quality of life.
Each type reflects varying degrees of acid reflux severity and may require different approaches for diagnosis and treatment.
Development of GERD: Progression and Complications
While GERD can often be managed with lifestyle changes and over-the-counter treatments, if left untreated, it can progressively worsen over time. As stomach acid continues to flow back into the esophagus, the repeated exposure can irritate and damage the lining of the esophagus, leading to inflammation and a range of complications.
One of the early stages in the development of GERD is esophagitis, where the esophagus becomes inflamed due to the irritation from acid reflux. As the condition progresses, more severe complications may arise, such as esophageal strictures—a narrowing of the esophagus caused by scar tissue—or the development of Barrett’s Esophagus, a serious condition where the lining of the esophagus begins to change, increasing the risk of esophageal cancer.
Addressing GERD early is crucial to prevent the condition from advancing and leading to these complications.
Causes of Acid Reflux (GERD)
GERD is primarily caused by dysfunction of the lower esophageal sphincter (LES) that allows stomach contents to flow back into the esophagus. The following factors contribute to this dysfunction:
- Weak or Relaxed Lower Esophageal Sphincter (LES): The LES fails to close properly, allowing acid to escape from the stomach.
- Hiatal Hernia: A condition where the upper part of the stomach pushes through the diaphragm into the chest cavity, weakening the LES.
- Obesity: Increased pressure on ...
Causes of Acid Reflux (GERD)
GERD is primarily caused by dysfunction of the lower esophageal sphincter (LES) that allows stomach contents to flow back into the esophagus. The following factors contribute to this dysfunction:
- Weak or Relaxed Lower Esophageal Sphincter (LES): The LES fails to close properly, allowing acid to escape from the stomach.
- Hiatal Hernia: A condition where the upper part of the stomach pushes through the diaphragm into the chest cavity, weakening the LES.
- Obesity: Increased pressure on the stomach can cause acid reflux, leading to GERD.
- Pregnancy: Hormonal changes and pressure on the stomach during pregnancy can cause GERD.
- Delayed Stomach Emptying: When the stomach doesn't empty properly, it increases the likelihood of reflux.
- Smoking: Smoking weakens the LES and increases stomach acid production.
- Overeating: Consuming large meals can place excessive pressure on the LES.
Acid Reflux (GERD) Risk Factors
Certain factors make individuals more prone to developing GERD. These include:
- Obesity: Excess body weight increases pressure on the abdomen, pushing stomach contents into the esophagus.
- Pregnancy: Hormonal changes and increased pressure on the stomach are common triggers.
- Age: Older adults are more likely to experience a weakened LES.
- Diet: Consumption of fatty or fried foods, chocolate, caffeine, alcohol, and acidic foods increases the risk of acid reflux.
- Medications: Certain medications like painkillers, muscle ...
Acid Reflux (GERD) Risk Factors
Certain factors make individuals more prone to developing GERD. These include:
- Obesity: Excess body weight increases pressure on the abdomen, pushing stomach contents into the esophagus.
- Pregnancy: Hormonal changes and increased pressure on the stomach are common triggers.
- Age: Older adults are more likely to experience a weakened LES.
- Diet: Consumption of fatty or fried foods, chocolate, caffeine, alcohol, and acidic foods increases the risk of acid reflux.
- Medications: Certain medications like painkillers, muscle relaxants, and blood pressure drugs can exacerbate GERD symptoms.
- Hiatal Hernia: This structural abnormality raises the likelihood of reflux.
Acid Reflux (GERD) Symptoms
GERD manifests with a range of symptoms that vary in intensity. Common signs include:
- Heartburn: A burning sensation in the chest, often after eating, which may worsen at night.
- Regurgitation: The sensation of acid backing up into the throat or mouth, leaving a sour or bitter taste.
- Chest Pain: Discomfort or pain in the chest, often mistaken for a heart attack.
- Difficulty Swallowing (Dysphagia): A feeling of food being stuck in the throat or chest.
- Chronic ...
Acid Reflux (GERD) Symptoms
GERD manifests with a range of symptoms that vary in intensity. Common signs include:
- Heartburn: A burning sensation in the chest, often after eating, which may worsen at night.
- Regurgitation: The sensation of acid backing up into the throat or mouth, leaving a sour or bitter taste.
- Chest Pain: Discomfort or pain in the chest, often mistaken for a heart attack.
- Difficulty Swallowing (Dysphagia): A feeling of food being stuck in the throat or chest.
- Chronic Cough: Persistent coughing, often worse at night.
- Hoarseness or Sore Throat: Acid reflux can irritate the throat and vocal cords.
- Nausea: Feeling sick to the stomach, especially after meals.
- Bad Breath: A sour or foul smell from acid regurgitation.
Acid Reflux (GERD) Diagnosis
Diagnosing GERD typically involves a combination of assessing symptoms and conducting specific tests to confirm the condition. A healthcare provider may recommend various diagnostic methods to evaluate the severity and determine the most appropriate treatment plan.
- Medical History and Symptom Assessment: The first step in diagnosing GERD is a thorough review of the patient's symptoms, such as heartburn, regurgitation, and difficulty swallowing. The doctor will also ask about any contributing factors, including diet, smoking, medications, and ...
Acid Reflux (GERD) Diagnosis
Diagnosing GERD typically involves a combination of assessing symptoms and conducting specific tests to confirm the condition. A healthcare provider may recommend various diagnostic methods to evaluate the severity and determine the most appropriate treatment plan.
- Medical History and Symptom Assessment: The first step in diagnosing GERD is a thorough review of the patient's symptoms, such as heartburn, regurgitation, and difficulty swallowing. The doctor will also ask about any contributing factors, including diet, smoking, medications, and lifestyle habits.
- Endoscopy: During an endoscopy, a thin, flexible tube with a camera is inserted into the esophagus to examine the lining for inflammation, damage, or other abnormalities. This is often done to rule out complications like esophagitis or Barrett’s esophagus.
- pH Monitoring: A pH monitoring test measures the acid levels in the esophagus over a 24-hour period. This test helps determine how frequently stomach acid enters the esophagus and confirms if it correlates with symptoms.
- Esophageal Manometry: This test assesses the pressure and function of the muscles in the esophagus, including the lower esophageal sphincter (LES). It helps to identify issues with esophageal motility, which could contribute to GERD symptoms.
- Barium Swallow (Upper GI Series): During a barium swallow, the patient drinks a liquid that coats the esophagus and stomach, allowing for clear X-ray images. This helps identify structural problems, such as a hiatal hernia, that could be causing GERD.
- Esophageal Biopsy: If inflammation or damage is found during an endoscopy, a biopsy may be performed to check for conditions like Barrett’s esophagus, which can be a precursor to esophageal cancer.
Natural Treatments for GERD
There are lot of various natural solutions to for acid reflux. Click on natural treatments for GERD to find a detailed list of all these natural treatments for GERD, including various natural therapies, diet programs, alternative medicine, vitamins, supplements, herbal medicine, and home remedies.
You can also go to www.aposbook.com to find all the natural treatments for any medical condition IN ONE CLICK.
Meanwhile, the natural solutions for GERD work on different aspects of this condition ...
Natural Treatments for GERD
There are lot of various natural solutions to for acid reflux. Click on natural treatments for GERD to find a detailed list of all these natural treatments for GERD, including various natural therapies, diet programs, alternative medicine, vitamins, supplements, herbal medicine, and home remedies.
You can also go to www.aposbook.com to find all the natural treatments for any medical condition IN ONE CLICK.
Meanwhile, the natural solutions for GERD work on different aspects of this condition. Some focus by balancing the pH levels in the stomach to reduce acidity while others work on easing the symptoms by eliminating stress. These natural solutions include:
- Herbs: some herbs, such as licorice or chamomile, help reduce the symptoms of GERD and provide quick relief. Licorice helps coat the esophagus and protects it from the damaging effects of the refluxing stomach acid.
- Relaxation techniques: some relaxing techniques can reduce the stress and anxiety that can trigger GERD symptoms.
- Food and nutrition: some foods, such as apple cider vinegar, work on balancing the pH levels in the stomach which helps treat GERD.
Medical Treatment for GERD
When lifestyle changes and natural remedies fail to relieve the symptoms of GERD, medical treatment becomes necessary to manage the condition and prevent further complications. These treatments focus on reducing acid production, improving the function of the lower esophageal sphincter (LES), and protecting the esophagus from damage.
- Antacids: Antacids are often the first line of treatment for GERD. They work by neutralizing stomach acid and providing quick relief from heartburn and acid reflux. Common over-the-counter antacids include ...
Medical Treatment for GERD
When lifestyle changes and natural remedies fail to relieve the symptoms of GERD, medical treatment becomes necessary to manage the condition and prevent further complications. These treatments focus on reducing acid production, improving the function of the lower esophageal sphincter (LES), and protecting the esophagus from damage.
- Antacids: Antacids are often the first line of treatment for GERD. They work by neutralizing stomach acid and providing quick relief from heartburn and acid reflux. Common over-the-counter antacids include magnesium hydroxide, calcium carbonate, and aluminum hydroxide. However, they are best for short-term relief as they don't address the underlying cause of GERD.
- H2 Blockers: H2 blockers, such as ranitidine, cimetidine, and famotidine, work by reducing the amount of acid the stomach produces. They provide longer-lasting relief compared to antacids and are often used for mild to moderate cases of GERD.
- Proton Pump Inhibitors (PPIs): PPIs, such as omeprazole, esomeprazole, and lansoprazole, are considered more effective than H2 blockers for treating GERD. They work by blocking the enzyme in the stomach lining that produces acid. PPIs are typically recommended for moderate to severe GERD cases and are used long-term to help heal the esophagus and prevent complications like esophagitis.
- Prokinetics: Medications like metoclopramide help the stomach empty more quickly and improve the function of the LES, reducing the risk of acid reflux. Prokinetics can be used alongside other GERD treatments, though they are less commonly prescribed due to side effects.
- Surgery (Fundoplication): In severe cases of GERD where medication does not provide sufficient relief, surgery may be recommended. The most common surgical procedure is fundoplication, which involves wrapping the top part of the stomach around the LES to strengthen the sphincter and prevent reflux. This can be done laparoscopically and is often considered when GERD significantly impacts quality of life.
- LINX Device: The LINX device is a newer, minimally invasive surgical option. A small ring of magnetic beads is placed around the LES to reinforce it. The beads allow food to pass through but prevent stomach acid from flowing back into the esophagus. This is an alternative to more invasive procedures like fundoplication.
- Endoscopic Treatments: Several endoscopic techniques are being developed to treat GERD, including procedures to tighten the LES or reduce acid production. These procedures may offer a less invasive option for patients who need more than medication but want to avoid surgery.
Medical treatment for GERD focuses on both symptom relief and preventing complications, with options ranging from medications to surgical interventions for more severe cases.
Frequently Asked Questions About Acid Reflux (GERD)
What is GERD?
Gastroesophageal reflux disease (GERD) is a chronic digestive disorder where stomach acid frequently flows back into the esophagus, causing symptoms like heartburn and acid regurgitation.
What causes GERD?
GERD is caused by the malfunction of the lower esophageal sphincter (LES), which fails to close properly, allowing stomach acid to flow back into the esophagus. Contributing factors include obesity, pregnancy, smoking, hiatal hernia, and certain foods or medications.
What are the ...
Frequently Asked Questions About Acid Reflux (GERD)
What is GERD?
Gastroesophageal reflux disease (GERD) is a chronic digestive disorder where stomach acid frequently flows back into the esophagus, causing symptoms like heartburn and acid regurgitation.
What causes GERD?
GERD is caused by the malfunction of the lower esophageal sphincter (LES), which fails to close properly, allowing stomach acid to flow back into the esophagus. Contributing factors include obesity, pregnancy, smoking, hiatal hernia, and certain foods or medications.
What are the symptoms of GERD?
Common symptoms of GERD include heartburn, regurgitation of food or sour liquid, difficulty swallowing, chest pain, and a chronic cough or sore throat.
How is GERD diagnosed?
GERD is diagnosed through various methods, including upper endoscopy, pH monitoring, esophageal manometry, and barium swallow tests. These tests help assess the esophagus and measure acid levels.
What are the natural treatments for GERD?
Natural treatments include lifestyle changes such as maintaining a healthy weight, avoiding trigger foods (like fatty, spicy, or acidic foods), elevating the head during sleep, and eating smaller meals. Herbal remedies such as licorice root, ginger, and chamomile tea may also help reduce symptoms.
Can GERD be cured?
While GERD is a chronic condition, symptoms can be managed with a combination of lifestyle changes, natural remedies, and medication. In severe cases, surgery may provide more permanent relief.
What foods should be avoided if I have GERD?
Foods that can trigger GERD symptoms include spicy foods, fatty and fried foods, citrus fruits, tomatoes, chocolate, peppermint, caffeine, and carbonated beverages.
Is surgery necessary for GERD?
Surgery is only considered for GERD when medications and lifestyle changes fail to manage symptoms effectively. The most common procedure is fundoplication, which strengthens the LES to prevent acid reflux.
What are the complications of untreated GERD?
If left untreated, GERD can lead to serious complications such as esophagitis (inflammation of the esophagus), Barrett's esophagus (a precancerous condition), and an increased risk of esophageal cancer.
Are proton pump inhibitors (PPIs) safe for long-term use?
While PPIs are effective for managing GERD, long-term use may lead to potential side effects, including nutrient deficiencies (like calcium and magnesium), increased risk of bone fractures, and gut infections. Consult your doctor for the best course of treatment.
-
React
-
[0]
- Comment (0)
Explore other Diseases and conditions
Natural Treatments for GERD (Acid Reflux)
GERD (Acid Reflux) Dos and Don'ts
Eating smaller portions throughout the day is important. This approach can help reduce the frequency and severity of acid reflux by minimizing the amount of food in the stomach at
Elevating the head of the bed is a recommended strategy for managing GERD symptoms, particularly nighttime reflux. This approach involves raising the upper part of the bed to
If you experience GERD symptoms, resting in an elevated position can help prevent acid reflux. Sleeping in a chair or on the back of a sofa can be an effective way to manage
Choosing the right foods can help manage GERD symptoms and promote overall digestive health. Opt for foods that are less likely to irritate the esophagus or increase stomach acid
Weight gain can significantly exacerbate GERD symptoms. Excess body weight, particularly around the abdominal area, increases pressure on the stomach. This additional pressure can
Wearing tight clothing can exacerbate GERD symptoms by increasing abdominal pressure. When clothing is snug around the waist, it can compress the stomach, pushing its contents
Smoking or chewing tobacco can significantly worsen GERD symptoms. Tobacco products can relax the lower esophageal sphincter (LES), the valve responsible for keeping stomach
Eating large meals or snacking shortly before bedtime can significantly exacerbate GERD symptoms. When you eat close to bedtime, the stomach remains full and the digestive process
Certain foods can exacerbate GERD symptoms by increasing stomach acid production or relaxing the lower esophageal sphincter (LES). Here’s a guide to foods and drinks that
Dos and Don'ts

Preventing GERD
Library center GERD (Acid Reflux)
Success storiess

Apple Cider Vinegar vs Acid Reflux - 6 Months Later plus FAQ





























Alice Cole
Can someone give me information on a disease call burning mouth, I would like to know if this can be treated with bee stinging, or anything for that matter. Can someone please contact me my phone number is (616)401-4488. Is in great need, I think I have the worst case of this and I need help to, relieve this horrible pain….. Thanks In Advance sincerely Alice Cole
Reply