Ready to leave?
Oops ! Condition name you have entered is invalid.
You are now leaving Aposbook.com and going to an external site managed by another organization.
Please confirm your email address and try to login again.
This account has been deleted. do you want to restore it?

Validate your email
A verification link will be sent to within the next 2 minutes. Please click it to validate your e mail.
*If you didn't get the link, please check your spam folder
Welcome to Aposbook,
As a registered user, you can benefit from the various free tools and services that we provide.
All you need to do is log in to start discussing with others, interacting, asking questions, and sharing your point of view about the various topics.
You can also write reviews and testimonials about any natural solution you have tried and share your experience. Your feedback can be very helpful.
If you are a health expert, you can add information about any topic or suggest text edit. You can also publish content, including articles and videos, about any topic from the related library section.
Together we can help.
The Aposbook Team
Forgot Password?
A validation link will be sent to you by email. Please confirm your address to log in
*If you didn't get the link, please check your spam folder
Please log in to use this feature
Your account has been suspended because you have violated our code of conduct. If you think this was a mistake, you can contact us by email at: support@aposbook.com "Contact us" form.
Success! Thank you for your feedback. Your contribution can make a difference. Together we can help each other.


Natural Compounds
Activated Charcoal
Activated Charcoal: Uses, Benefits, Side Effects, and More
Complete Guide to Activated Charcoal
What is Activated Charcoal
Activated charcoal is a highly porous substance created by heating natural carbon sources such as wood, coconut shells, or peat to extremely high temperatures. This process, known as "activation," increases its surface area, allowing it to absorb toxins and chemicals. Unlike regular charcoal, activated charcoal is specifically processed for medical, industrial, and cosmetic purposes. Its uses range from emergency poison treatments to detoxification and even beauty products
Types of Activated Charcoal
There are different types ...
What is Activated Charcoal
Activated charcoal is a highly porous substance created by heating natural carbon sources such as wood, coconut shells, or peat to extremely high temperatures. This process, known as "activation," increases its surface area, allowing it to absorb toxins and chemicals. Unlike regular charcoal, activated charcoal is specifically processed for medical, industrial, and cosmetic purposes. Its uses range from emergency poison treatments to detoxification and even beauty products
Types of Activated Charcoal
There are different types of activated charcoal, which vary based on their source material and the method of activation. These differences affect their pore size, surface area, and specific uses. Here are the main types of activated charcoal:
- Powdered Activated Charcoal (PAC): This is finely ground and has the highest adsorption rate. It's commonly used in medical applications like treating poisoning or in water purification.
- Granular Activated Charcoal (GAC): This type has larger particles compared to PAC and is typically used in industrial filtration systems, such as air and water filters.
- Extruded Activated Charcoal (EAC): Produced by combining activated charcoal powder with a binder, it forms cylindrical pellets. EAC is durable and often used in air filtration systems.
- Impregnated Activated Charcoal: This variety is treated with chemicals (e.g., silver, iodine) to enhance specific properties, such as antibacterial effects. It’s used in medical applications or advanced water purification.
- Specialized Charcoal (e.g., coconut shell-based): Coconut shell charcoal is highly porous and often used for medical and cosmetic purposes due to its fine structure and efficiency in adsorbing small molecules.
Each type is tailored to specific applications, with differences in adsorption capacity and reactivity. The right type depends on whether it’s for industrial, medical, or cosmetic use.
Components of Activated Charcoal
Activated charcoal is derived from natural carbon-rich materials subjected to high heat and activation processes. The activation process removes impurities and creates a porous structure, essential for its adsorptive properties. While the base material—whether coconut shells, hardwood, or bamboo—can influence its characteristics, the fundamental components of activated charcoal remain consistent.
Accordingly, activated charcoal primarily consists of elemental carbon in an amorphous form, arranged in a porous network. This structure gives it a massive surface area, crucial ...
Components of Activated Charcoal
Activated charcoal is derived from natural carbon-rich materials subjected to high heat and activation processes. The activation process removes impurities and creates a porous structure, essential for its adsorptive properties. While the base material—whether coconut shells, hardwood, or bamboo—can influence its characteristics, the fundamental components of activated charcoal remain consistent.
Accordingly, activated charcoal primarily consists of elemental carbon in an amorphous form, arranged in a porous network. This structure gives it a massive surface area, crucial for adsorption. During activation, impurities and non-carbon elements, such as hydrogen, nitrogen, and oxygen, are eliminated or significantly reduced, leaving behind a material with high carbon purity.
Natural Sources of Activated Charcoal
The choice of raw material plays a role in determining the pore size distribution, surface area, and adsorption capacity of the final product:
- Coconut Shells: Produces charcoal with micropores ideal for adsorbing small molecules. Preferred in medical and cosmetic applications for its high purity and effectiveness.
- Hardwoods: Commonly used in general-purpose activated charcoal. Offers a balance of micropores and macropores, making it versatile for various applications.
- Peat and Coal: Industrial-grade sources, often used in large-scale filtration systems. May have a broader pore size distribution but lower purity compared to coconut or hardwood-based charcoal.
- Bamboo: Known for its rapid growth and sustainability. Produces charcoal with properties similar to hardwood, but it is increasingly popular in eco-friendly applications.
Do Components Differ Between Sources?
The primary component—carbon—remains the same across all sources. However, the type of source material influences the pore size, surface area, and efficiency of the charcoal. For example:
- Coconut shell charcoal typically has a higher percentage of micropores, making it more suitable for adsorbing gases and toxins in medical applications.
- Hardwood and bamboo charcoals often have a mix of micro- and macropores, making them effective for water filtration or industrial purposes.
- Ultimately, while the fundamental components of activated charcoal do not differ, the source material and activation process determine its specific properties and best use cases.
How Activated Charcoal Works in the Body
Activated charcoal works by a mechanism called adsorption (not absorption), where toxins and chemicals adhere to the charcoal's surface. Here's how it operates:
- Micropore action: The high surface area of activated charcoal creates countless tiny pores that trap molecules, preventing their absorption into the bloodstream.
- Selective binding: While it binds strongly to many toxins, gases, and chemicals, it does not adsorb nutrients like vitamins and minerals.
- Non-digestive activity: Activated charcoal passes through the ...
How Activated Charcoal Works in the Body
Activated charcoal works by a mechanism called adsorption (not absorption), where toxins and chemicals adhere to the charcoal's surface. Here's how it operates:
- Micropore action: The high surface area of activated charcoal creates countless tiny pores that trap molecules, preventing their absorption into the bloodstream.
- Selective binding: While it binds strongly to many toxins, gases, and chemicals, it does not adsorb nutrients like vitamins and minerals.
- Non-digestive activity: Activated charcoal passes through the gastrointestinal tract without being metabolized, ensuring that trapped toxins are eliminated through feces.
This mechanism makes it effective for binding ingested toxins, though its usefulness is limited to substances still present in the stomach or intestines.
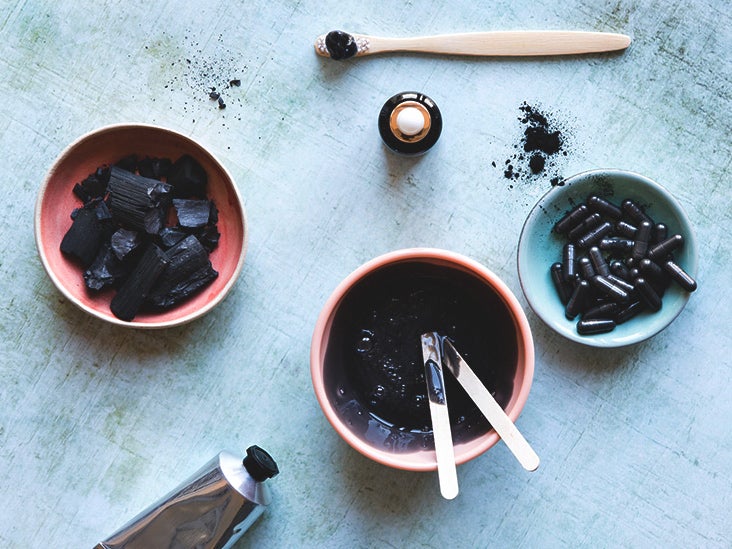
Dose and Forms of Activated Charcoal
Activated charcoal is available in several forms, each with specific guidelines for usage:
- Capsules or tablets: Common for general detox or gas relief. Typical dose: 500–1,000 mg per day for detoxification; up to 500 mg per dose for gas or bloating.
- Powder: Used in emergencies (e.g., poisoning) or as a detox drink. Preparation: Mix 1–2 teaspoons of powder with water or juice. Emergency dosage: Usually administered under medical supervision.
- Liquid ...
Dose and Forms of Activated Charcoal
Activated charcoal is available in several forms, each with specific guidelines for usage:
- Capsules or tablets: Common for general detox or gas relief. Typical dose: 500–1,000 mg per day for detoxification; up to 500 mg per dose for gas or bloating.
- Powder: Used in emergencies (e.g., poisoning) or as a detox drink. Preparation: Mix 1–2 teaspoons of powder with water or juice. Emergency dosage: Usually administered under medical supervision.
- Liquid suspension: Designed for quick use in cases of poisoning or overdoses. Dose is determined based on body weight and administered in clinical settings.
- Topical formulations (for non-ingestive use): Used in face masks or poultices for skin detox.
Always follow specific product instructions or consult a healthcare professional to ensure proper and safe use, especially for high doses or medical emergencies.
Activated Charcoal benefits
Activated charcoal offers a range of health benefits due to its unique ability to adsorb toxins, chemicals, and impurities. It works by trapping unwanted substances in its porous structure, preventing their absorption into the body and facilitating their elimination. Here's a closer look at its benefits, with detailed explanations:
- Emergency Poisoning Treatment: Activated charcoal is used in poisoning cases because it binds to toxins in the stomach and intestines, preventing their absorption into the bloodstream. This helps ...
Activated Charcoal benefits
Activated charcoal offers a range of health benefits due to its unique ability to adsorb toxins, chemicals, and impurities. It works by trapping unwanted substances in its porous structure, preventing their absorption into the body and facilitating their elimination. Here's a closer look at its benefits, with detailed explanations:
- Emergency Poisoning Treatment: Activated charcoal is used in poisoning cases because it binds to toxins in the stomach and intestines, preventing their absorption into the bloodstream. This helps to minimize the harmful effects of ingested poisons, reducing their ability to reach vital organs like the liver or kidneys.
- Alleviates Gas and Bloating: Activated charcoal can help relieve gas and bloating by trapping gas molecules in the digestive system. It works by adsorbing the gases produced by fermentation in the intestines, reducing discomfort and promoting easier digestion.
- Detoxification Support: Activated charcoal aids in detoxification by adsorbing toxins and impurities from the gastrointestinal tract. It helps cleanse the body of harmful substances, including chemicals from food, air, and environmental exposure, by preventing their absorption and facilitating their elimination.
- Improves Kidney Function: By adsorbing waste products such as urea, creatinine, and other toxins from the bloodstream, activated charcoal can reduce the workload on the kidneys, particularly in individuals with kidney disease. This helps lower the accumulation of waste in the body, supporting overall kidney function.
- Whitens Teeth and Improves Oral Health: Activated charcoal binds to plaque, bacteria, and surface stains on teeth. Its abrasive properties gently scrub the surface of teeth, while its adsorptive capabilities help remove stains and toxins, resulting in a brighter smile and better oral health.
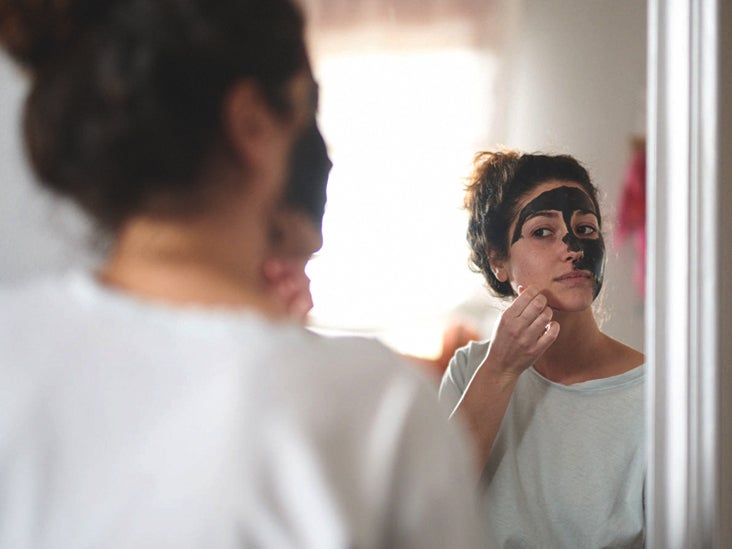
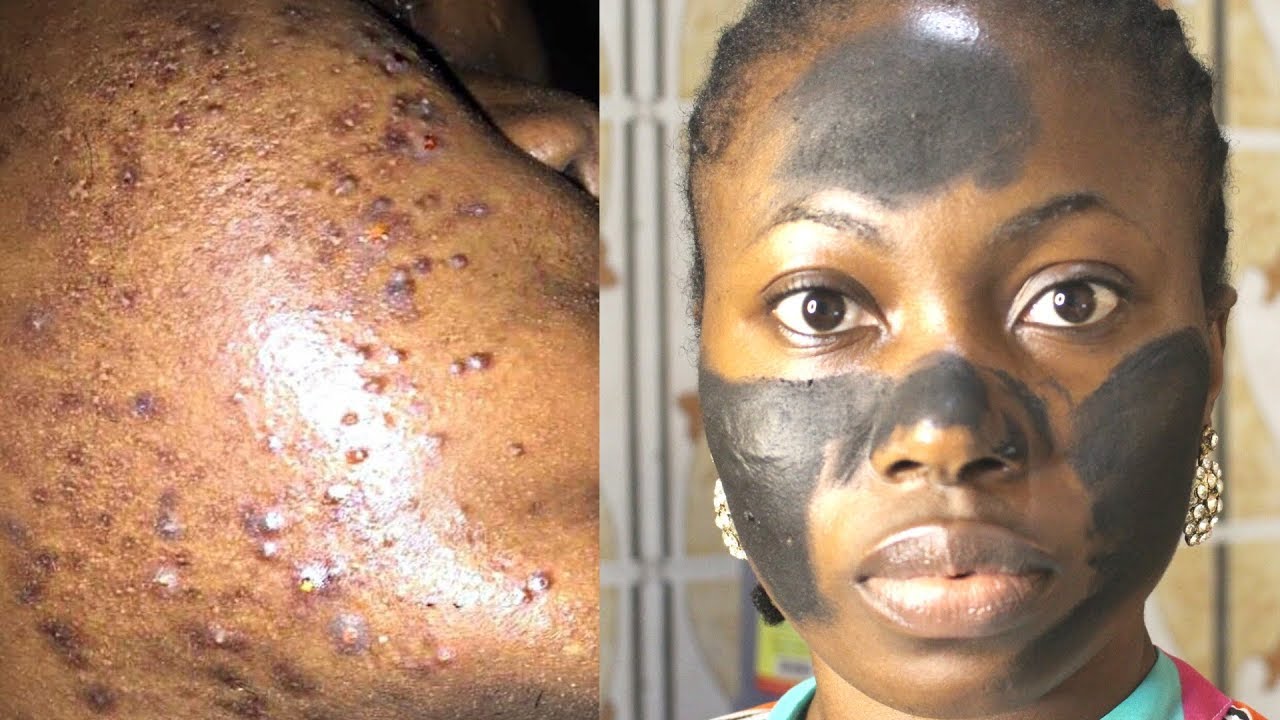
- Treats Skin Conditions: When applied topically, activated charcoal absorbs excess oil, bacteria, and other impurities from the skin. This helps reduce acne and other skin blemishes by preventing clogged pores and promoting clearer, healthier skin.
- Addresses Drug Overdose: In medical emergencies, activated charcoal is used to treat overdoses of specific medications, such as painkillers or certain toxins. By adsorbing the drugs in the gastrointestinal tract, it prevents further absorption into the bloodstream, helping to mitigate the overdose's harmful effects.
Activated Charcoal Precautions
Using activated charcoal requires careful consideration to ensure safety and efficacy. Key precautions include:
- Timing with Medications: Avoid taking activated charcoal within two hours of other medications, as it can interfere with their absorption.
- Hydration: Drink plenty of water to prevent dehydration and constipation, which can result from its binding properties.
- Medical Supervision for Emergency Use: Use activated charcoal for poisoning or overdoses only under medical supervision.
- Allergies or Sensitivities: Check for potential allergic reactions to any ...
Activated Charcoal Precautions
Using activated charcoal requires careful consideration to ensure safety and efficacy. Key precautions include:
- Timing with Medications: Avoid taking activated charcoal within two hours of other medications, as it can interfere with their absorption.
- Hydration: Drink plenty of water to prevent dehydration and constipation, which can result from its binding properties.
- Medical Supervision for Emergency Use: Use activated charcoal for poisoning or overdoses only under medical supervision.
- Allergies or Sensitivities: Check for potential allergic reactions to any added ingredients in charcoal products.
- Pre-existing Conditions: Consult a healthcare professional if you have gastrointestinal issues, as activated charcoal may worsen blockages or other conditions.
Activated Charcoal Side Effects
While activated charcoal is generally safe when used appropriately, it can cause side effects in some individuals. Common symptoms and complications include:
- Constipation: Its adsorptive properties can slow bowel movements.
- Dehydration: Activated charcoal may absorb water from the gastrointestinal tract, increasing the risk of dehydration.
- Black Stools: A harmless but common effect, black stools occur due to the charcoal passing through the digestive system.
- Nausea or Vomiting: Some individuals experience gastrointestinal discomfort.
- Blockages in the Digestive ...
Activated Charcoal Side Effects
While activated charcoal is generally safe when used appropriately, it can cause side effects in some individuals. Common symptoms and complications include:
- Constipation: Its adsorptive properties can slow bowel movements.
- Dehydration: Activated charcoal may absorb water from the gastrointestinal tract, increasing the risk of dehydration.
- Black Stools: A harmless but common effect, black stools occur due to the charcoal passing through the digestive system.
- Nausea or Vomiting: Some individuals experience gastrointestinal discomfort.
- Blockages in the Digestive Tract: Rarely, excessive or improper use can lead to intestinal obstruction, especially in those with pre-existing conditions.
- Interference with Nutrient Absorption: Prolonged use may reduce absorption of vitamins and minerals by adsorbing them in the gut.
It is crucial to use activated charcoal as directed and consult a healthcare professional if side effects persist or worsen.
Frequently Asked Questions About Activated Charcoal
What is activated charcoal?
Activated charcoal is a highly porous form of carbon created by heating natural materials like wood, coconut shells, or coal at very high temperatures. This process "activates" it by removing impurities and enhancing its surface area, enabling it to trap toxins, chemicals, and gases effectively. It is widely used for medical, cosmetic, and industrial purposes.
How does activated charcoal work?
Activated charcoal operates through a process called adsorption, not to ...
Frequently Asked Questions About Activated Charcoal
What is activated charcoal?
Activated charcoal is a highly porous form of carbon created by heating natural materials like wood, coconut shells, or coal at very high temperatures. This process "activates" it by removing impurities and enhancing its surface area, enabling it to trap toxins, chemicals, and gases effectively. It is widely used for medical, cosmetic, and industrial purposes.
How does activated charcoal work?
Activated charcoal operates through a process called adsorption, not to be confused with absorption. In adsorption, toxins and unwanted substances chemically bind to the surface of the charcoal. Its large surface area, filled with tiny pores, allows it to trap substances like toxins and gases, making it effective for detoxification and filtration.
What are the common uses of activated charcoal?
Activated charcoal has versatile applications. It is used to treat poison ingestion in emergencies, purify water, filter air, whiten teeth, reduce gas and bloating, and as an ingredient in skincare products. Its ability to adsorb impurities makes it essential in both health and industrial settings.
Is activated charcoal safe to consume?
It is generally safe for short-term use when following recommended dosages. However, frequent or excessive use can reduce the absorption of essential nutrients and medications. To avoid complications, activated charcoal should be taken under the guidance of a healthcare professional, especially if you are on medications.
How long does activated charcoal last?
Activated charcoal does not spoil in a sealed, airtight container. However, its effectiveness may decrease if exposed to air for long periods, as it can absorb ambient toxins, moisture, or odors. Proper storage ensures its potency remains intact.
What is the difference between activated charcoal and activated carbon?
While they are essentially the same substance, "activated charcoal" is more commonly used in consumer products like supplements or beauty items. "Activated carbon," on the other hand, is a term often used for industrial applications such as water treatment, gas purification, and large-scale filtration.
Can activated charcoal expire?
Technically, activated charcoal does not expire, but its adsorptive capacity can diminish over time if stored improperly or exposed to pollutants. Keeping it in an airtight, dry environment maintains its efficiency for extended periods.
Are there different types of activated charcoal?
Yes, there are various types based on the raw materials used, such as wood, coconut shells, bamboo, or coal. Each type is suited for specific uses. For example, coconut-based charcoal is often used in cosmetic and food-grade products due to its fine texture, while coal-based charcoal is common in industrial filtration.
What is reactivated charcoal?
Reactivated charcoal is used charcoal that has been treated to remove the absorbed substances, restoring much of its original adsorptive capacity. This process is typically done in controlled industrial settings and is primarily utilized for large-scale water or air purification systems.
Is activated charcoal environmentally friendly?
The production process can be energy-intensive, but activated charcoal itself can contribute to eco-friendliness when used in water and air purification, reducing pollution. Some types, like bamboo-based charcoal, are more sustainable, as bamboo is a rapidly renewable resource. Efforts to reuse or reactivate charcoal further reduce environmental impact.
Disclaimer: The published information is based on research and published medical sources. It is provided for educational purposes only and is not intended to replace professional medical advice. Always consult with your doctor or healthcare provider regarding any questions you may have about your health. We are not responsible for any actions taken based on this information, nor for any errors, omissions, or inaccuracies in the content. Medical research is constantly evolving, and the information presented may not reflect the most current medical standards.
December 2024
AposBook
Explore other Natural Compounds
Suggested benefits of Activated Charcoal
What science says about Activated Charcoal
Views in favor
Views against
The Ultimate Guide To Activated Charcoal
Library center Activated Charcoal





 Buy now
Buy now


























[1]