Ready to leave?
Oops ! Condition name you have entered is invalid.
You are now leaving Aposbook.com and going to an external site managed by another organization.
Please confirm your email address and try to login again.
This account has been deleted. do you want to restore it?

Validate your email
A verification link will be sent to within the next 2 minutes. Please click it to validate your e mail.
*If you didn't get the link, please check your spam folder
Welcome to Aposbook,
As a registered user, you can benefit from the various free tools and services that we provide.
All you need to do is log in to start discussing with others, interacting, asking questions, and sharing your point of view about the various topics.
You can also write reviews and testimonials about any natural solution you have tried and share your experience. Your feedback can be very helpful.
If you are a health expert, you can add information about any topic or suggest text edit. You can also publish content, including articles and videos, about any topic from the related library section.
Together we can help.
The Aposbook Team
Forgot Password?
A validation link will be sent to you by email. Please confirm your address to log in
*If you didn't get the link, please check your spam folder
Please log in to use this feature
Your account has been suspended because you have violated our code of conduct. If you think this was a mistake, you can contact us by email at: support@aposbook.com "Contact us" form.
Success! Thank you for your feedback. Your contribution can make a difference. Together we can help each other.


Beauty and hygiene
Skin Aging
Skin Aging: Causes, Prevention, and Natural Treatments
Complete Guide to Skin Aging
Skin Aging Overview
The skin is the largest organ in the human body, covering every part of the body and acting as a vital protective barrier. It shields the body from harmful pathogens and bacteria, regulates body temperature, controls sweat levels, and synthesizes vitamin D, which is essential for bone health. Healthy skin has a smooth texture, an even tone, and no signs of redness, wrinkles, or cracks. However, as we age, the skin gradually loses its natural elasticity, firmness ...
Skin Aging Overview
The skin is the largest organ in the human body, covering every part of the body and acting as a vital protective barrier. It shields the body from harmful pathogens and bacteria, regulates body temperature, controls sweat levels, and synthesizes vitamin D, which is essential for bone health. Healthy skin has a smooth texture, an even tone, and no signs of redness, wrinkles, or cracks. However, as we age, the skin gradually loses its natural elasticity, firmness, and moisture, leading to visible signs of aging.
Skin aging is a multifaceted process influenced by both intrinsic (natural) and extrinsic (external) factors. Intrinsic aging occurs as part of the body's natural aging process, where collagen production slows, and cell turnover decreases. Extrinsic aging is driven by environmental influences such as sun exposure, pollution, and lifestyle choices.
There are distinct stages of skin aging:
- Early Stage (20s to 30s): During this stage, the skin begins to show subtle signs of aging, such as fine lines and a slight decrease in elasticity. Sun damage may not yet be visible, but it has already started accumulating under the surface.
- Middle Stage (40s to 50s): Wrinkles deepen, skin loses more elasticity, and dryness becomes more common. Age spots may begin to appear, especially in areas frequently exposed to the sun.
- Advanced Stage (60+): The skin becomes thinner, more fragile, and sagging is more pronounced. There is a significant loss of firmness, and the skin's ability to retain moisture is greatly diminished, leading to a more aged appearance.
Understanding the process of skin aging is key to choosing the right preventive measures and treatments. Recognizing how both internal and external factors play a role can help slow down the visible effects of aging.
Causes of Skin Aging
Several internal and external factors contribute to skin aging, each affecting the skin differently. Understanding these causes allows for better prevention and management of aging skin.
- Decreased collagen production: Collagen is a key protein that maintains skin’s structure and firmness. As we age, the body's ability to produce collagen declines, leading to sagging and wrinkles. With less collagen, the skin becomes less elastic, making it more prone to fine lines and deeper wrinkles.
- Oxidative ...
Causes of Skin Aging
Several internal and external factors contribute to skin aging, each affecting the skin differently. Understanding these causes allows for better prevention and management of aging skin.
- Decreased collagen production: Collagen is a key protein that maintains skin’s structure and firmness. As we age, the body's ability to produce collagen declines, leading to sagging and wrinkles. With less collagen, the skin becomes less elastic, making it more prone to fine lines and deeper wrinkles.
- Oxidative stress: This occurs when the body has an imbalance between free radicals and antioxidants. Free radicals, which are unstable molecules, attack skin cells and break down collagen and elastin, key components for youthful skin. Oxidative stress is caused by environmental factors like pollution, smoking, and even certain unhealthy foods. When oxidative stress persists, it accelerates the aging process, leading to rougher, more wrinkled skin.
- Sun exposure: Ultraviolet (UV) rays from the sun are the most significant environmental cause of skin aging, often called photoaging. UV rays penetrate the skin, damaging collagen and elastin fibers, which support skin firmness. Long-term exposure can result in wrinkles, age spots, and an uneven skin tone. UVB rays, responsible for sunburn, and UVA rays, which penetrate deeper, both contribute to aging. Sun damage often appears more rapidly in warmer climates, but UV exposure can also be harmful in cooler environments, especially at higher altitudes.
- Environmental conditions: Extreme environmental conditions, such as heat, cold, and wind, can significantly impact the skin. Prolonged exposure to heat can lead to dehydration, causing the skin to dry out and lose its elasticity. Hot climates, especially in humid areas, also contribute to pore enlargement and a dull complexion. Conversely, cold weather strips moisture from the skin, leading to dryness, cracking, and a rough texture. Both extremes weaken the skin's natural barrier, making it more susceptible to aging. Pollution is another environmental factor that can cause damage by increasing oxidative stress and degrading skin cells.
- Lifestyle factors: Personal habits play a crucial role in how quickly skin ages. Smoking introduces toxins into the body that constrict blood vessels, reducing oxygen and nutrient flow to the skin. This weakens skin repair processes and results in premature wrinkles, particularly around the mouth. Poor diet, particularly one high in processed foods, sugar, and unhealthy fats, accelerates skin aging by depriving the body of essential nutrients like antioxidants and vitamins. Sleep deprivation affects the body’s ability to repair and regenerate skin cells, leading to dull skin, dark circles, and an aged appearance.
- Hormonal changes: Hormones, particularly estrogen, play a vital role in maintaining skin moisture and elasticity. As women age, particularly during menopause, estrogen levels drop, which reduces collagen production and skin thickness. This can result in increased sagging, dryness, and more pronounced wrinkles. Hormonal imbalances at any age can accelerate these effects, contributing to premature aging.
By recognizing and mitigating these causes, it’s possible to slow down the visible effects of skin aging and maintain healthier, more resilient skin.
Skin Aging Risk Factors
arious risk factors can increase the speed at which skin ages, making some individuals more prone to visible aging signs earlier than others. These factors, while not direct causes, significantly increase vulnerability to skin damage.
Excessive sun exposure: People who spend a lot of time outdoors without proper protection are at higher risk of premature skin aging. The skin is particularly vulnerable in regions with high UV radiation, such as tropical or high-altitude areas, where sunlight ...
Skin Aging Risk Factors
arious risk factors can increase the speed at which skin ages, making some individuals more prone to visible aging signs earlier than others. These factors, while not direct causes, significantly increase vulnerability to skin damage.
Excessive sun exposure: People who spend a lot of time outdoors without proper protection are at higher risk of premature skin aging. The skin is particularly vulnerable in regions with high UV radiation, such as tropical or high-altitude areas, where sunlight exposure is intense. Long-term unprotected exposure leads to faster breakdown of collagen and elastin, resulting in early wrinkles and sunspots.
Skin type and tone: Individuals with lighter skin tones are at a greater risk of sun-induced aging (photoaging). Lighter skin has less melanin, the pigment that provides some protection against UV rays. As a result, fair-skinned individuals are more prone to sunburns and skin damage, which accelerates aging. In contrast, people with darker skin tones have more melanin, offering more natural defense but are still at risk of aging signs due to other factors like pollution or lifestyle choices.
Chronic stress: Long-term stress affects not only mental health but also the skin. Cortisol, the stress hormone, accelerates the breakdown of collagen and elastin, weakening the skin's structure. Stress also disrupts normal sleep patterns, limiting the skin’s ability to repair itself. As a result, people under constant stress may see more rapid development of wrinkles, dull skin, and sagging.
Alcohol consumption: Frequent alcohol use dehydrates the skin and reduces its ability to retain moisture, causing dryness and dullness. It also dilates blood vessels, leading to redness, particularly around the nose and cheeks. Chronic alcohol use may exacerbate the development of wrinkles and sagging by reducing the skin's nutrient absorption.
Living in polluted environments: Urban areas with high levels of air pollution expose the skin to harmful particles and chemicals that trigger oxidative stress. Pollution particles penetrate deep into the skin, causing inflammation and accelerating aging. Those living in cities or industrial regions are at higher risk of premature wrinkles, uneven skin tone, and fine lines due to this constant exposure.
Repetitive facial expressions: Frequently repeating the same facial expressions, such as squinting or frowning, can lead to the formation of deep expression lines. Over time, the skin loses its ability to bounce back, and the lines become permanent. People who work in conditions where they squint often (such as bright outdoor environments) or who have habits like frowning or raising their eyebrows may notice wrinkles form earlier in life.
Indoor environmental conditions: Prolonged exposure to air conditioning or heating systems can negatively impact skin health. Air conditioners remove moisture from the air, leaving skin dry and more prone to cracking and premature aging. Heating systems, especially in colder climates, have a similar effect, stripping the skin of essential moisture and leading to rough texture and fine lines.
Sleep quality: Those who consistently get poor sleep are at risk of premature skin aging. The skin undergoes its repair and regeneration process during deep sleep. Without adequate rest, this renewal is hindered, leading to a dull complexion, puffiness, and early development of fine lines. Chronic sleep deprivation also increases stress levels, which in turn speeds up the aging process.
Occupation and lifestyle choices: Certain professions expose individuals to environments that may increase the risk of skin aging. For instance, outdoor workers, such as farmers or construction workers, are exposed to the elements for long periods, leading to more UV damage. On the other hand, office workers sitting under artificial lighting for extended hours may experience similar issues with skin hydration and stress levels, though to a lesser degree.
Identifying these risk factors allows for proactive measures to slow down skin aging and maintain a youthful appearance longer.
Skin Aging Symptoms
Skin aging manifests through various visible signs, and while some may be subtle, others become more pronounced over time. These symptoms include:
- Fine lines and wrinkles: Most noticeable around the eyes, mouth, and forehead, these are early signs of aging.
- Sagging skin: Loss of collagen and elastin causes the skin to droop, particularly around the jawline and cheeks.
- Dryness and rough texture: Aging skin loses moisture faster, making it feel drier and more textured.
- Age spots: Sun ...
Skin Aging Symptoms
Skin aging manifests through various visible signs, and while some may be subtle, others become more pronounced over time. These symptoms include:
- Fine lines and wrinkles: Most noticeable around the eyes, mouth, and forehead, these are early signs of aging.
- Sagging skin: Loss of collagen and elastin causes the skin to droop, particularly around the jawline and cheeks.
- Dryness and rough texture: Aging skin loses moisture faster, making it feel drier and more textured.
- Age spots: Sun damage over time results in dark spots, usually on areas frequently exposed to the sun, like the face and hands.
- Thinning skin: Skin becomes thinner with age, making it more susceptible to bruising and injury.
Skin Aging Diagnosis
While skin aging is a visible process, diagnosing the extent of aging and differentiating between intrinsic and extrinsic factors can help guide treatment:
- Visual examination: Dermatologists assess wrinkles, texture, elasticity, and pigmentation to determine the degree of skin aging.
- Skin elasticity tests: Pinching the skin can give clues to how much collagen remains and how firm the skin is.
- UV photography: This technique highlights sun damage under the skin’s surface, revealing areas that may develop age spots ...
Skin Aging Diagnosis
While skin aging is a visible process, diagnosing the extent of aging and differentiating between intrinsic and extrinsic factors can help guide treatment:
- Visual examination: Dermatologists assess wrinkles, texture, elasticity, and pigmentation to determine the degree of skin aging.
- Skin elasticity tests: Pinching the skin can give clues to how much collagen remains and how firm the skin is.
- UV photography: This technique highlights sun damage under the skin’s surface, revealing areas that may develop age spots or wrinkles.
- Moisture level analysis: Tests for hydration levels help assess dryness and overall skin health.
This comprehensive approach ensures a better understanding of the skin's condition, enabling more targeted treatment plans.
Natural Treatments for Skin Anti-Aging
There are several natural remedies for skin aging that can help support skin health and combat aging signs. Click on natural treatments for skin anti-aging to find all the natural solutions to treat skin aging and improve skin health, including various natural methods, diet programs, alternative medicine, vitamins, supplements, herbal medicine, and home remedies. You can also go to www.aposbook.com to find all the natural treatments for any medical condition IN ONE CLICK.
Some ...
Natural Treatments for Skin Anti-Aging
There are several natural remedies for skin aging that can help support skin health and combat aging signs. Click on natural treatments for skin anti-aging to find all the natural solutions to treat skin aging and improve skin health, including various natural methods, diet programs, alternative medicine, vitamins, supplements, herbal medicine, and home remedies. You can also go to www.aposbook.com to find all the natural treatments for any medical condition IN ONE CLICK.
Some of the most common natural solutions for skin anti-aging include:
Diet programs
Certain diet programs can provide a balanced approach to slowing down skin aging by emphasizing nutrient-rich foods that support skin health.
- Mediterranean diet: Known for its high intake of fruits, vegetables, whole grains, and healthy fats (like olive oil), this diet provides essential antioxidants and omega-3 fatty acids that reduce inflammation and protect the skin from aging.
- Anti-inflammatory diet: This plan focuses on reducing chronic inflammation, a key contributor to skin aging. It emphasizes foods like fatty fish, leafy greens, and whole grains, which help protect against oxidative stress and collagen breakdown.
- Paleo diet: This diet eliminates processed foods and includes lean meats, fish, nuts, seeds, and fresh produce. Its focus on whole foods helps promote skin regeneration and reduces premature aging caused by dietary toxins.
Herbal medicine
Herbal remedies support skin health by promoting hydration, collagen production, and protection from environmental damage.
Green tea: Rich in antioxidants (especially EGCG), green tea helps protect against UV damage and reduces the breakdown of collagen and elastin.
Ginseng: Known for improving skin elasticity and firmness, ginseng stimulates collagen synthesis and reduces the appearance of wrinkles.
Aloe vera: Consumed as juice or applied topically, aloe vera hydrates the skin and promotes healing, helping to combat dryness and fine lines.
Vitamins and supplements
These nutrients play a key role in keeping the skin youthful and resilient.
- Vitamin C: Essential for collagen synthesis, vitamin C protects the skin from sun damage and improves overall skin brightness and texture.
- Vitamin E: An antioxidant that prevents free radical damage, vitamin E helps the skin retain moisture and reduces the appearance of wrinkles.
- Collagen supplements: Taking collagen peptides can improve skin elasticity, hydration, and reduce the depth of wrinkles over time.
Alternative medicine
Non-invasive treatments that focus on overall skin wellness.
- Acupuncture: Facial acupuncture boosts blood circulation and collagen production, helping to reduce fine lines and sagging skin.
- Ayurvedic treatments: Herbs like ashwagandha and turmeric are used in Ayurvedic practices to combat oxidative stress and slow down the aging process.
- Facial massage: Regular facial massages stimulate lymphatic drainage and circulation, which can reduce puffiness and promote skin firmness.
Before starting any natural treatments for skin anti-aging, including diet changes, herbal remedies, or supplements, it’s important to consult with a healthcare professional to ensure they are safe and appropriate for your specific condition and treatment plan.
Medical Treatment for Akin Aging
Medical treatments are effective solutions to combat skin aging, particularly for individuals seeking more immediate and visible results. These treatments are based on pharmaceutical or chemical methods and are usually performed or recommended by dermatologists.
- Retinoids (Retinol, Tretinoin): Retinoids are vitamin A derivatives commonly prescribed to boost collagen production and accelerate cell turnover, reducing wrinkles, fine lines, and age spots. They also improve skin texture and tone by stimulating new skin growth.
- Chemical peels: Chemical ...
Medical Treatment for Akin Aging
Medical treatments are effective solutions to combat skin aging, particularly for individuals seeking more immediate and visible results. These treatments are based on pharmaceutical or chemical methods and are usually performed or recommended by dermatologists.
- Retinoids (Retinol, Tretinoin): Retinoids are vitamin A derivatives commonly prescribed to boost collagen production and accelerate cell turnover, reducing wrinkles, fine lines, and age spots. They also improve skin texture and tone by stimulating new skin growth.
- Chemical peels: Chemical peels use acids such as glycolic acid, salicylic acid, or trichloroacetic acid (TCA) to remove the top layers of skin. This stimulates collagen production and reveals smoother, younger-looking skin beneath. Regular chemical peels can reduce the appearance of wrinkles, sun damage, and uneven pigmentation.
- Botox: Botulinum toxin injections work by relaxing facial muscles that cause expression lines and wrinkles, particularly around the forehead, eyes, and mouth. Botox temporarily smooths these areas, offering a more youthful appearance.
- Dermal fillers: Hyaluronic acid fillers, such as Juvederm or Restylane, are injected into the skin to restore volume, smooth wrinkles, and enhance facial contours. Fillers plump up the skin, reducing the appearance of sagging or hollow areas.
- Laser therapy: Laser treatments, like fractional laser resurfacing, target damaged skin by promoting collagen production and resurfacing the skin. These therapies reduce wrinkles, age spots, and scarring, resulting in smoother, firmer skin over time.
- Microneedling: This treatment uses tiny needles to create controlled micro-injuries in the skin. These injuries stimulate the body’s natural healing process, producing new collagen and elastin, which improve skin texture and reduce fine lines.
- Prescription creams: Dermatologists may prescribe specialized creams that contain peptides, growth factors, or hydroquinone to treat aging signs. These products promote collagen production, lighten dark spots, and improve skin tone and texture.
These medical treatments offer a more immediate, visible approach to managing skin aging and are best suited for individuals looking for faster results or more targeted solutions.
Before starting any medical treatment for skin anti-aging, it is important to consult with a healthcare professional to ensure that the prescribed medications and therapies are suitable for your individual health needs and medical conditions.
Frequently Asked Questions About Skin Aging
What is skin aging, and why does it happen?
Skin aging is the process where the skin loses its elasticity, firmness, and moisture over time. This happens due to factors like reduced collagen production, environmental exposure, and changes in cellular repair mechanisms.
What are the main signs of skin aging?
The most common signs include wrinkles, fine lines, sagging skin, age spots, and dryness. Other indicators include uneven skin tone, loss of firmness, and ...
Frequently Asked Questions About Skin Aging
What is skin aging, and why does it happen?
Skin aging is the process where the skin loses its elasticity, firmness, and moisture over time. This happens due to factors like reduced collagen production, environmental exposure, and changes in cellular repair mechanisms.
What are the main signs of skin aging?
The most common signs include wrinkles, fine lines, sagging skin, age spots, and dryness. Other indicators include uneven skin tone, loss of firmness, and dullness.
Can natural treatments slow down skin aging?
Yes, natural treatments such as structured diets, herbal remedies, and specific vitamins and supplements can slow down the aging process by nourishing the skin and reducing oxidative stress.
What is the best diet for preventing skin aging?
The Mediterranean diet is often recommended as it is rich in antioxidants, healthy fats, and anti-inflammatory foods, which help protect the skin and maintain its elasticity.
Do collagen supplements really help with skin aging?
Collagen supplements can help improve skin hydration and elasticity, reducing the appearance of wrinkles and dryness. Many studies suggest that regular collagen supplementation can support skin health.
Are herbal treatments effective for anti-aging?
Herbal treatments such as green tea, ginseng, and aloe vera have been shown to offer anti-aging benefits by reducing inflammation, promoting collagen production, and hydrating the skin.
How does stress affect skin aging?
Chronic stress accelerates skin aging by increasing cortisol levels, which break down collagen and elastin. This leads to premature wrinkles, dull skin, and sagging.
Can facial acupuncture really reduce signs of aging?
Facial acupuncture is a popular alternative therapy that promotes blood flow, boosts collagen production, and helps reduce the appearance of fine lines and wrinkles naturally.
What vitamins should I take to reduce skin aging?
Vitamins C and E are particularly effective for skin health. Vitamin C boosts collagen production and brightens skin, while vitamin E protects against free radical damage and helps retain moisture.
Is sun exposure the leading cause of skin aging?
Yes, UV radiation from sun exposure is one of the primary causes of premature skin aging. It accelerates collagen breakdown and leads to wrinkles, age spots, and loss of skin elasticity.
Explore other Beauty and hygiene
Natural Treatments for Skin Aging
Skin Aging Dos and Don'ts
Sleeping is very important for skin anti-aging. It will make you look younger because your skin makes new collagen when you sleep, which prevents sagging. Getting 5 hours
High intensity interval training (HIIT) is good for skin anti-aging because it increases IGF hormone which reduces skin wrinkling. HIIT also increases telomerase
Alcohol can add years to your face and accelerate you skin aging. Alcohol causes wrinkles, puffiness, dryness, red cheeks and purple capillaries. It also dehydrates your
Consume less carbs and sugar to reduce insulin production in the body. Higher glucose levels are associated with a higher perceived age.
Don't take hot showers because hot water can cause inflammation in the skin, resulting in a loss of moisture and leading to wrinkles. For example, when you spend long time
Do not rub your eyes because the skin around the eyes is very delicate and susceptible to damage. This action puts a lot of pressure and tension on the eyes and make the skin
Dos and Don'ts
Library center Skin Aging
Success storiess
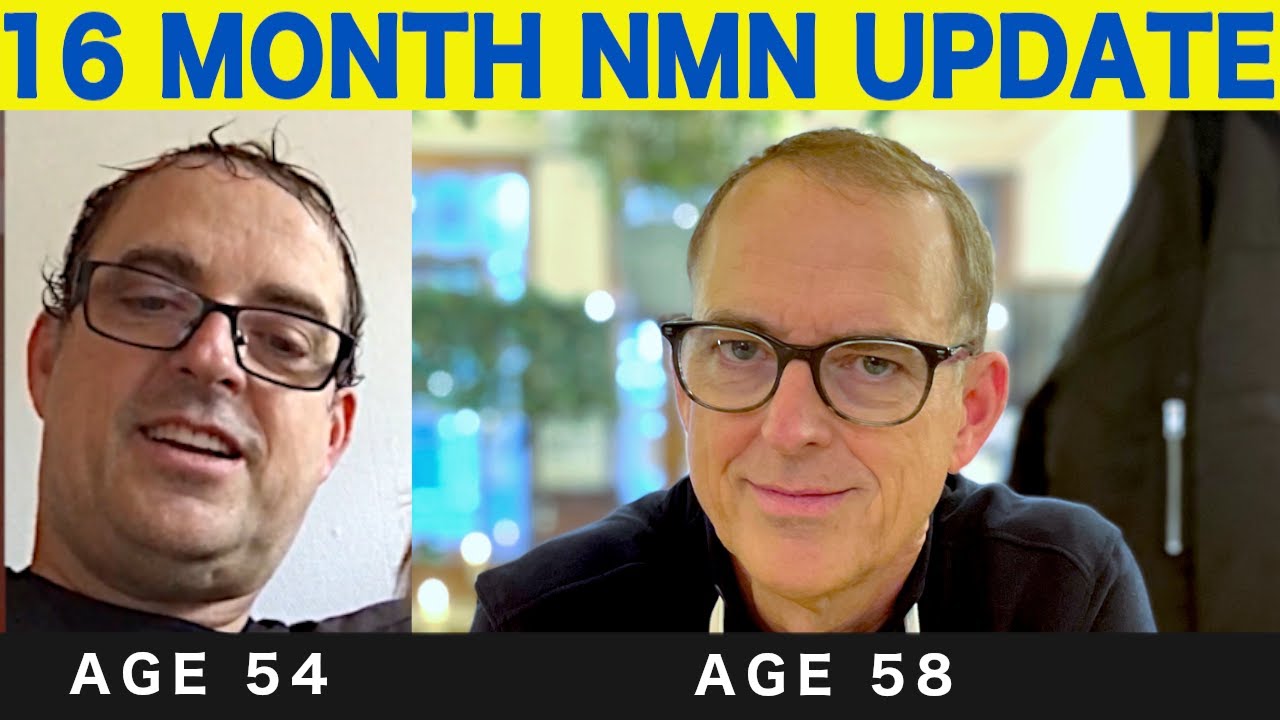
Turning 58 And Celebrating NMN

Get Glowing, Dewy Skin with Coconut Oil!

How The Paleo Diet Can Drastically Improve Your Skin





































































[0]