Frequently Asked Questions About Glycine
What is glycine?
Glycine is a non-essential amino acid that serves as a building block for proteins and plays important roles in various metabolic processes.
What foods are high in glycine?
Foods rich in glycine include collagen-rich meats (such as chicken skin, tendons, and pork), fish (especially those with skin and bones), bone broth, gelatin, eggs, legumes, and dairy products.
How does the body use glycine?
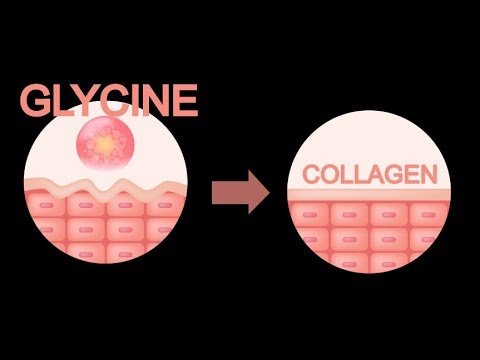
Glycine is involved in protein synthesis, helps produce neurotransmitters ...
Frequently Asked Questions About Glycine
What is glycine?
Glycine is a non-essential amino acid that serves as a building block for proteins and plays important roles in various metabolic processes.
What foods are high in glycine?
Foods rich in glycine include collagen-rich meats (such as chicken skin, tendons, and pork), fish (especially those with skin and bones), bone broth, gelatin, eggs, legumes, and dairy products.
How does the body use glycine?
Glycine is involved in protein synthesis, helps produce neurotransmitters, supports the formation of collagen, and plays a role in detoxification processes in the liver.
What are the dietary sources of glycine?
Glycine can be obtained from both animal and plant sources, with animal products like meat, fish, and dairy being the richest sources, while legumes and certain nuts provide smaller amounts.
How much glycine should I take daily?
While the body can produce glycine, a typical supplemental dose ranges from 1 to 3 grams per day, depending on individual needs. It’s best to consult with a healthcare provider for specific recommendations.
Can glycine supplements be taken with other amino acids?
Yes, glycine supplements can be taken alongside other amino acids and protein supplements, as they can complement each other’s effects and support overall protein synthesis.
Is glycine safe to consume?
Glycine is generally considered safe for most people when taken in appropriate doses. However, as with any supplement, it is advisable to consult a healthcare professional before starting.
What are the different forms of glycine supplements?
Glycine is available in various forms, including powder, capsules, and tablets, allowing for flexibility in dosing and ease of consumption based on personal preference.
How should glycine supplements be stored?
Glycine supplements should be stored in a cool, dry place, away from direct sunlight and moisture, to maintain their potency and shelf life.
Does glycine have any flavor?
Glycine is known to have a slightly sweet taste, making it palatable when mixed with beverages or foods. This sweetness is often utilized in the food industry for flavor enhancement.
Disclaimer: The published information is based on research and published medical sources. It is provided for educational purposes only and is not intended to replace professional medical advice. Always consult with your doctor or healthcare provider regarding any questions you may have about your health. We are not responsible for any actions taken based on this information, nor for any errors, omissions, or inaccuracies in the content. Medical research is constantly evolving, and the information presented may not reflect the most current medical standards.
October 2024
AposBook







 Buy now
Buy now

















[0]