Ready to leave?
Oops ! Condition name you have entered is invalid.
You are now leaving Aposbook.com and going to an external site managed by another organization.
Please confirm your email address and try to login again.
This account has been deleted. do you want to restore it?

Validate your email
A verification link will be sent to within the next 2 minutes. Please click it to validate your e mail.
*If you didn't get the link, please check your spam folder
Welcome to Aposbook,
As a registered user, you can benefit from the various free tools and services that we provide.
All you need to do is log in to start discussing with others, interacting, asking questions, and sharing your point of view about the various topics.
You can also write reviews and testimonials about any natural solution you have tried and share your experience. Your feedback can be very helpful.
If you are a health expert, you can add information about any topic or suggest text edit. You can also publish content, including articles and videos, about any topic from the related library section.
Together we can help.
The Aposbook Team
Forgot Password?
A validation link will be sent to you by email. Please confirm your address to log in
*If you didn't get the link, please check your spam folder
Please log in to use this feature
Your account has been suspended because you have violated our code of conduct. If you think this was a mistake, you can contact us by email at: support@aposbook.com "Contact us" form.
Success! Thank you for your feedback. Your contribution can make a difference. Together we can help each other.


Natural Compounds
NAD (Nicotinamide Adenine Dinucleotide)
NAD: Uses, Benefits, Side Effects, and More
Complete Guide to NAD (Nicotinamide Adenine Dinucleotide)
What is NAD
NAD (Nicotinamide Adenine Dinucleotide) is a crucial molecule found in every cell of the body, playing a key role in energy production, metabolism, and cellular repair. It helps convert food into energy by supporting key processes in the cells, particularly in the mitochondria, which are responsible for generating energy. NAD is also vital for maintaining DNA health and regulating important proteins that control aging and cellular function. As we age, NAD levels naturally decline, which can lead ...
What is NAD
NAD (Nicotinamide Adenine Dinucleotide) is a crucial molecule found in every cell of the body, playing a key role in energy production, metabolism, and cellular repair. It helps convert food into energy by supporting key processes in the cells, particularly in the mitochondria, which are responsible for generating energy. NAD is also vital for maintaining DNA health and regulating important proteins that control aging and cellular function. As we age, NAD levels naturally decline, which can lead to reduced energy, slower recovery, and increased vulnerability to age-related diseases. Maintaining healthy NAD levels is important for overall vitality and longevity.
Types of NAD
There are different forms of NAD, each playing a specific role in the body. Below are the key types of NAD, including their unique functions:
- NAD+ (Nicotinamide Adenine Dinucleotide): NAD+ is the active form of NAD. It plays a vital role in redox reactions, helping cells convert nutrients into energy. It also regulates enzymes that repair DNA, repair oxidative damage, and control cellular functions related to aging. NAD+ is essential for sustaining healthy cellular activity and mitochondrial function.
- NADH (Nicotinamide Adenine Dinucleotide + Hydrogen): NADH is the reduced form of NAD+, meaning it carries an extra electron. It plays a crucial role in energy production, particularly in the electron transport chain within mitochondria. NADH is involved in generating ATP, the body’s primary energy currency, making it essential for cellular metabolism.
- NADP+ (Nicotinamide Adenine Dinucleotide Phosphate): NADP+ is a phosphorylated version of NAD+, primarily involved in biosynthetic reactions. Unlike NAD+, which is mainly used in catabolic processes (breaking down molecules for energy), NADP+ is primarily used in anabolic processes (building molecules like lipids and nucleic acids). It is essential in cellular growth and the production of antioxidants.
- NADPH (Nicotinamide Adenine Dinucleotide Phosphate + Hydrogen): NADPH is the reduced form of NADP+ and is vital for cellular protection. It acts as an antioxidant, neutralizing reactive oxygen species (ROS) and helping to protect the cell from oxidative stress. NADPH also supports fat synthesis and cellular growth.
Precursors of NAD
To maintain adequate NAD+ levels, the body relies on several compounds that act as precursors to NAD+ production. These compounds are converted into NAD+ through various biochemical pathways:
- Niacin (Vitamin B3): Niacin is one of the most direct precursors to NAD+ in the body. It is converted into NAD+ through the Preiss-Handler pathway. Niacin supplementation is commonly used to boost NAD+ levels, especially in individuals who may have insufficient dietary intake of B vitamins. Niacin is a well-established, affordable means to support NAD+ production.
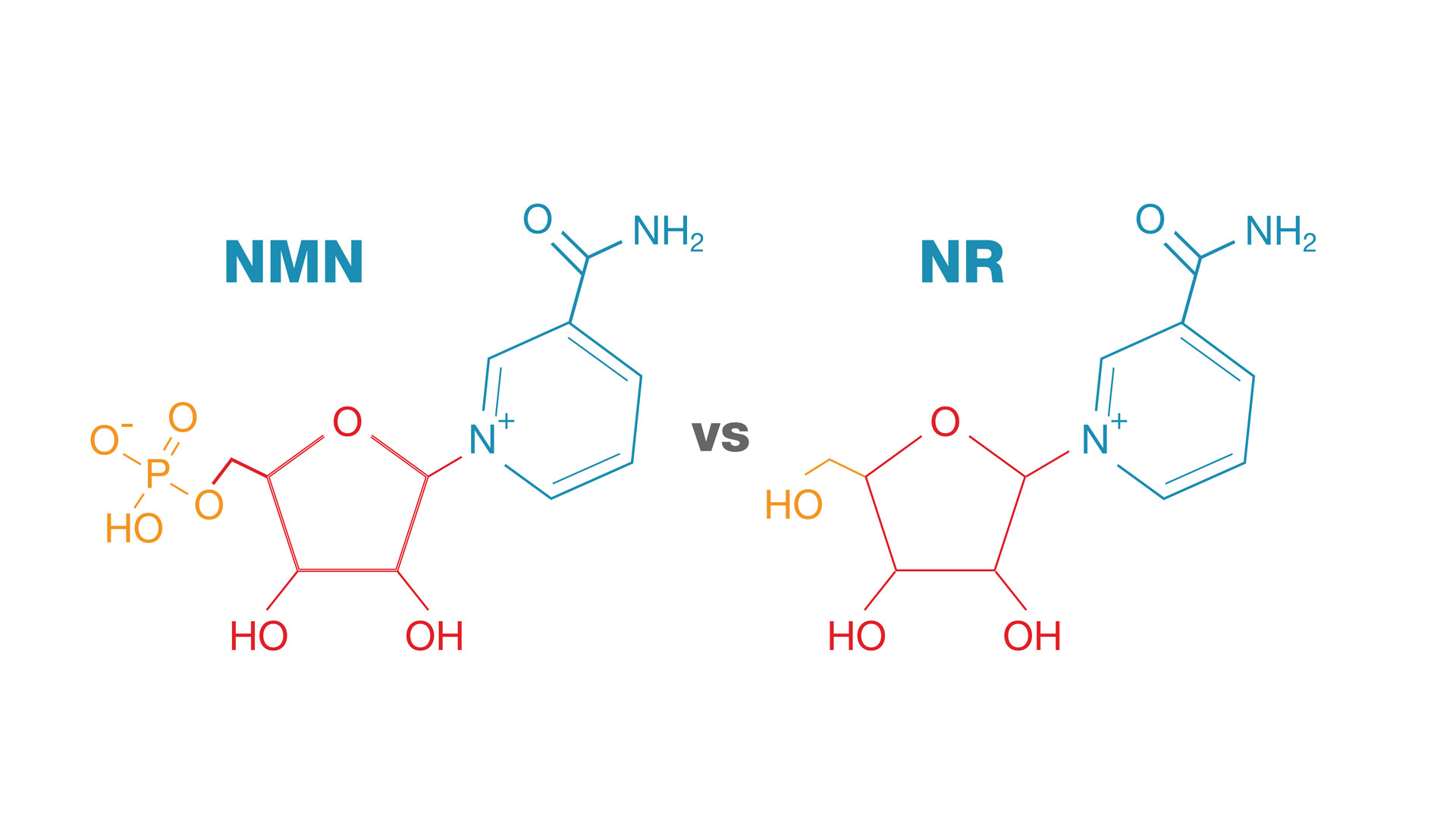
- Nicotinamide Riboside (NMR): Nicotinamide Riboside is a form of vitamin B3 that is converted into NAD+ via a different pathway from niacin. NMR has gained attention for its higher bioavailability compared to other NAD+ precursors, meaning it is more readily absorbed by cells and can quickly elevate NAD+ levels. Studies suggest NMR supplementation can improve metabolic health, enhance muscle function, and support cognitive health by boosting NAD+ levels.
- Nicotinamide Mononucleotide (NMN): NMN is another precursor to NAD+ that has garnered popularity in recent years for its potential anti-aging effects. Like NMR, NMN is converted into NAD+ within the body, but it follows a more direct pathway. NMN supplementation has shown promise in improving energy metabolism, supporting mitochondrial function, and reducing the signs of aging. Some studies suggest NMN may be more efficient than NMR in raising NAD+ levels due to its simpler conversion process.
- Tryptophan: Tryptophan is an essential amino acid found in protein-rich foods. It serves as a precursor to NAD+ via a complex biochemical process. While it is not as potent as niacin, NMN, or NMR in raising NAD+ levels, tryptophan supplementation can still contribute to NAD+ synthesis, especially when other precursors are limited in the diet.
NAD Food Sources
NAD (Nicotinamide Adenine Dinucleotide) is not directly found in food in significant amounts, but the body can produce it from precursors found in certain foods. The key nutrients that support NAD production include niacin (vitamin B3) and its derivatives, like niacinamide and nicotinamide riboside (NR). Foods rich in these precursors help maintain optimal NAD+ levels. Here are some foods that promote NAD production:
- Turkey: A great source of niacin, which can be converted into NAD.
- Chicken: Like ...
NAD Food Sources
NAD (Nicotinamide Adenine Dinucleotide) is not directly found in food in significant amounts, but the body can produce it from precursors found in certain foods. The key nutrients that support NAD production include niacin (vitamin B3) and its derivatives, like niacinamide and nicotinamide riboside (NR). Foods rich in these precursors help maintain optimal NAD+ levels. Here are some foods that promote NAD production:
- Turkey: A great source of niacin, which can be converted into NAD.
- Chicken: Like turkey, chicken is rich in niacin.
- Fish: Salmon, tuna, and other fish are high in niacin.
- Peanuts: Rich in niacinamide, they contribute to NAD synthesis.
- Mushrooms: Particularly shiitake mushrooms, which are excellent sources of niacin.
- Avocados: Contain small amounts of niacin and support overall metabolism.
- Green Vegetables: Spinach, broccoli, and other greens offer small amounts of NAD precursors.
While NAD itself is not directly abundant in food, a diet rich in these niacin-rich foods helps your body produce the necessary compounds for NAD+ synthesis.
How NAD Works in the Body
NAD is crucial for energy production, maintaining cellular health, supporting DNA repair, and regulating metabolism. Here's how it works:
- Energy Production: NAD is central to cellular metabolism, particularly in the mitochondria—the powerhouses of cells. It assists in redox reactions, where it helps transfer electrons during processes like glycolysis, the citric acid cycle, and oxidative phosphorylation. These processes convert food into energy (ATP), which powers all cell functions.
- DNA Repair: NAD activates enzymes known as ...
How NAD Works in the Body
NAD is crucial for energy production, maintaining cellular health, supporting DNA repair, and regulating metabolism. Here's how it works:
- Energy Production: NAD is central to cellular metabolism, particularly in the mitochondria—the powerhouses of cells. It assists in redox reactions, where it helps transfer electrons during processes like glycolysis, the citric acid cycle, and oxidative phosphorylation. These processes convert food into energy (ATP), which powers all cell functions.
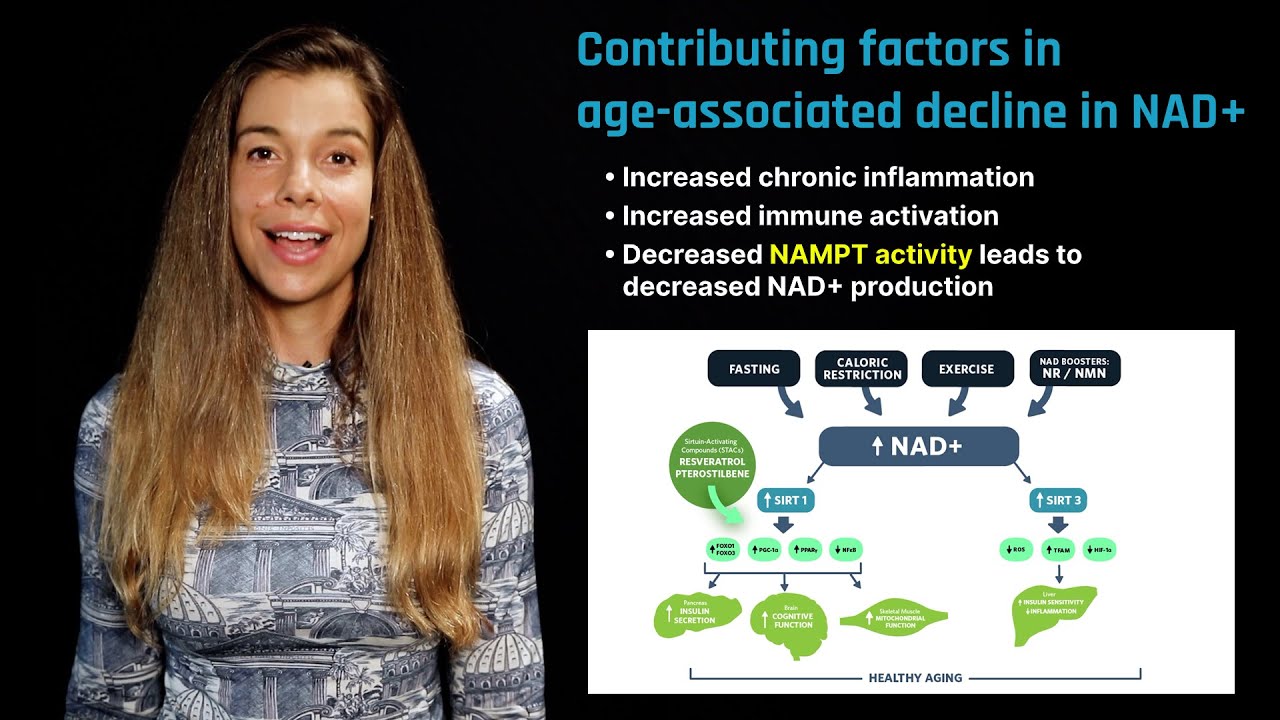
- DNA Repair: NAD activates enzymes known as sirtuins and PARPs (Poly (ADP-ribose) polymerases). These enzymes are involved in DNA repair and maintenance, protecting the cell from genetic damage and promoting longevity. Sirtuins also regulate key processes like inflammation, metabolism, and cellular stress responses.
- Cellular Communication: NAD plays a role in cell signaling, helping to regulate the function of calcium ions and other signaling molecules that affect various cellular functions, including muscle contraction, nerve signaling, and the immune response.
- Gene Expression: By influencing sirtuins, NAD also impacts the regulation of gene expression, particularly genes involved in stress resistance, metabolism, and aging processes.
Dose and Forms of NAD
NAD supplements are commonly used to boost levels of NAD+ in the body, supporting cellular energy and repair processes. They come in several forms, each with specific dosing recommendations and usage methods. Here’s a look at the common forms:
- Capsules: The most popular form, NAD+ capsules or their precursors (like NMN or NR) are taken orally. Typical doses range from 250 mg to 500 mg per day, though some users may start with lower doses ...
Dose and Forms of NAD
NAD supplements are commonly used to boost levels of NAD+ in the body, supporting cellular energy and repair processes. They come in several forms, each with specific dosing recommendations and usage methods. Here’s a look at the common forms:
- Capsules: The most popular form, NAD+ capsules or their precursors (like NMN or NR) are taken orally. Typical doses range from 250 mg to 500 mg per day, though some users may start with lower doses and increase as needed. Capsules are convenient and generally well-tolerated.
- Powder: NAD powder can be mixed with water or juice. This form allows for customizable dosing, often starting at 250 mg daily and adjusted according to individual needs. It’s absorbed quickly but requires precise measurement.
- Sublingual Tablets or Powders: Taken under the tongue, sublingual forms of NAD are absorbed directly into the bloodstream, bypassing the digestive tract for faster absorption. Typical doses are between 250 mg and 500 mg per day, though instructions vary by brand.
- Injections: NAD+ injections are administered under medical supervision, usually in clinics. Doses are highly individualized, often used in anti-aging and rehabilitation clinics, and vary widely depending on therapeutic goals.
- IV Drip: Administered intravenously by healthcare providers, NAD+ IV drips deliver NAD directly into the bloodstream. This is usually done in specialized clinics with individualized dosing protocols and is most commonly used for rapid NAD+ replenishment in therapeutic settings.
It’s recommended to consult a healthcare provider before beginning NAD supplementation, especially with injectable or IV forms, as these require medical oversight.
Benefits of NAD Supplements
NAD offers a wide range of potential health benefits due to its role in cellular repair, metabolism, and energy production. Here’s a breakdown of its effects:
- Supports Cellular Energy: NAD is essential for ATP production in cells. It aids in converting food into usable energy, helping to combat fatigue and enhance overall energy levels.
- Enhances Cognitive Function: By supporting neuronal health and promoting mitochondrial function, NAD may improve cognitive function, memory, and focus, potentially benefiting those ...
Benefits of NAD Supplements
NAD offers a wide range of potential health benefits due to its role in cellular repair, metabolism, and energy production. Here’s a breakdown of its effects:
- Supports Cellular Energy: NAD is essential for ATP production in cells. It aids in converting food into usable energy, helping to combat fatigue and enhance overall energy levels.
- Enhances Cognitive Function: By supporting neuronal health and promoting mitochondrial function, NAD may improve cognitive function, memory, and focus, potentially benefiting those with age-related cognitive decline.
- Aids in DNA Repair: NAD activates enzymes like PARPs that are involved in DNA repair. This function helps reduce cell damage from environmental factors, potentially lowering cancer risk and slowing aging.
- Promotes Healthy Aging: By activating sirtuins, NAD helps regulate genes involved in aging and longevity. It may contribute to longer telomeres, reduced cellular damage, and better metabolic health over time.
- Supports Metabolism: NAD plays a key role in metabolic processes, making it beneficial for maintaining a healthy weight and reducing the risk of metabolic disorders like diabetes by enhancing insulin sensitivity.
- Boosts Muscle and Physical Performance: Through its role in energy production and muscle function, NAD may improve physical performance and endurance, especially in those experiencing age-related muscle decline.
- Improves Cardiovascular Health: NAD helps protect blood vessels and heart muscle cells, potentially lowering the risk of heart disease by supporting vascular health and improving blood flow.
- Enhances Immune Function: NAD assists in maintaining cellular integrity and supports the immune response, which can help the body fend off infections and manage inflammation.
- Promotes Skin Health: By aiding in cellular repair and supporting collagen production, NAD may reduce the visible effects of skin aging, such as wrinkles and fine lines.
NAD Precautions
While NAD supplements offer various health benefits, it’s important to consider specific precautions to ensure safe and effective use. Certain groups, like those with pre-existing health conditions or on medication, should exercise extra caution. Here are key precautions to keep in mind:
- Consult a Healthcare Provider: Especially important for high doses or injectable forms, consulting a professional ensures appropriate dosing and reduces the risk of adverse effects.
- Cancer Risk Concerns: Individuals with a history of cancer, active cancer ...
NAD Precautions
While NAD supplements offer various health benefits, it’s important to consider specific precautions to ensure safe and effective use. Certain groups, like those with pre-existing health conditions or on medication, should exercise extra caution. Here are key precautions to keep in mind:
- Consult a Healthcare Provider: Especially important for high doses or injectable forms, consulting a professional ensures appropriate dosing and reduces the risk of adverse effects.
- Cancer Risk Concerns: Individuals with a history of cancer, active cancer, or high risk of developing cancer should consult a healthcare provider before using NAD+ supplements. While NAD+ supports cellular repair and metabolism, there is concern that boosting NAD+ levels might inadvertently stimulate cancer cell growth alongside normal cells, although definitive human studies are still lacking.
- Allergic Reactions: If you have known allergies, check product ingredients for potential allergens and start with a small dose if possible to monitor for any reactions.
- Interactions with Medications: NAD can interact with certain medications, especially those that affect metabolism or cellular energy. Speak to a healthcare provider if you’re on any medications.
- Avoid During Pregnancy or Nursing: There is insufficient research on the effects of NAD supplements during pregnancy or breastfeeding, so it’s best to avoid them unless otherwise advised by a physician.
- Start with Lower Doses: Some individuals may experience mild side effects at higher doses, so beginning with a smaller dose and gradually increasing can help assess tolerance.
NAD Side Effects
Although NAD supplements are generally well-tolerated, some people may experience mild side effects, especially at higher doses or with certain forms of the supplement. Common side effects include:
- Nausea: Particularly when taken without food.
- Headaches: Often seen in the first few days of use as the body adjusts.
- Digestive Upset: Symptoms such as bloating or diarrhea may occur, usually subsiding over time.
- Flushing: A warming sensation may occur, though it’s less common with NAD than with niacin.
- Fatigue ...
NAD Side Effects
Although NAD supplements are generally well-tolerated, some people may experience mild side effects, especially at higher doses or with certain forms of the supplement. Common side effects include:
- Nausea: Particularly when taken without food.
- Headaches: Often seen in the first few days of use as the body adjusts.
- Digestive Upset: Symptoms such as bloating or diarrhea may occur, usually subsiding over time.
- Flushing: A warming sensation may occur, though it’s less common with NAD than with niacin.
- Fatigue: Some users report temporary fatigue, particularly at higher doses.
- Mild Anxiety: Rare in most cases but can occur in sensitive individuals.
If you experience severe or persistent side effects, discontinue use and consult a healthcare professional for guidance.
Frequently Asked Questions About NAD
What is NAD, and why is it important?
NAD, or Nicotinamide Adenine Dinucleotide, is a coenzyme found in all cells and is essential for energy production, cellular metabolism, and supporting cellular repair functions.
How does NAD work in the body?
NAD helps convert nutrients into cellular energy (ATP) and plays a key role in DNA repair, cell survival, and regulating metabolic functions.
Do NAD levels decrease with age?
Yes, NAD levels naturally decline as we ...
Frequently Asked Questions About NAD
What is NAD, and why is it important?
NAD, or Nicotinamide Adenine Dinucleotide, is a coenzyme found in all cells and is essential for energy production, cellular metabolism, and supporting cellular repair functions.
How does NAD work in the body?
NAD helps convert nutrients into cellular energy (ATP) and plays a key role in DNA repair, cell survival, and regulating metabolic functions.
Do NAD levels decrease with age?
Yes, NAD levels naturally decline as we age, which can impact cellular energy and contribute to other aging-related changes in the body.
What are natural food sources of NAD?
Foods that provide NAD precursors include milk, fish, chicken, yeast, and green vegetables. These foods help maintain NAD levels through compounds like niacin.
Is NAD the same as niacin (Vitamin B3)?
No, NAD and niacin are different, but niacin (a form of Vitamin B3) is a precursor to NAD, meaning it can be converted into NAD within the body.
Are there supplements available to boost NAD levels?
Yes, there are NAD-boosting supplements, such as NMN (Nicotinamide Mononucleotide) and NR (Nicotinamide Riboside), which are NAD precursors that help raise NAD levels in the body.
How safe are NAD supplements?
Generally, NAD supplements are considered safe, though mild side effects like nausea, headaches, or digestive discomfort can occur, particularly at higher doses.
How does NAD impact energy levels?
NAD is crucial for cellular energy production, helping cells convert nutrients into ATP, which powers various bodily functions and supports overall vitality.
Can NAD be taken in different supplement forms?
Yes, NAD can be found in capsule, powder, and even injectable forms. Capsules are the most common for general use, while other forms may be used under medical supervision.
Is NAD supplementation necessary if I already consume Vitamin B3?
While Vitamin B3 can support NAD levels, supplementation with NAD precursors like NMN or NR is sometimes considered for those aiming to further enhance NAD levels, especially as they age.
Disclaimer: The published information is based on research and published medical sources. It is provided for educational purposes only and is not intended to replace professional medical advice. Always consult with your doctor or healthcare provider regarding any questions you may have about your health. We are not responsible for any actions taken based on this information, nor for any errors, omissions, or inaccuracies in the content. Medical research is constantly evolving, and the information presented may not reflect the most current medical standards.
November 2024
AposBook
Suggested benefits of NAD (Nicotinamide Adenine Dinucleotide)
What science says about Nad (Nicotinamide Adenine Dinucleotide)
Views in favor
Views against
The FDA Has Banned NMN Supplements!
Library center NAD (Nicotinamide Adenine Dinucleotide)





 Buy now
Buy now







































[0]