Ready to leave?
Oops ! Condition name you have entered is invalid.
You are now leaving Aposbook.com and going to an external site managed by another organization.
Please confirm your email address and try to login again.
This account has been deleted. do you want to restore it?

Validate your email
A verification link will be sent to within the next 2 minutes. Please click it to validate your e mail.
*If you didn't get the link, please check your spam folder
Welcome to Aposbook,
As a registered user, you can benefit from the various free tools and services that we provide.
All you need to do is log in to start discussing with others, interacting, asking questions, and sharing your point of view about the various topics.
You can also write reviews and testimonials about any natural solution you have tried and share your experience. Your feedback can be very helpful.
If you are a health expert, you can add information about any topic or suggest text edit. You can also publish content, including articles and videos, about any topic from the related library section.
Together we can help.
The Aposbook Team
Forgot Password?
A validation link will be sent to you by email. Please confirm your address to log in
*If you didn't get the link, please check your spam folder
Please log in to use this feature
Your account has been suspended because you have violated our code of conduct. If you think this was a mistake, you can contact us by email at: support@aposbook.com "Contact us" form.
Success! Thank you for your feedback. Your contribution can make a difference. Together we can help each other.


Can NAD Help for Alzheimer: Why and How?
Complete Guide to NAD/NMN For Alzheimer / Dementia
Causes of Alzheimer Addressed by NAD
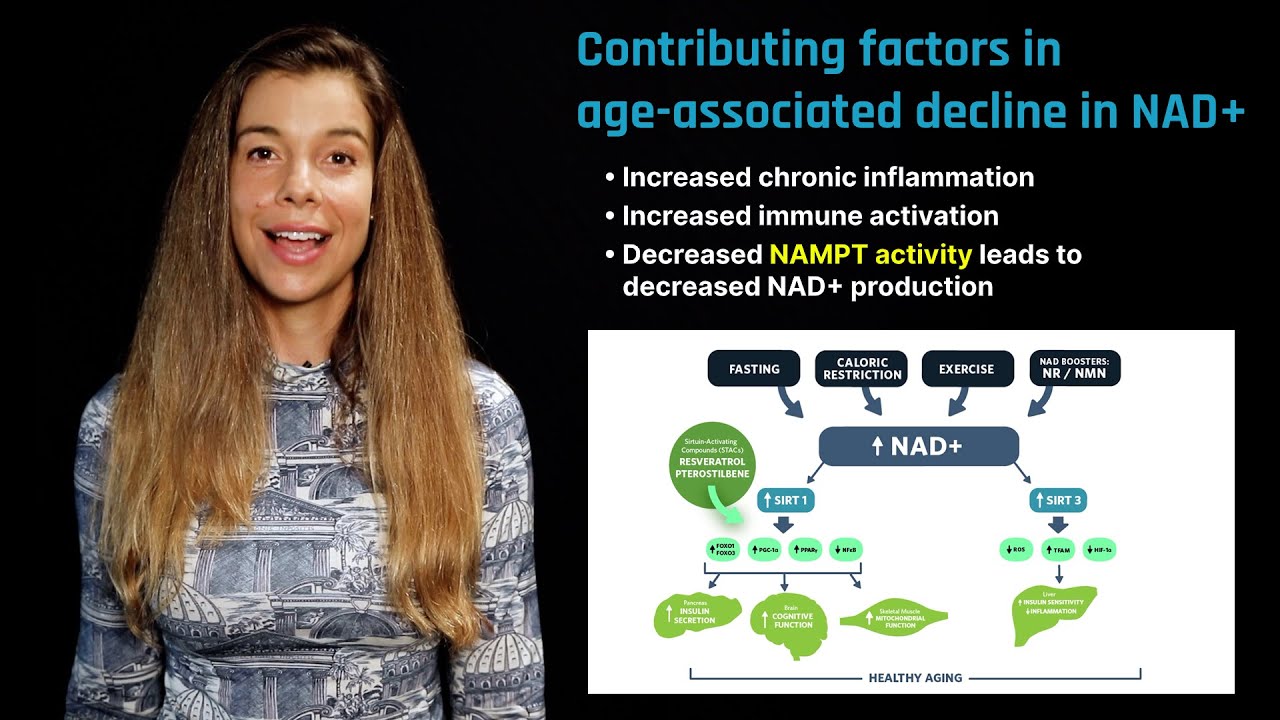
Alzheimer's disease is a progressive neurodegenerative disorder that causes memory loss, confusion, and a decline in cognitive abilities. It is primarily associated with the accumulation of amyloid plaques and tau tangles in the brain, leading to neuronal damage. There are various causes of Alzheimer’s, including genetic predisposition, oxidative stress, mitochondrial dysfunction, and inflammation. These factors disrupt normal brain function, contributing to the disease’s progression. Meanwhile, the specific Causes of Alzheimer’s That NAD+ Can Address ...
Causes of Alzheimer Addressed by NAD
Alzheimer's disease is a progressive neurodegenerative disorder that causes memory loss, confusion, and a decline in cognitive abilities. It is primarily associated with the accumulation of amyloid plaques and tau tangles in the brain, leading to neuronal damage. There are various causes of Alzheimer’s, including genetic predisposition, oxidative stress, mitochondrial dysfunction, and inflammation. These factors disrupt normal brain function, contributing to the disease’s progression. Meanwhile, the specific Causes of Alzheimer’s That NAD+ Can Address:
- Mitochondrial Dysfunction: NAD+ is essential for cellular energy production, and its decline in Alzheimer’s patients exacerbates mitochondrial dysfunction, leading to neuronal damage.
- Oxidative Stress: NAD+ plays a critical role in regulating oxidative stress, and its depletion can lead to an increase in free radicals, further damaging brain cells.
- Neuroinflammation: Chronic inflammation in the brain is a hallmark of Alzheimer’s disease, and NAD+ supports the sirtuin proteins that help regulate inflammation.
- Amyloid Plaque Formation: Some studies suggest that NAD+ levels may influence amyloid plaque buildup, which is implicated in Alzheimer’s pathology.
Learn everything about Alzheimer and find all the natural solutions to treat Alzheimer's naturally, including various diet programs, alternative medicine, vitamins, supplements, herbal medicine, and home remedies.
Why NAD Helps for Alzheimer
NAD+ supplementation has shown promise in addressing some of the underlying causes of Alzheimer's disease. Since NAD+ is involved in key cellular processes, such as energy metabolism, oxidative stress regulation, and inflammation control, increasing NAD+ levels may help restore balance in the brain and slow disease progression.
- Mitochondrial Dysfunction: NAD+ boosts mitochondrial function, which is crucial for sustaining brain cell energy and preventing the neuronal degeneration seen in Alzheimer’s disease.
- Oxidative Stress: NAD+ aids in the ...
Why NAD Helps for Alzheimer
NAD+ supplementation has shown promise in addressing some of the underlying causes of Alzheimer's disease. Since NAD+ is involved in key cellular processes, such as energy metabolism, oxidative stress regulation, and inflammation control, increasing NAD+ levels may help restore balance in the brain and slow disease progression.
- Mitochondrial Dysfunction: NAD+ boosts mitochondrial function, which is crucial for sustaining brain cell energy and preventing the neuronal degeneration seen in Alzheimer’s disease.
- Oxidative Stress: NAD+ aids in the activity of antioxidant enzymes that neutralize free radicals, potentially reducing oxidative damage that accelerates brain aging and cognitive decline in Alzheimer’s patients.
- Neuroinflammation: By activating sirtuins, NAD+ helps control neuroinflammation, a major contributor to Alzheimer’s pathology. This may reduce brain cell damage and improve cognitive function.
- Amyloid Plaque Formation: Evidence suggests that NAD+ might inhibit the formation of amyloid plaques, providing a potential therapeutic avenue for slowing disease progression in Alzheimer’s patients.
Accordingly, NAD+ could be a valuable adjunct in the treatment of Alzheimer’s disease, as it targets several mechanisms involved in the disease’s development. However, it is unlikely to serve as a standalone solution. NAD+ supplementation should be considered as part of a comprehensive treatment plan, particularly in conjunction with other therapies that target amyloid plaque reduction or neuroprotective strategies.
While NAD+ can help support mitochondrial function, reduce oxidative stress, and alleviate neuroinflammation, more research is needed to establish its long-term effectiveness. Compared to other therapies, NAD+ has a unique advantage in supporting cellular metabolism and promoting brain health at a molecular level.
How NAD works for Alzheimer's Disease
NAD+ plays a crucial role in maintaining cellular functions, and its effects extend to the mechanisms that underlie Alzheimer’s disease. By improving mitochondrial function, reducing oxidative stress, regulating inflammation, and potentially modulating amyloid plaque formation, NAD+ supplementation targets several key contributors to the disease’s progression. Below are the mechanisms through which NAD+ exerts its beneficial effects in Alzheimer's.
- Mitochondrial Support: NAD+ facilitates ATP production in mitochondria, supporting energy production in neurons, which is essential for ...
How NAD works for Alzheimer's Disease
NAD+ plays a crucial role in maintaining cellular functions, and its effects extend to the mechanisms that underlie Alzheimer’s disease. By improving mitochondrial function, reducing oxidative stress, regulating inflammation, and potentially modulating amyloid plaque formation, NAD+ supplementation targets several key contributors to the disease’s progression. Below are the mechanisms through which NAD+ exerts its beneficial effects in Alzheimer's.
- Mitochondrial Support: NAD+ facilitates ATP production in mitochondria, supporting energy production in neurons, which is essential for maintaining cognitive function. When NAD+ is replenished, it may help restore normal mitochondrial activity, reducing cellular damage and supporting brain health.
- Reducing Oxidative Stress: NAD+ activates enzymes like PARP and SIRT1 that are involved in the cellular response to oxidative stress. By enhancing these pathways, NAD+ helps protect neurons from the damage caused by free radicals, a key factor in Alzheimer’s disease progression.
- Regulating Neuroinflammation: NAD+ activates sirtuins, proteins that regulate inflammatory pathways in the brain. This may help reduce the chronic inflammation that is often present in Alzheimer's and protect neurons from inflammation-induced damage.
- Amyloid Plaque Regulation: NAD+ may influence enzymes involved in amyloid beta processing, thus potentially limiting the buildup of amyloid plaques in the brain. This can help mitigate one of the key factors driving Alzheimer's pathology.
Dose and Forms of NAD for Alzheimer
There are no universally agreed-upon dosage guidelines for NAD+ specifically for Alzheimer’s disease. However, studies generally recommend a range based on preliminary research and clinical observations:
- Oral Doses: Typically, oral doses of NAD+ precursors, such as nicotinamide riboside (NR) or nicotinamide mononucleotide (NMN), are used in amounts ranging from 250 mg to 500 mg daily. This range has shown benefits for cellular energy support without significant side effects.
- IV Therapy Doses: IV NAD ...
Dose and Forms of NAD for Alzheimer
There are no universally agreed-upon dosage guidelines for NAD+ specifically for Alzheimer’s disease. However, studies generally recommend a range based on preliminary research and clinical observations:
- Oral Doses: Typically, oral doses of NAD+ precursors, such as nicotinamide riboside (NR) or nicotinamide mononucleotide (NMN), are used in amounts ranging from 250 mg to 500 mg daily. This range has shown benefits for cellular energy support without significant side effects.
- IV Therapy Doses: IV NAD+ therapy may range from 500 mg to 1,000 mg administered in a clinic setting. IV NAD+ provides immediate availability to cells, but dosing may vary based on the individual’s response and needs.
It’s advisable to start with the lower end of the dosage spectrum and increase under medical supervision to monitor tolerance and any potential side effects, particularly for patients with Alzheimer’s who may be sensitive to high doses.
Best Types of NAD+ for Alzheimer’s
Two main forms of NAD+ supplementation are commonly used in Alzheimer's research and treatment:
- NAD+ Precursors (NR and NMN): These are precursors that convert to NAD+ within the body. NR and NMN are among the most researched forms and are valued for their effectiveness in raising NAD+ levels through oral administration.
- IV NAD+: This form delivers NAD+ directly into the bloodstream, offering higher bioavailability and quicker absorption compared to oral supplements. However, it requires a clinical setting and professional supervision.
While both NAD+ precursors (like NR or NMN) and IV NAD+ are used for Alzheimer's, NR or NMN supplements are often preferred for regular, at-home use due to their ease and effectiveness in supporting cellular NAD+ levels consistently. IV NAD+ may be beneficial for intensive, short-term support under medical supervision.
Available Forms of NAD+ for Alzheimer's
NAD+ for Alzheimer's support is available in several forms, each with its own advantages:
- Capsules/Tablets: Common for NR and NMN, suitable for daily oral intake.
- Powder: NMN and NR are also available in powder form, offering customizable dosing.
- IV Solution: Administered in medical facilities for immediate NAD+ replenishment and high bioavailability.
Taking NAD for Alzheimer: Precautions
Before using NAD+ supplements for Alzheimer’s, certain precautions should be considered to ensure safety and effectiveness:
- Monitoring and Professional Guidance: Alzheimer’s patients are often sensitive to medications and supplements. It is essential to consult healthcare providers for personalized advice on NAD+ dosing and administration, especially when considering IV therapy.
- Cancer Risks and Monitoring: There are concerns that NAD+ supplementation, due to its role in cellular metabolism and energy production, might also support the growth of ...
Taking NAD for Alzheimer: Precautions
Before using NAD+ supplements for Alzheimer’s, certain precautions should be considered to ensure safety and effectiveness:
- Monitoring and Professional Guidance: Alzheimer’s patients are often sensitive to medications and supplements. It is essential to consult healthcare providers for personalized advice on NAD+ dosing and administration, especially when considering IV therapy.
- Cancer Risks and Monitoring: There are concerns that NAD+ supplementation, due to its role in cellular metabolism and energy production, might also support the growth of existing or latent cancer cells. While research is ongoing and evidence is inconclusive, individuals with a history of cancer, those at high risk, or those with a family history of cancer should consult their healthcare provider before using NAD+ supplements. Regular monitoring and cautious, lower dosing might be advisable for these individuals.
- Interactions with Other Medications: NAD+ supplementation may interact with medications used to manage Alzheimer’s symptoms or coexisting health conditions. Monitoring by a medical professional is advisable.
- Long-term Safety: While NAD+ is generally considered safe, the long-term effects of continuous NAD+ elevation in Alzheimer’s patients are not fully established. Periodic assessment of cognitive health and metabolic markers is recommended.
Taking NAD for Alzheimer: Side Effects
When using NAD+ for Alzheimer’s, potential side effects may vary depending on the form and dosage:
- Digestive Issues: Oral NAD+ precursors like NR and NMN may cause mild nausea, stomach upset, or bloating in some patients.
- Headache and Fatigue: High doses or initial use of NAD+ can lead to headaches or a temporary increase in fatigue, as cells adjust to the elevated NAD+ levels.
- Injection Site Discomfort (IV NAD+): When administered via IV, some ...
Taking NAD for Alzheimer: Side Effects
When using NAD+ for Alzheimer’s, potential side effects may vary depending on the form and dosage:
- Digestive Issues: Oral NAD+ precursors like NR and NMN may cause mild nausea, stomach upset, or bloating in some patients.
- Headache and Fatigue: High doses or initial use of NAD+ can lead to headaches or a temporary increase in fatigue, as cells adjust to the elevated NAD+ levels.
- Injection Site Discomfort (IV NAD+): When administered via IV, some patients may experience discomfort, redness, or inflammation at the injection site.
FAQ About NAD for Alzheimer
How does NAD affect Alzheimer’s disease?
NAD is crucial for cellular energy and repair, functions often impaired in Alzheimer’s. NAD may help protect brain cells, support mitochondrial health, and reduce neuroinflammation, potentially slowing Alzheimer’s progression.
Can NAD prevent Alzheimer’s or reduce the risk?
Research suggests NAD may lower the risk of neurodegenerative diseases like Alzheimer’s by promoting brain cell health, reducing oxidative stress, and supporting DNA repair, though more studies are needed for conclusive evidence ...
FAQ About NAD for Alzheimer
How does NAD affect Alzheimer’s disease?
NAD is crucial for cellular energy and repair, functions often impaired in Alzheimer’s. NAD may help protect brain cells, support mitochondrial health, and reduce neuroinflammation, potentially slowing Alzheimer’s progression.
Can NAD prevent Alzheimer’s or reduce the risk?
Research suggests NAD may lower the risk of neurodegenerative diseases like Alzheimer’s by promoting brain cell health, reducing oxidative stress, and supporting DNA repair, though more studies are needed for conclusive evidence.
Is NAD therapy effective for early-stage Alzheimer’s?
NAD therapy may be more effective in the early stages of Alzheimer’s, where it can help support brain cell health and improve energy production, potentially delaying cognitive decline.
Can NAD improve memory in people with Alzheimer’s?
NAD may enhance memory by boosting brain energy levels and protecting neurons. While results vary, some studies and anecdotal reports suggest improved cognitive clarity and memory with NAD support.
What NAD dosage is recommended for Alzheimer’s patients?
There is no established dosage for Alzheimer’s treatment; doses of NAD precursors, such as NMN or NR, generally range from 250-500 mg daily in studies. It’s essential to consult a healthcare provider for personalized dosing.
Does NAD cross the blood-brain barrier to affect Alzheimer’s?
NAD precursors like NMN and NR are believed to cross the blood-brain barrier more effectively than NAD itself, making them promising options for targeting brain health in Alzheimer’s.
Are there side effects of using NAD for Alzheimer’s?
NAD supplements are typically safe but may cause mild side effects like nausea or fatigue. IV NAD therapy requires medical supervision, especially for Alzheimer’s patients, due to potential sensitivities.
Is NAD therapy safe for elderly Alzheimer’s patients?
NAD is generally safe for elderly patients when used as a supplement, but higher-dose IV therapy should only be administered by a healthcare provider to monitor for any adverse reactions.
Can NAD improve quality of life in Alzheimer’s patients?
By potentially enhancing energy, cognitive function, and mood, NAD may contribute to a better quality of life in some Alzheimer’s patients, though individual responses can vary.
Is NAD therapy a cure for Alzheimer’s?
NAD is not a cure for Alzheimer’s, but it may help manage symptoms and slow disease progression by protecting brain cells and supporting cognitive function. It is used as part of a complementary approach rather than a standalone treatment.
Disclaimer: The published information is based on research and published medical sources. It is provided for educational purposes only and is not intended to replace professional medical advice. Always consult with your doctor or healthcare provider regarding any questions you may have about your health. We are not responsible for any actions taken based on this information, nor for any errors, omissions, or inaccuracies in the content. Medical research is constantly evolving, and the information presented may not reflect the most current medical standards.
November 2024
AposBook
Reviews & Testimonials
-
Overall rating
-
Success Rate
-
Effectiveness
-
Accessiblity
-
Safety
-
Fast result
-
Ease of use
Add review
Was solution successfull?
Overall rating score
Rate each parameters
Effective
Accessible
Safe
Fast results
Easy to apply
Review title
Add images to support your review(if any)
Support images
You can review a solution if you have used it personally. Please remain objective and genuine. Your input can help others.
You have already reviewed this
Please rate all parameters.
Success! Thank you for your feedback. Your contribution can make a difference. Together we can help each other.
What science says about Nad/Nmn For Alzheimer / Dementia
Library center NAD/NMN For Alzheimer / Dementia
Additional benefits of NAD (Nicotinamide Adenine Dinucleotide)





 Buy now
Buy now






























[0]