Ready to leave?
Oops ! Condition name you have entered is invalid.
You are now leaving Aposbook.com and going to an external site managed by another organization.
Please confirm your email address and try to login again.
This account has been deleted. do you want to restore it?

Validate your email
A verification link will be sent to within the next 2 minutes. Please click it to validate your e mail.
*If you didn't get the link, please check your spam folder
Welcome to Aposbook,
As a registered user, you can benefit from the various free tools and services that we provide.
All you need to do is log in to start discussing with others, interacting, asking questions, and sharing your point of view about the various topics.
You can also write reviews and testimonials about any natural solution you have tried and share your experience. Your feedback can be very helpful.
If you are a health expert, you can add information about any topic or suggest text edit. You can also publish content, including articles and videos, about any topic from the related library section.
Together we can help.
The Aposbook Team
Forgot Password?
A validation link will be sent to you by email. Please confirm your address to log in
*If you didn't get the link, please check your spam folder
Please log in to use this feature
Your account has been suspended because you have violated our code of conduct. If you think this was a mistake, you can contact us by email at: support@aposbook.com "Contact us" form.
Success! Thank you for your feedback. Your contribution can make a difference. Together we can help each other.


Can Blood Type Diet help for Heart Disease?
Complete Guide to Blood Type Diet for Heart Disease
Possible causes of Heart Disease from the Blood Type Diet perspective
Heart disease refers to a range of conditions that can cause disorders in the heart.
Common heart disease include cardiovascular disease (CVD) which refers to conditions affecting the heart or blood vessels.
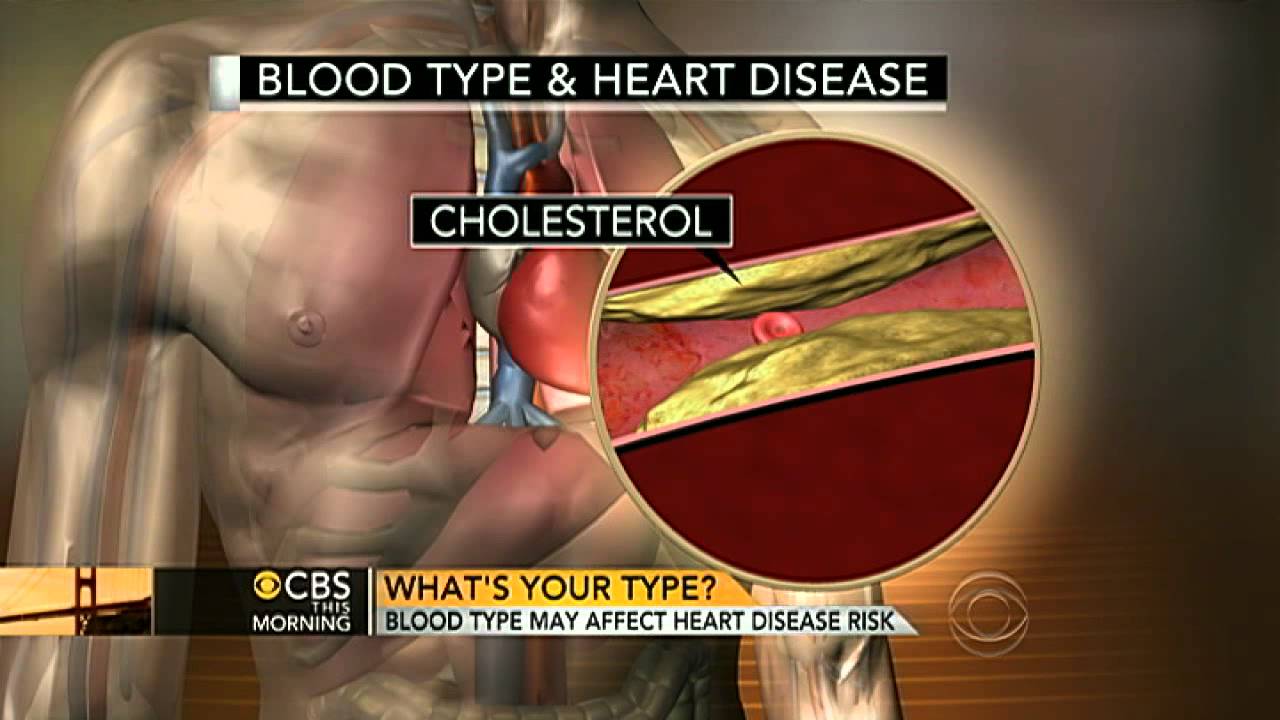
CVD is mostly associated with atherosclerosis, which is a build-up of plaque that consists mainly of fat, cholesterol, calcium, and other substances.
This buildup narrows the arteries, making it harder for blood to flow through them ...
Possible causes of Heart Disease from the Blood Type Diet perspective
Heart disease refers to a range of conditions that can cause disorders in the heart.
Common heart disease include cardiovascular disease (CVD) which refers to conditions affecting the heart or blood vessels.
CVD is mostly associated with atherosclerosis, which is a build-up of plaque that consists mainly of fat, cholesterol, calcium, and other substances.
This buildup narrows the arteries, making it harder for blood to flow through them. This can lead to the formation of blood clots, which block blood flow to the heart or brain, causing a heart attack or stroke.
According to the blood type diet, two main factors can increase the risk of heart disease.
1- High levels of blood clotting factors: Blood type A and AB individuals are more at risk of developing high cholesterol levels and cardiovascular diseases because they have more “blood clotting factors” in the blood compared to other blood types.
2- High cholesterol and triglyceride levels: Type A and AB individuals are more at risk of heart disease compared to other blood types because they metabolize fats differently. Their inability to break down fats increases their triglyceride and cholesterol levels. If these lipids build up in the blood, they can stick to the artery walls and block blood flow to the heart, causing heart disease.
Blood type O and blood type B individuals can be at risk of heart disease if they eat a lot of carbohydrates as carbs can cause an increase in triglyceride and cholesterol level as well as weight gain.
Recent studies also show a clear link between a person’s blood type and their risk of developing heart disease. According to a 2012 study titled, “ABO Blood Group and Risk of Coronary Heart Disease in Two Prospective Cohort Studies,” blood type O individuals were less at risk for coronary heart disease than blood type A, B, and AB individuals.
In addition, another study conducted in 2013 titled, “Beyond immunohaematology: the role of the ABO blood group in human diseases” also showed that blood type is linked to some particular diseases, especially heart disease.
Learn everything about heart disease and find all the natural solutions to treat and prevent cardiovascular disease naturally, including various diet programs, alternative medicine, vitamins, supplements, herbal medicine, and home remedies.
Why Blood Type Diet helps treat and prevent Heart Disease
The blood type diet helps treat and prevent heart disease because it provides each blood type with the proper foods to maintain heart health. These foods do not contain lectins that react negatively with blood type antigens and increase the levels of triglycerides and cholesterol in the blood.
The recommended foods based on every blood type would help control the body’s triglyceride and cholesterol levels. This reduces people’s risk of ...
Why Blood Type Diet helps treat and prevent Heart Disease
The blood type diet helps treat and prevent heart disease because it provides each blood type with the proper foods to maintain heart health. These foods do not contain lectins that react negatively with blood type antigens and increase the levels of triglycerides and cholesterol in the blood.
The recommended foods based on every blood type would help control the body’s triglyceride and cholesterol levels. This reduces people’s risk of heart disease because lipids will not build up and block the heart’s arteries, limiting blood supply to the heart.
Furthermore, the diet reduces heart disease in blood types A and AB that have more clotting factors in their blood. It prescribes suitable foods that do not contain harmful lectins to each blood type to counteract the presence of increased clotting factors.
This stops the blood from coagulating around the lectins and blocking the blood supply to the heart, reducing blood type A and AB's risk of heart disease.
How Blood Type Diet works for Heart Disease / Atherosclerosis
The blood type diet works by prescribing specific foods for each blood type to lower the lipid levels in a person’s blood. If a person with a particular blood type avoids foods that increases cholesterol and triglyceride levels, that person will reduce the risk of developing heart disease because the lipids will not build up in the blood and cause blood clots or restrict blood flow to the heart.
According to ...
How Blood Type Diet works for Heart Disease / Atherosclerosis
The blood type diet works by prescribing specific foods for each blood type to lower the lipid levels in a person’s blood. If a person with a particular blood type avoids foods that increases cholesterol and triglyceride levels, that person will reduce the risk of developing heart disease because the lipids will not build up in the blood and cause blood clots or restrict blood flow to the heart.
According to scientific research conducted on different blood groups, blood type A and AB individuals have more clotting factors in their blood than blood type O and B.
One of these clotting factors, factor VIII, is especially high in blood types A and AB. It can cause more frequent blood clots and slow down blood flow in the heart’s arteries, which supply blood to the rest of the body. This makes them more prone to heart disease.
Therefore, they should avoid meat and limit dairy products because they contain harmful lectins that cause the blood to coagulate in different areas in the body.
In addition, people with blood type A and AB are more at risk of heart disease than people with blood type O or B because they have lower levels of an enzyme called Intestinal Alkaline Phosphatase (IAP).
AIP helps break down cholesterol and fats in the body that may be present in meats, and because types A and AB have lower levels of IAP, they might not break down the fats in meats easily.
This leads to increased levels of cholesterol and triglycerides in the blood. People with blood type A and AB should avoid meat to reduce the amount of cholesterol and triglycerides in their diet, minimizing their risk of heart disease.
Blood type O and B individuals can be at risk for heart disease if they eat wheat or wheat-based products. This is because these foods may induce “Metabolic Syndrome,” which is a group of symptoms that lead to heart disease, stroke, and diabetes.
These symptoms are high blood pressure, high cholesterol levels, high triglyceride levels, high blood sugar, and excess fat around the waist. Therefore, people with blood type O and blood type B need to eliminate wheat from their diet to prevent “Metabolic Syndrome.”
That way, they keep their cholesterol levels low and maintain a healthy weight, which helps prevent heart disease.
Blood Type Diet foods for Heart Disease / Atherosclerosis
The blood type is not based on the amounts of macronutrients or calories your body consumes. Instead, it focuses on restricting food groups for each blood type to help maintain proper body functions and prevent and treat medical conditions.
Below, is a list of food types for each blood type:
- Blood Type O: can eat lean meat, poultry, fish, and vegetables, and fewer grains, beans, and dairy.
- Blood Type A: can eat more ...
Blood Type Diet foods for Heart Disease / Atherosclerosis
The blood type is not based on the amounts of macronutrients or calories your body consumes. Instead, it focuses on restricting food groups for each blood type to help maintain proper body functions and prevent and treat medical conditions.
Below, is a list of food types for each blood type:
- Blood Type O: can eat lean meat, poultry, fish, and vegetables, and fewer grains, beans, and dairy.
- Blood Type A: can eat more fruits and vegetables, beans and legumes, and whole grains with little to no meat (vegetarian diet).
- Blood Type B: can eat green leafy vegetables, eggs, most meats (except chicken and pork), and low-fat dairy. They should avoid wheat, corn, lentils, tomatoes, peanuts, and sesame seeds.
- Blood Type AB: can eat seafood, tofu, dairy, beans, and grains. They should avoid kidney beans, corn, beef, and chicken.
Blood Type Diet for Heart Disease: what you should eat by blood type
Each blood type can prevent heart disease if they eat specific foods that improve heart health and function. Below is the list of foods that help maintain heart health for each blood type, according to the blood type diet:
Foods for Blood Type O
People who are blood type O can eat these foods which are good for the heart:
- Lean and organic lamb and mutton ...
Blood Type Diet for Heart Disease: what you should eat by blood type
Each blood type can prevent heart disease if they eat specific foods that improve heart health and function. Below is the list of foods that help maintain heart health for each blood type, according to the blood type diet:
Foods for Blood Type O
People who are blood type O can eat these foods which are good for the heart:
- Lean and organic lamb and mutton
- Richly-oiled cold water fish
- Olive oil
- Walnuts
- Seaweed
- Broccoli
- Spinach and kale
- Maitake mushrooms
- Pineapples
- Blueberries, elderberries, and cherries
- Turmeric
- Green tea
Foods for Blood Type A
People who are blood type A can eat these foods which are good for the heart:
- Soy foods
- Richly-oiled cold water fish
- Olive oil
- Walnuts
- Seaweed
- Broccoli
- Spinach and kale
- Mushrooms (maitake or silver dollar)
- Pineapples
- Blueberries, elderberries, and cherries
- Ginger
- Herbal teas
Foods for Blood Type B
People who are blood type B can eat these foods which are good for the heart:
- Lean and organic lamb and mutton
- Richly-oiled cold water fish
- Olive oil
- Cultured dairy foods (yogurt, kefir)
- Black walnuts
- Broccoli
- Collards, kale, and mustard greens
- Shiitake mushrooms
- Pineapples
- Cranberries
- Turmeric
- Herbal teas (dandelion, licorice root)
- Green tea
Foods for Blood Type AB
People who are blood type AB can eat these foods which are good for the heart:
- Soy foods
- Richly-oiled cold water fish
- Cultured dairy foods (yogurt, kefir)
- Olive oil
- Walnuts
- Leafy green vegetables
- Maitake mushrooms
- Pineapples
- Gooseberries, loganberries, and cherries
- Garlic
- Ginger
- Green tea
Blood Type Diet for Cardiovascular Disease: Recommendations to Follow
- Eat fresh and organic fruits and vegetables: fresh or organic fruits and vegetables have more nutrients. If people eat fruits and vegetables have been sprayed with pesticides, the chemicals in the pesticides could cause the body to believe it is under attack and overwork the body’s immune system, eventually weakening it.
- Take certain supplements depending on your blood type: the diet restricts the consumption of meat and dairy for specific blood types ...
Blood Type Diet for Cardiovascular Disease: Recommendations to Follow
- Eat fresh and organic fruits and vegetables: fresh or organic fruits and vegetables have more nutrients. If people eat fruits and vegetables have been sprayed with pesticides, the chemicals in the pesticides could cause the body to believe it is under attack and overwork the body’s immune system, eventually weakening it.
- Take certain supplements depending on your blood type: the diet restricts the consumption of meat and dairy for specific blood types. This may result in malnutrition, so some blood types must take nutritional supplements to ensure that they get the vitamins and minerals their body needs.
o Blood type O individuals need to take Vitamin C, B12, iron, and folic acid supplements.
o Blood type A individuals need to take Vitamin B, K, calcium, and licorice supplements.
o Blood type B individuals need to take magnesium, ginkgo, licorice, and lecithin supplements.
o Blood type AB individuals need to take Vitamin C, B12, and iron supplements.
- Exercise regularly: the diet recommends different kinds of exercise based on your blood type:
o Blood type O: People who are type O should engage in intense exercising activities like jogging or biking.
o Blood type A: People who are type A should focus on low-level activity and stress-relieving exercises like yoga or tai chi.
o Blood type B: People who are type B should focus on moderate-level exercise and can include yoga or other mindfulness practices.
o Blood type AB: People with type AB blood can combine exercises from blood types A and B.
Blood Type Diet for Atherosclerosis: what you should avoid
All of the blood types should avoid:
- Processed meats: this is because processed meats contain more salt and preservatives that are not good for your body
- Foods high in sugar: high sugar foods can cause imbalances in the body
- Simple carbohydrates: simple carbohydrates can cause weight gain
- Water with meals: drinking water during mealtimes can slow down digestion
Specific foods to avoid for each blood type
The different blood types should avoid the following foods to maintain a healthy heart:
Foods to avoid for Type O
o Dairy products because Type O individuals can’t digest them
o Wheat and wheat-based products because they can increase your fat levels
o Beans because some contain lectins that are hard to digest
Foods to avoid for Type A
o Red meat is hard for Type A’s to digest because they have low levels of stomach acid
o Fresh milk products like cow’s milk because they can cause mucus production
o Wheat and wheat-derived foods because they can cause weight gain
Foods to avoid for Type B
Type B’s should avoid the following foods because they cause weight gain and increase triglyceride and cholesterol levels.
o Wheat
o Corn
o Chicken
o Buckwheat
o Lentils
o Potatoes
Foods to avoid for Type AB
o Red meat is hard for Type AB’s to digest because they have low levels of stomach acid
o Fresh milk products like cow’s milk because they can cause mucus production
o Wheat and wheat-derived foods because they can cause weight gain
Blood Type Diet for Heart Disease: precautions
The diet can be restrictive for some blood types, like type A and type O, so the person must be careful to receive the vitamins and minerals that the body needs from other food sources.
Always consult with a health expert before starting any diet, especially if you have a chronic health condition like diabetes, heart disease, or if you are taking any medication.
Always consult with a healthcare professional before starting any ...
Blood Type Diet for Heart Disease: precautions
The diet can be restrictive for some blood types, like type A and type O, so the person must be careful to receive the vitamins and minerals that the body needs from other food sources.
Always consult with a health expert before starting any diet, especially if you have a chronic health condition like diabetes, heart disease, or if you are taking any medication.
Always consult with a healthcare professional before starting any new diet or treatment.
Reviews & Testimonials
-
Overall rating
-
Success Rate
-
Effectiveness
-
Accessiblity
-
Safety
-
Fast result
-
Ease of use
Add review
Was solution successfull?
Overall rating score
Rate each parameters
Effective
Accessible
Safe
Fast results
Easy to apply
Review title
Add images to support your review(if any)
Support images
You can review a solution if you have used it personally. Please remain objective and genuine. Your input can help others.
You have already reviewed this
Please rate all parameters.
Success! Thank you for your feedback. Your contribution can make a difference. Together we can help each other.
What science says about Blood Type Diet For Heart Disease
Views in favor
The PLOS / 'Blood Type Diet' Study: A Look at the Core Data
Views against
Theory behind popular blood-type diet debunked
Library center Blood Type Diet for Heart Disease
Additional benefits of Blood Type Diet
- Cusack, L., De Buck, E., Compernolle, V., & Vandekerckhove, P. (2013). Blood type diets lack supporting evidence: A systematic review. The American Journal of Clinical Nutrition, 98(1), 99-104. doi:10.3945/ajcn.113.058693
- D’Adamo P, Whitney C. (2002) Eat Right 4 Your Type. London: Penguin.
- He, M., Wolpin, B., Rexrode, K., Manson, J. E., Rimm, E., Hu, F. B., & Qi, L. (2012). ABO Blood Group and Risk of Coronary Heart Disease in Two Prospective Cohort Studies. Arteriosclerosis, Thrombosis, and Vascular Biology, 32(9), 2314–2320. doi: 10.1161/atvbaha.112.248757
- Liumbruno, G. M., Franchini, J. (2013). Beyond immunohaematology: the role of the ABO blood group in human diseases. Blood Transfus, 11(4), 491–499. doi: 10.2450/2013.0152-13
-Wang, J., García-Bailo, B., Nielsen, D. E., & El-Sohemy, A. (2014). ABO Genotype, ‘Blood-Type’ Diet and Cardiometabolic Risk Factors. PLoS ONE, 9(1). doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0084749
- Wang, J., Jamnik, J., García-Bailo, B., Nielsen, D. E., Jenkins, D. J., & El-Sohemy, A. (2018). ABO Genotype Does Not Modify the Association between the “Blood-Type” Diet and Biomarkers of Cardiometabolic Disease in Overweight Adults. The Journal of Nutrition, 148(4), 518–525. doi: 10.1093/jn/nxx074



















[0]