Ready to leave?
Oops ! Condition name you have entered is invalid.
You are now leaving Aposbook.com and going to an external site managed by another organization.
Please confirm your email address and try to login again.
This account has been deleted. do you want to restore it?

Validate your email
A verification link will be sent to within the next 2 minutes. Please click it to validate your e mail.
*If you didn't get the link, please check your spam folder
Welcome to Aposbook,
As a registered user, you can benefit from the various free tools and services that we provide.
All you need to do is log in to start discussing with others, interacting, asking questions, and sharing your point of view about the various topics.
You can also write reviews and testimonials about any natural solution you have tried and share your experience. Your feedback can be very helpful.
If you are a health expert, you can add information about any topic or suggest text edit. You can also publish content, including articles and videos, about any topic from the related library section.
Together we can help.
The Aposbook Team
Forgot Password?
A validation link will be sent to you by email. Please confirm your address to log in
*If you didn't get the link, please check your spam folder
Please log in to use this feature
Your account has been suspended because you have violated our code of conduct. If you think this was a mistake, you can contact us by email at: support@aposbook.com "Contact us" form.
Success! Thank you for your feedback. Your contribution can make a difference. Together we can help each other.


Health and wellness
Back Pain
Lower Back Pain: Causes, Prevention, and Natural Cures
Complete Guide to Back Pain
Overview of Back Pain
Back pain, particularly lower back pain, is one of the most common medical complaints globally, affecting people of all ages and backgrounds. According to the World Health Organization (WHO), approximately 60-70% of adults will experience back pain at some point in their lives, with lower back pain being the leading cause of disability worldwide. Its impact is not just physical—it can severely affect an individual’s quality of life, work performance, and overall mental well-being.
Lower back ...
Overview of Back Pain
Back pain, particularly lower back pain, is one of the most common medical complaints globally, affecting people of all ages and backgrounds. According to the World Health Organization (WHO), approximately 60-70% of adults will experience back pain at some point in their lives, with lower back pain being the leading cause of disability worldwide. Its impact is not just physical—it can severely affect an individual’s quality of life, work performance, and overall mental well-being.
Lower back pain can be acute, lasting just a few days to weeks, or it can become a chronic condition that persists for three months or longer. Chronic pain often leads to long-term discomfort, limiting mobility and reducing the ability to perform daily activities. The distinction between acute and chronic pain is important, as each requires different approaches to management and treatment.
One of the main challenges with lower back pain is its multifactorial nature. It can be caused by physical issues, such as muscle strain or spinal abnormalities, but psychological factors—like stress or anxiety—can exacerbate pain. Environmental factors, including poor posture, sedentary lifestyles, and inadequate ergonomics, are also significant contributors to the rise in lower back pain cases, especially in an increasingly digital world. With more people spending hours sitting in front of screens, the modern lifestyle is creating new challenges for spinal health.
Common Causes of Back Pain
Lower back pain can be triggered by a variety of causes, ranging from simple muscle strains to more serious structural issues. The most common causes include:
- Muscle or ligament strain: Heavy lifting, awkward movements, or overuse can strain the muscles and ligaments, leading to discomfort.
- Herniated disc: A slipped or ruptured disc can press on nerves, causing pain in the lower back or even radiating down the legs.
- Degenerative disc disease: With age, discs between ...
Common Causes of Back Pain
Lower back pain can be triggered by a variety of causes, ranging from simple muscle strains to more serious structural issues. The most common causes include:
- Muscle or ligament strain: Heavy lifting, awkward movements, or overuse can strain the muscles and ligaments, leading to discomfort.
- Herniated disc: A slipped or ruptured disc can press on nerves, causing pain in the lower back or even radiating down the legs.
- Degenerative disc disease: With age, discs between the vertebrae lose flexibility, height, and hydration, which can result in pain.
- Arthritis: Osteoarthritis can affect the spine and lead to stiffness and discomfort, particularly in the lower back.
- Skeletal irregularities: Conditions such as scoliosis or lordosis can alter the alignment of the spine, creating pain points in the lower back.
Back Pain Risk Factors
Certain factors increase the likelihood of experiencing lower back pain. Understanding these risk factors can help in prevention and management.
- Age: People over 30 are more likely to experience back pain due to wear and tear of spinal structures.
- Lack of physical activity: Weak muscles and lack of regular exercise can contribute to back pain.
- Obesity: Excess body weight places additional stress on the spine, leading to pain.
- Improper posture: Sitting or standing in poor ...
Back Pain Risk Factors
Certain factors increase the likelihood of experiencing lower back pain. Understanding these risk factors can help in prevention and management.
- Age: People over 30 are more likely to experience back pain due to wear and tear of spinal structures.
- Lack of physical activity: Weak muscles and lack of regular exercise can contribute to back pain.
- Obesity: Excess body weight places additional stress on the spine, leading to pain.
- Improper posture: Sitting or standing in poor postures for extended periods puts pressure on the back.
- Occupational hazards: Jobs that require heavy lifting, bending, or prolonged sitting can increase the risk of lower back pain.
Back Pain Symptoms
Lower back pain manifests in several ways, depending on the underlying cause and severity. Some of the most common symptoms include:
- Dull, aching pain: This is typically localized to the lower back and may worsen with movement or prolonged sitting.
- Sharp or shooting pain: Some individuals experience pain that radiates down the legs, often caused by nerve compression.
- Limited range of motion: Stiffness or pain may restrict movement, making it difficult to bend or stand up straight ...
Back Pain Symptoms
Lower back pain manifests in several ways, depending on the underlying cause and severity. Some of the most common symptoms include:
- Dull, aching pain: This is typically localized to the lower back and may worsen with movement or prolonged sitting.
- Sharp or shooting pain: Some individuals experience pain that radiates down the legs, often caused by nerve compression.
- Limited range of motion: Stiffness or pain may restrict movement, making it difficult to bend or stand up straight.
- Muscle spasms: Sudden, involuntary contractions in the lower back muscles can occur, causing sharp pain.
- Tingling or numbness: In cases where nerves are involved, sensations of tingling or numbness in the legs or feet may accompany the pain.
Back Pain Diagnosis
A proper diagnosis is crucial for identifying the source of lower back pain and determining the best treatment approach. The process typically involves:
- Physical examination: A doctor will check your range of motion, reflexes, and sensations to identify any visible problems.
- Medical history: Providing a detailed account of your pain, including its onset, triggers, and associated symptoms, helps in narrowing down potential causes.
- Imaging tests: X-rays, MRIs, and CT scans can be used to detect structural problems ...
Back Pain Diagnosis
A proper diagnosis is crucial for identifying the source of lower back pain and determining the best treatment approach. The process typically involves:
- Physical examination: A doctor will check your range of motion, reflexes, and sensations to identify any visible problems.
- Medical history: Providing a detailed account of your pain, including its onset, triggers, and associated symptoms, helps in narrowing down potential causes.
- Imaging tests: X-rays, MRIs, and CT scans can be used to detect structural problems such as herniated discs or fractures.
- Nerve tests: Electromyography (EMG) may be performed to assess nerve function if radiating pain is present.
Natural Treatments for Back Pain
There are several natural remedies to manage back pain. Click on natural treatments for back pain to find a detailed list of all the natural solutions to treat and prevent lower back pain, including various natural therapies, diet programs, alternative medicine, vitamins, supplements, herbal medicine, and home remedies. You can also go to www.aposbook.com to find all natural treatments for any medical condition IN ONE CLICK.
Some of the most common natural solutions for ...
Natural Treatments for Back Pain
There are several natural remedies to manage back pain. Click on natural treatments for back pain to find a detailed list of all the natural solutions to treat and prevent lower back pain, including various natural therapies, diet programs, alternative medicine, vitamins, supplements, herbal medicine, and home remedies. You can also go to www.aposbook.com to find all natural treatments for any medical condition IN ONE CLICK.
Some of the most common natural solutions for back pain include:
Diet Programs for Back Pain Relief
- Anti-inflammatory Diet: This diet helps to reduce chronic inflammation in the body, which often exacerbates lower back pain. It includes foods high in omega-3 fatty acids, vegetables, fruits, and nuts, helping to combat inflammation at the cellular level.
- Collagen Diet: Collagen supports joint health, and a collagen-focused diet emphasizes foods and supplements that promote collagen production, like bone broth, vitamin C-rich foods, and collagen peptides. This can help maintain spinal health and prevent further degeneration of discs and joints.
- Mediterranean Diet: Known for its anti-inflammatory properties, the Mediterranean diet includes whole grains, lean proteins, healthy fats, and a variety of fruits and vegetables, all of which contribute to better joint and muscle health, reducing the risk of back pain.
- Keto Diet: A low-carb, high-fat diet that some people find beneficial for reducing inflammation and pain. The keto diet encourages fat metabolism over glucose, which can reduce chronic pain in some individuals.
Herbal Medicine for Back Pain
- Turmeric: A potent anti-inflammatory herb that contains curcumin, which can help reduce chronic inflammation linked to back pain. Consuming turmeric in supplements or meals can provide long-term pain relief.
- Ginger: Ginger is widely recognized for its anti-inflammatory and muscle-relaxing properties. It can help ease muscle soreness and inflammation contributing to lower back discomfort.
- Devil’s Claw: This herb is often used for conditions like arthritis and back pain due to its ability to reduce inflammation and stiffness, improving mobility and reducing pain.
- Willow Bark: Willow bark has natural pain-relieving properties similar to aspirin. It’s effective in treating lower back pain and reducing inflammation.
Vitamins and Supplements for Back Pain
- Vitamin D: Essential for bone health, vitamin D helps strengthen the spine and prevents bone-related pain. A deficiency in vitamin D is linked to chronic pain, including back pain.
- Omega-3 Fatty Acids: Omega-3s, commonly found in fish oil supplements, are powerful anti-inflammatories that can reduce joint and muscle pain.
- Magnesium: Known for its muscle-relaxing properties, magnesium supplements can help ease muscle spasms and tension, which are common causes of lower back pain.
- Glucosamine and Chondroitin: These supplements support joint health and can reduce pain associated with degenerative conditions, such as osteoarthritis, that affect the spine.
Alternative Medicine for Back Pain
- Acupuncture: This traditional Chinese practice involves inserting thin needles into specific points on the body to relieve pain. Acupuncture is effective in treating chronic lower back pain by improving blood flow and releasing endorphins.
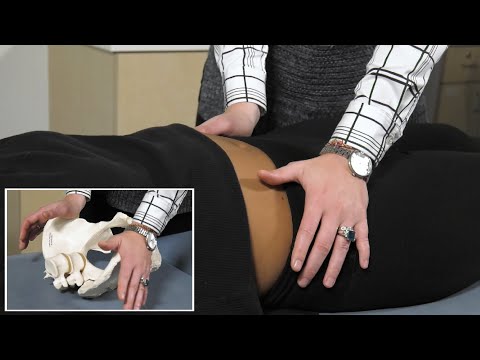
- Chiropractic Care: Chiropractors specialize in spinal manipulation, realigning the spine and reducing nerve pressure. Many people with lower back pain experience significant relief through chiropractic adjustments.
- Massage Therapy: Therapeutic massage can reduce muscle tension, improve circulation, and alleviate pain. Regular massages are especially beneficial for lower back pain caused by muscle strain or tightness.
- Yoga: Yoga helps strengthen the muscles around the spine, improves flexibility, and promotes relaxation, making it an excellent practice for preventing and managing lower back pain.
Medical Treatment for Back Pain
Medical treatments for back pain are focused on relieving pain and addressing the underlying cause, often through medications or physical interventions. These treatments range from pain relievers to surgical procedures for severe cases.
Medications for Back Pain
Medications are typically the first step in managing acute or chronic back pain. Depending on the severity, doctors may prescribe:
- Nonsteroidal Anti-inflammatory Drugs (NSAIDs): These are commonly prescribed for lower back pain to reduce inflammation and pain, with options ...
Medical Treatment for Back Pain
Medical treatments for back pain are focused on relieving pain and addressing the underlying cause, often through medications or physical interventions. These treatments range from pain relievers to surgical procedures for severe cases.
Medications for Back Pain
Medications are typically the first step in managing acute or chronic back pain. Depending on the severity, doctors may prescribe:
- Nonsteroidal Anti-inflammatory Drugs (NSAIDs): These are commonly prescribed for lower back pain to reduce inflammation and pain, with options like ibuprofen and naproxen.
- Muscle Relaxants: These are used to treat muscle spasms that can accompany back pain. They help to relax tense muscles and relieve pain.
- Opioids: In severe cases, opioids may be prescribed for short-term relief. However, they are used with caution due to the risk of dependency.
- Corticosteroids: For severe inflammation, corticosteroid injections may be used to provide temporary relief by reducing swelling around the affected nerves.
Surgery for Back Pain
Surgery is considered when other treatments fail or when there’s a serious structural issue, such as a herniated disc or spinal stenosis, contributing to chronic pain. Common surgeries for back pain include:
- Discectomy: Removing part of a herniated disc that is pressing on a nerve.
- Spinal Fusion: Fusing two or more vertebrae to stabilize the spine and reduce pain from excessive motion between vertebrae.
- Laminectomy: Removing part of the vertebra to relieve pressure on the spinal nerves, particularly in cases of spinal stenosis.
Back Pain FAQ
What are the specific causes of lower back pain?
Lower back pain can be caused by issues such as herniated discs, spinal stenosis, muscle or ligament strain, and degenerative disc disease. Conditions like sciatica, where nerve pain radiates from the lower back into the legs, are also specific to the lower back.
How can I relieve lower back pain at home?
Home remedies for lower back pain include using a combination of heat and ice therapy, performing ...
Back Pain FAQ
What are the specific causes of lower back pain?
Lower back pain can be caused by issues such as herniated discs, spinal stenosis, muscle or ligament strain, and degenerative disc disease. Conditions like sciatica, where nerve pain radiates from the lower back into the legs, are also specific to the lower back.
How can I relieve lower back pain at home?
Home remedies for lower back pain include using a combination of heat and ice therapy, performing targeted stretches, and taking over-the-counter pain relievers. Maintaining good posture and using supportive seating can also help.
What are some effective treatments for chronic lower back pain?
Chronic lower back pain may benefit from physical therapy, which includes exercises to strengthen the back and improve flexibility. Other treatments include lifestyle changes, like weight management and ergonomic adjustments, and potentially prescription medications or injections.
How can I distinguish between lower back pain and sciatica?
Lower back pain is localized to the lower back, while sciatica involves pain that radiates from the lower back down one or both legs, often accompanied by numbness, tingling, or weakness. Sciatica is usually caused by irritation or compression of the sciatic nerve.
What role does exercise play in managing lower back pain?
Exercise plays a crucial role in managing lower back pain by strengthening the muscles that support the spine, improving flexibility, and reducing stiffness. Low-impact activities like walking, swimming, and specific stretching exercises are particularly beneficial.
What are the most common causes of general back pain?
General back pain can be caused by muscle strain, poor posture, herniated discs, and degenerative disc disease. Other factors include heavy lifting, sports injuries, and prolonged sitting or standing.
Can back pain be a symptom of a more serious condition?
Yes, back pain can sometimes be a symptom of more serious conditions such as spinal infections, fractures, or tumors. It’s important to consult a healthcare provider if the pain is severe, persistent, or accompanied by other symptoms like weight loss or fever.
How can poor posture contribute to general back pain?
Poor posture can lead to general back pain by placing extra stress on the spine and muscles. Prolonged periods of sitting or standing with poor alignment can strain back muscles and spinal structures, leading to discomfort and pain.
Are there preventive measures for avoiding general back pain?
Preventive measures include maintaining a healthy weight, engaging in regular exercise to strengthen the back and core muscles, practicing good posture, and avoiding activities that put excessive strain on the back.
What should I do if my back pain does not improve with home treatment?
If back pain does not improve with home treatment, you should consult a healthcare provider for a comprehensive evaluation. They may recommend further diagnostic tests, physical therapy, or other interventions to address the underlying cause.
Explore other Health and wellness
Natural Treatments for Back Pain
Back Pain Dos and Don'ts
Choosing the right shoes is crucial for managing and preventing back pain. Footwear that lacks proper support, cushioning, or has poor design can disrupt your posture and
Cold and heat therapies are both effective methods for managing back pain, but they serve different purposes. Cold therapy is typically used for acute injuries and inflammation,
Strengthening your core and lower back muscles is essential for preventing and managing back pain. When your core muscles are weak, your body compensates by relying on your
Stretching plays a crucial role in preventing and alleviating back pain by improving flexibility, reducing muscle tension, and increasing your range of motion. Tight muscles,
Sitting for long hours behind a desk can put lot of pressure on the lower back and spine especially if the posture is bad. This may cause muscle stiffness and pain across the
Getting quality sleep is essential for managing and preventing back pain. Poor sleep or inadequate rest can exacerbate back discomfort and hinder recovery. During sleep, your body
The quality and type of your mattress play a crucial role in managing and preventing back pain. An unsuitable mattress can lead to poor sleep posture, resulting in discomfort and
The type and quality of your pillow play a significant role in managing and preventing back pain. An uncomfortable or improperly chosen pillow can disrupt your sleep and trigger
Stress has a significant impact on the body, often manifesting in physical ways, including back pain. When you’re stressed, your body tends to tighten up, especially in
Daily activities like carrying grocery bags, moving household items, or lifting children can often lead to back pain if not done with proper technique. Even though these objects
While strength training is essential for building muscle and supporting your spine, improper weight training techniques can lead to serious back pain or injuries. Lifting too much
Sleeping on your stomach is one of the worst positions for your spine. In this position, your lower back is forced into an unnatural arch, which puts extra pressure on the spine
Carrying a heavy backpack, purse, or shoulder bag regularly can cause significant strain on your back. When you overload your bag, the weight can pull your spine into an unnatural
Dos and Don'ts
Library center Back Pain
Success storiess

Server with 7 years of Constipation and Low back pain FIXED by Dr Suh Gonstead

Wet Cupping | I Had A-lot of BAD Blood...

CHRONIC PAIN - GONSTEAD Chiropractic Adjustment















































[0]