Ready to leave?
Oops ! Condition name you have entered is invalid.
You are now leaving Aposbook.com and going to an external site managed by another organization.
Please confirm your email address and try to login again.
This account has been deleted. do you want to restore it?

Validate your email
A verification link will be sent to within the next 2 minutes. Please click it to validate your e mail.
*If you didn't get the link, please check your spam folder
Welcome to Aposbook,
As a registered user, you can benefit from the various free tools and services that we provide.
All you need to do is log in to start discussing with others, interacting, asking questions, and sharing your point of view about the various topics.
You can also write reviews and testimonials about any natural solution you have tried and share your experience. Your feedback can be very helpful.
If you are a health expert, you can add information about any topic or suggest text edit. You can also publish content, including articles and videos, about any topic from the related library section.
Together we can help.
The Aposbook Team
Forgot Password?
A validation link will be sent to you by email. Please confirm your address to log in
*If you didn't get the link, please check your spam folder
Please log in to use this feature
Your account has been suspended because you have violated our code of conduct. If you think this was a mistake, you can contact us by email at: support@aposbook.com "Contact us" form.
Success! Thank you for your feedback. Your contribution can make a difference. Together we can help each other.


Natural Compounds
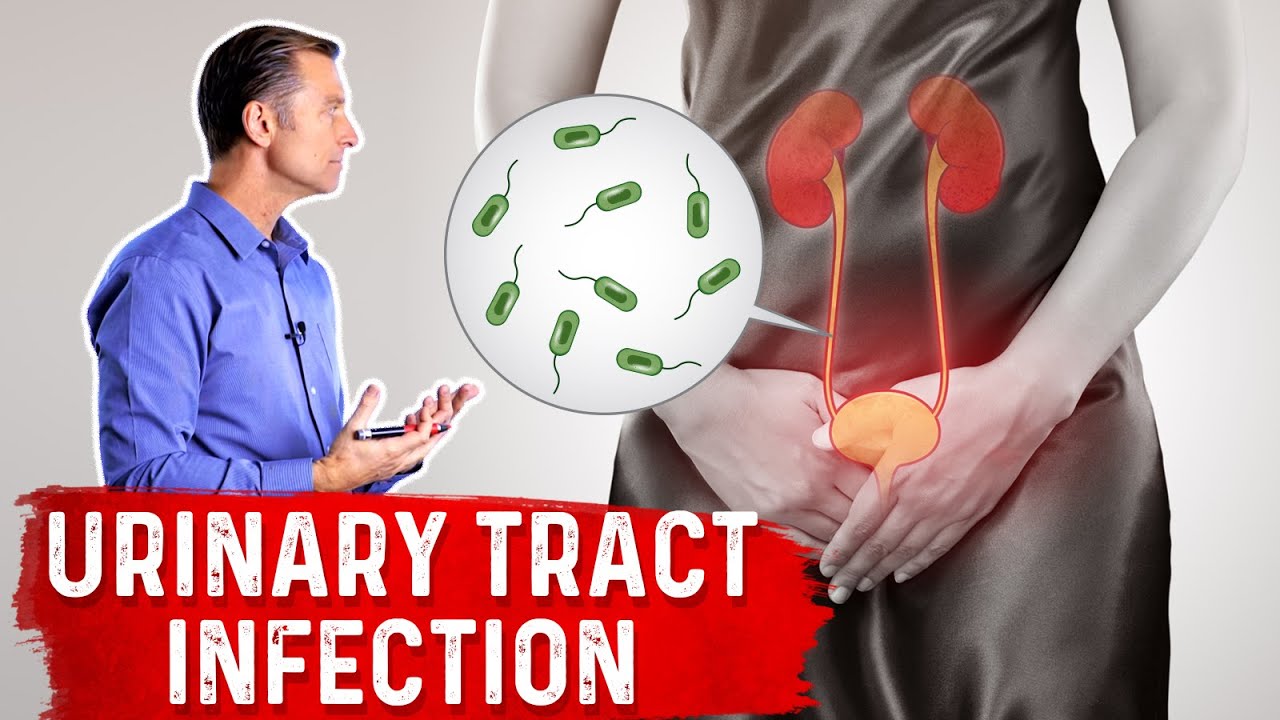
Probiotics For UTI (Urinary Tract Infection)
Probiotics for UTI: All you Need to Know
Complete Guide to Probiotics For UTI (Urinary Tract Infection)
Causes of UTI Addressed by Probiotics
A urinary tract infection (UTI) occurs when harmful bacteria, primarily Escherichia coli (E. coli), invade the urinary tract, causing inflammation and symptoms such as burning during urination, urgency, and pelvic pain. Recurrent UTIs are common and often linked to an imbalance in the urinary and vaginal microbiota, which provides a protective barrier against pathogens.
General causes of UTIs include bacterial infections, hormonal changes, poor hygiene practices, a weakened immune system, or the use of ...
Causes of UTI Addressed by Probiotics
A urinary tract infection (UTI) occurs when harmful bacteria, primarily Escherichia coli (E. coli), invade the urinary tract, causing inflammation and symptoms such as burning during urination, urgency, and pelvic pain. Recurrent UTIs are common and often linked to an imbalance in the urinary and vaginal microbiota, which provides a protective barrier against pathogens.
General causes of UTIs include bacterial infections, hormonal changes, poor hygiene practices, a weakened immune system, or the use of antibiotics that disrupt the microbiome. Specific causes that probiotics may address include:
- Disrupted Vaginal Microbiota: An imbalance in the vaginal flora, particularly a decline in beneficial Lactobacillus species, can allow pathogenic bacteria to colonize and ascend to the urinary tract.
- Overgrowth of Pathogenic Bacteria: Harmful bacteria like E. coli thrive when the urinary or vaginal microbiota lacks diversity and protective species.
- Antibiotic Overuse: Antibiotics used to treat or prevent UTIs can eliminate beneficial bacteria, further disrupting the microbiome and increasing susceptibility to future infections.
- Immune System Suppression: A weakened immune response can reduce the body's ability to control bacterial growth, allowing infections to persist.
Click to learn everything about urinary tract infection (UTI) and find all the natural solutions to treat UTI naturally, including various diet programs, alternative medicine, vitamins, supplements, herbal medicine, and home remedies.
Why Probiotics help for UTI (Urinary Tract Infection)
Probiotics help manage and prevent UTIs by restoring and maintaining a healthy microbial balance, particularly in the urinary and vaginal microbiomes. By increasing beneficial bacteria, probiotics create an environment that inhibits pathogen colonization and strengthens the body's defenses.
- Restoring Vaginal Microbiota Balance: Probiotics, especially Lactobacillus species, replenish the beneficial bacteria that maintain an acidic vaginal pH. A low pH discourages the growth of harmful bacteria, reducing the risk of infections.
- Inhibiting Pathogenic Bacteria ...
Why Probiotics help for UTI (Urinary Tract Infection)
Probiotics help manage and prevent UTIs by restoring and maintaining a healthy microbial balance, particularly in the urinary and vaginal microbiomes. By increasing beneficial bacteria, probiotics create an environment that inhibits pathogen colonization and strengthens the body's defenses.
- Restoring Vaginal Microbiota Balance: Probiotics, especially Lactobacillus species, replenish the beneficial bacteria that maintain an acidic vaginal pH. A low pH discourages the growth of harmful bacteria, reducing the risk of infections.
- Inhibiting Pathogenic Bacteria Growth: Beneficial strains produce antimicrobial compounds, such as hydrogen peroxide and lactic acid, that directly inhibit pathogenic bacteria, including E. coli.
- Counteracting Antibiotic-Induced Disruption: Probiotics help replenish the beneficial bacteria eliminated by antibiotics, preventing further microbiota imbalance and reducing recurrence risk.
- Strengthening Immune Response: By enhancing the local immune system's activity, probiotics support the body's ability to recognize and clear bacterial infections more effectively.
In conclusion, probiotics are a supportive solution for UTIs rather than a standalone treatment. They are most effective for prevention and in reducing recurrence when combined with other interventions, such as proper hygiene, hydration, and, if needed, antibiotics.
While probiotics provide unique benefits by restoring microbiota balance and offering long-term protection against recurrent infections, their effectiveness can vary among individuals. Their primary advantage over other solutions is their ability to improve microbiota health without the adverse effects associated with antibiotics.
How Probiotics Work for UTI (Urinary Tract Infection)
The mechanisms of probiotics in managing and preventing UTIs involve various biological actions that restore and maintain a healthy microbial balance, inhibit harmful bacterial activity, and enhance the body’s defenses. Below is a detailed explanation of how probiotics achieve these outcomes:
- Restoring Vaginal Microbiota Balance: Probiotics such as Lactobacillus crispatus and Lactobacillus reuteri colonize the vaginal and urinary tracts, producing lactic acid to maintain an acidic environment unfavorable to pathogens.
- Inhibiting Pathogenic ...
How Probiotics Work for UTI (Urinary Tract Infection)
The mechanisms of probiotics in managing and preventing UTIs involve various biological actions that restore and maintain a healthy microbial balance, inhibit harmful bacterial activity, and enhance the body’s defenses. Below is a detailed explanation of how probiotics achieve these outcomes:
- Restoring Vaginal Microbiota Balance: Probiotics such as Lactobacillus crispatus and Lactobacillus reuteri colonize the vaginal and urinary tracts, producing lactic acid to maintain an acidic environment unfavorable to pathogens.
- Inhibiting Pathogenic Bacteria Growth: Beneficial strains produce bacteriocins and hydrogen peroxide, which have antimicrobial properties that prevent the colonization of pathogens like E. coli.
- Counteracting Antibiotic-Induced Disruption: Probiotics like Bifidobacterium species promote microbiota recovery after antibiotic use by outcompeting harmful bacteria and restoring microbial diversity.
- Strengthening Immune Response: Probiotics enhance mucosal immunity by stimulating the production of secretory IgA (immunoglobulin A) and modulating cytokine responses, which help clear infections.
By targeting these mechanisms, probiotics offer a multi-faceted approach to managing and preventing UTIs.
Dose and Forms of Probiotics for UTI
There is no universally agreed-upon dose of probiotics for UTIs. However, general guidelines suggest:
- Daily dose: Probiotic supplements typically provide between 1–10 billion CFUs (colony-forming units) per day. Some studies indicate that higher doses, such as 20 billion CFUs or more, might be beneficial for recurring UTIs.
- Duration: For active UTI management, probiotics may need to be taken daily for at least 8–12 weeks to observe significant effects. For prevention, long-term supplementation is ...
Dose and Forms of Probiotics for UTI
There is no universally agreed-upon dose of probiotics for UTIs. However, general guidelines suggest:
- Daily dose: Probiotic supplements typically provide between 1–10 billion CFUs (colony-forming units) per day. Some studies indicate that higher doses, such as 20 billion CFUs or more, might be beneficial for recurring UTIs.
- Duration: For active UTI management, probiotics may need to be taken daily for at least 8–12 weeks to observe significant effects. For prevention, long-term supplementation is often recommended.
Best Types of Probiotics for UTIs
Certain probiotic strains stand out for their targeted benefits in preventing and managing UTIs, based on their mechanisms of action and clinical effectiveness:
- Lactobacillus rhamnosus: This strain is effective in adhering to the urinary tract epithelium, preventing pathogenic bacteria such as E. coli from attaching and colonizing. Its anti-inflammatory properties also help alleviate irritation in the urinary tract.
- Lactobacillus reuteri: Produces reuterin, an antimicrobial substance that directly inhibits common UTI-causing bacteria. It also supports a balanced microbiome, reducing recurrence risk.
- Lactobacillus crispatus: Particularly beneficial for women prone to recurrent UTIs, as it restores vaginal microbiota, reducing the migration of harmful bacteria to the urinary tract. Studies highlight its role in reducing UTI recurrence by improving local defenses.
- Bifidobacterium species: These strains enhance gut health, which indirectly supports the immune system and reduces systemic inflammation, lowering the risk of UTIs.
In conclusion, the best types of probiotics for UTIs are Lactobacillus rhamnosus and Lactobacillus crispatus, as they directly address the primary causes of UTIs—bacterial colonization and vaginal microbiome imbalance.
While Lactobacillus reuteri and Bifidobacterium species are supportive, they are better suited for complementary use. For recurrent cases, combining L. crispatus with L. rhamnosus is particularly effective due to their complementary actions on the urinary and vaginal microbiota.
Available Forms of Probiotics for UTI
Probiotics for UTIs come in various forms, allowing flexibility based on personal preferences and medical needs:
- Capsules and Tablets: The most widely available forms, offering precise dosing and convenience for daily use.
- Powders: A versatile option for mixing with water, juice, or smoothies, suitable for those who dislike swallowing pills.
- Liquid Formulas: Often recommended for individuals with swallowing difficulties or who prefer a drinkable format. Liquid forms may provide slightly faster absorption.
- Vaginal Suppositories: These are particularly effective for restoring vaginal flora in women, directly targeting microbiome imbalances that contribute to UTIs.
- Chewable Tablets or Gummies: Suitable for those who find capsules difficult to take, though they may have lower CFU counts.
Each form is equally effective in delivering probiotics to the body, provided the product contains the appropriate strains and CFU count. Vaginal suppositories stand out for their localized action in recurrent UTI cases, while capsules are best for systemic support and prevention.
Probiotics for UTI: Precautions
Before starting probiotics for UTIs, consider the following:
- Consultation: Always consult a healthcare provider, especially if you have underlying health conditions, are immunocompromised, or are pregnant.
- Allergies: Some probiotic products may contain allergens like dairy or soy, which can trigger adverse reactions in sensitive individuals.
- Concurrent Medications: Probiotics are generally safe with antibiotics but should be taken at least 2–4 hours apart to ensure effectiveness.
- Proper Strain Selection: Not all probiotics work for UTIs; using inappropriate strains ...
Probiotics for UTI: Precautions
Before starting probiotics for UTIs, consider the following:
- Consultation: Always consult a healthcare provider, especially if you have underlying health conditions, are immunocompromised, or are pregnant.
- Allergies: Some probiotic products may contain allergens like dairy or soy, which can trigger adverse reactions in sensitive individuals.
- Concurrent Medications: Probiotics are generally safe with antibiotics but should be taken at least 2–4 hours apart to ensure effectiveness.
- Proper Strain Selection: Not all probiotics work for UTIs; using inappropriate strains may yield no benefits or worsen symptoms.
- Duration of Use: Long-term use may be needed for chronic or recurrent cases. Ensure to monitor for signs of tolerance or ineffectiveness.
Probiotics for UTI: Side Effects
While probiotics are generally safe, some individuals may experience mild side effects:
- Digestive Issues: Temporary bloating, gas, or diarrhea may occur as the body adjusts to probiotics.
- Infections in Vulnerable Populations: Rarely, immunocompromised individuals may develop infections from live probiotics.
- Allergic Reactions: Symptoms like rash, itching, or respiratory issues can occur if allergic to certain probiotic components.
- Risk of Overdose: Extremely high doses of probiotics may cause discomfort, such as excessive gas or nausea, though this ...
Probiotics for UTI: Side Effects
While probiotics are generally safe, some individuals may experience mild side effects:
- Digestive Issues: Temporary bloating, gas, or diarrhea may occur as the body adjusts to probiotics.
- Infections in Vulnerable Populations: Rarely, immunocompromised individuals may develop infections from live probiotics.
- Allergic Reactions: Symptoms like rash, itching, or respiratory issues can occur if allergic to certain probiotic components.
- Risk of Overdose: Extremely high doses of probiotics may cause discomfort, such as excessive gas or nausea, though this is rare.
Most side effects are mild and resolve on their own within a few days. However, any persistent or severe symptoms should be discussed with a healthcare provider.
FAQ About Probiotics for UTI
Can probiotics prevent recurrent UTIs?
Yes, probiotics, especially strains like Lactobacillus crispatus and Lactobacillus rhamnosus, help restore and maintain a healthy urinary and vaginal microbiota. By inhibiting the growth of UTI-causing bacteria such as E. coli, they can significantly reduce the frequency of recurrent UTIs.
How long does it take for probiotics to show results for UTIs?
Probiotics typically begin influencing microbiota balance within a few days. For noticeable improvement in UTI symptoms or prevention, consistent ...
FAQ About Probiotics for UTI
Can probiotics prevent recurrent UTIs?
Yes, probiotics, especially strains like Lactobacillus crispatus and Lactobacillus rhamnosus, help restore and maintain a healthy urinary and vaginal microbiota. By inhibiting the growth of UTI-causing bacteria such as E. coli, they can significantly reduce the frequency of recurrent UTIs.
How long does it take for probiotics to show results for UTIs?
Probiotics typically begin influencing microbiota balance within a few days. For noticeable improvement in UTI symptoms or prevention, consistent use for 4–12 weeks is often recommended.
Are vaginal probiotic suppositories more effective than oral probiotics for UTIs?
Vaginal suppositories target local microbiota imbalances directly, making them highly effective for recurrent UTIs in women. However, oral probiotics are better for systemic support and are often combined with vaginal options for enhanced results.
What is the best time of day to take probiotics for UTI prevention?
Probiotics can be taken at any time, but consistency is key. Many experts suggest taking them with or shortly after a meal to enhance bacterial survival through the digestive system.
Can probiotics replace antibiotics for UTIs?
Probiotics cannot replace antibiotics for treating active UTIs, but they are highly effective as a complementary therapy. They help reduce recurrence risk and support gut and vaginal microbiota during and after antibiotic use.
Do all probiotics work for UTIs?
No, only specific strains such as Lactobacillus crispatus, Lactobacillus rhamnosus, and Lactobacillus reuteri have proven benefits for UTI prevention and management. Choosing a product with the right strains is crucial.
Are probiotics safe for pregnant women prone to UTIs?
Probiotics are generally safe for pregnant women and may help reduce UTI risk by supporting vaginal and urinary health. However, it is essential to consult a healthcare provider before starting any probiotic regimen during pregnancy.
Can probiotics reduce the side effects of antibiotics used for UTIs?
Yes, probiotics help restore gut and vaginal microbiota disrupted by antibiotics, reducing side effects like diarrhea and yeast infections. They also support faster recovery of the microbiome after antibiotic treatment.
How should probiotics be stored to remain effective?
Storage recommendations depend on the specific product. Some probiotics require refrigeration, while others are stable at room temperature. Always check the packaging for instructions to maintain potency.
Can probiotics help with asymptomatic bacteriuria?
While probiotics may not directly treat asymptomatic bacteriuria, they help maintain a healthy urinary microbiome, potentially reducing the risk of it developing into symptomatic UTIs. Regular use is especially beneficial for individuals at high risk, such as the elderly or those with diabetes.
Disclaimer: The published information is based on research and published medical sources. It is provided for educational purposes only and is not intended to replace professional medical advice. Always consult with your doctor or healthcare provider regarding any questions you may have about your health. We are not responsible for any actions taken based on this information, nor for any errors, omissions, or inaccuracies in the content. Medical research is constantly evolving, and the information presented may not reflect the most current medical standards.
November 2024
AposBook
Reviews & Testimonials
-
Overall rating
-
Success Rate
-
Effectiveness
-
Accessiblity
-
Safety
-
Fast result
-
Ease of use
Add review
Was solution successfull?
Overall rating score
Rate each parameters
Effective
Accessible
Safe
Fast results
Easy to apply
Review title
Add images to support your review(if any)
Support images
You can review a solution if you have used it personally. Please remain objective and genuine. Your input can help others.
You have already reviewed this
Please rate all parameters.
Success! Thank you for your feedback. Your contribution can make a difference. Together we can help each other.
What science says about Probiotics For Uti (Urinary Tract Infection)
Library center Probiotics For UTI (Urinary Tract Infection)





 Buy now
Buy now

















[0]