Ready to leave?
Oops ! Condition name you have entered is invalid.
You are now leaving Aposbook.com and going to an external site managed by another organization.
Please confirm your email address and try to login again.
This account has been deleted. do you want to restore it?

Validate your email
A verification link will be sent to within the next 2 minutes. Please click it to validate your e mail.
*If you didn't get the link, please check your spam folder
Welcome to Aposbook,
As a registered user, you can benefit from the various free tools and services that we provide.
All you need to do is log in to start discussing with others, interacting, asking questions, and sharing your point of view about the various topics.
You can also write reviews and testimonials about any natural solution you have tried and share your experience. Your feedback can be very helpful.
If you are a health expert, you can add information about any topic or suggest text edit. You can also publish content, including articles and videos, about any topic from the related library section.
Together we can help.
The Aposbook Team
Forgot Password?
A validation link will be sent to you by email. Please confirm your address to log in
*If you didn't get the link, please check your spam folder
Please log in to use this feature
Your account has been suspended because you have violated our code of conduct. If you think this was a mistake, you can contact us by email at: support@aposbook.com "Contact us" form.
Success! Thank you for your feedback. Your contribution can make a difference. Together we can help each other.


Diseases and conditions
Insomnia
Insomnia: Causes, Prevention, and Natural Treatments
Complete Guide to Insomnia
What is Insomnia
Insomnia is a common sleep disorder characterized by difficulty falling asleep, staying asleep, or waking up too early without being able to go back to sleep. People with insomnia often feel tired upon waking, which can affect their daily activities, work performance, and overall quality of life.
The average adult requires 7 to 9 hours of sleep per night to function optimally. However, individuals with insomnia often get less than this, and consistently getting fewer than 6 ...
What is Insomnia
Insomnia is a common sleep disorder characterized by difficulty falling asleep, staying asleep, or waking up too early without being able to go back to sleep. People with insomnia often feel tired upon waking, which can affect their daily activities, work performance, and overall quality of life.
The average adult requires 7 to 9 hours of sleep per night to function optimally. However, individuals with insomnia often get less than this, and consistently getting fewer than 6 hours of sleep is typically considered a sign of insomnia. As a result, insomnia can affect your energy level because you would feel continuously tired if you don't get enough sleep. Insomnia can also affect your mood, as you might experience anger, sadness, or frustration.
Insomnia can occur on its own or as a result of other health conditions, and it can be either acute (short-term) or chronic (long-term), depending on its duration and persistence.
There are two primary types of insomnia:
- Primary Insomnia: Not linked to another health condition or external factor. It may result from emotional stress, lifestyle habits, or environmental disruptions.
- Secondary Insomnia: Caused by medical conditions, mental health issues, or substance use (such as alcohol or certain medications).
In addition to total sleep time, REM sleep (Rapid Eye Movement) is an important aspect of sleep quality. People with insomnia may not reach the deep stages of REM sleep, which is crucial for cognitive function, emotional regulation, and overall health. A lack of REM sleep can lead to mental fog, emotional instability, and a general feeling of unrest, even if the person spent a significant amount of time in bed.
Insomnia also has developmental stages. In the initial stage, individuals struggle with falling asleep, leading to frustration and restlessness. Over time, it can progress to middle-stage insomnia, where people wake up frequently during the night, and finally, late-stage insomnia, characterized by waking up too early and being unable to return to sleep.
Insomnia Causes
Insomnia can be triggered by various physical, psychological, and environmental factors. These can range from temporary stress to underlying health conditions that persist over time. Understanding the root cause is crucial in addressing and managing insomnia effectively.
- Stress: High levels of stress, whether from work, relationships, or life events, can keep the mind active at night.
- Mental Health Disorders: Anxiety and depression are strongly linked to insomnia due to the racing thoughts and emotional distress they cause.
- Poor ...
Insomnia Causes
Insomnia can be triggered by various physical, psychological, and environmental factors. These can range from temporary stress to underlying health conditions that persist over time. Understanding the root cause is crucial in addressing and managing insomnia effectively.
- Stress: High levels of stress, whether from work, relationships, or life events, can keep the mind active at night.
- Mental Health Disorders: Anxiety and depression are strongly linked to insomnia due to the racing thoughts and emotional distress they cause.
- Poor Sleep Habits: Irregular bedtimes, using electronics before bed, or consuming stimulants late in the day can disrupt sleep.
- Medical Conditions: Conditions such as asthma, arthritis, or chronic pain make it difficult to sleep comfortably.
- Substance Use: Caffeine, alcohol, and nicotine are known to interfere with sleep cycles.
- Shift Work or Travel: Irregular work schedules or frequent travel across time zones can disturb the body's circadian rhythm.
- Overuse of Sleep Aids: Relying too heavily on sleep medications can disrupt natural sleep patterns over time.
Insomnia Risk Factors
Certain factors increase the likelihood of developing insomnia. Being aware of these can help individuals take preventive steps or seek appropriate interventions.
- Age: Older adults experience changes in sleep patterns, making insomnia more common.
- Gender: Hormonal fluctuations in women, especially during menopause or pregnancy, can contribute to insomnia.
- Chronic Stress: Long-term stress from personal or work-related situations can make it difficult to maintain healthy sleep habits.
- Lifestyle Choices: Irregular sleep schedules, excessive screen time, or lack of ...
Insomnia Risk Factors
Certain factors increase the likelihood of developing insomnia. Being aware of these can help individuals take preventive steps or seek appropriate interventions.
- Age: Older adults experience changes in sleep patterns, making insomnia more common.
- Gender: Hormonal fluctuations in women, especially during menopause or pregnancy, can contribute to insomnia.
- Chronic Stress: Long-term stress from personal or work-related situations can make it difficult to maintain healthy sleep habits.
- Lifestyle Choices: Irregular sleep schedules, excessive screen time, or lack of physical activity can increase insomnia risk.
- Mental Health Conditions: Individuals with mental health issues like depression or PTSD are more likely to develop insomnia.
- Genetics: Family history of sleep disorders can make individuals more susceptible to insomnia.
- Cognitive Overactivity: People who tend to overthink or have an active mind at night are at higher risk of insomnia.
Insomnia Symptoms
Insomnia manifests in several ways, and its symptoms can vary depending on the severity and duration of the disorder. Recognizing these symptoms early is important for diagnosis and treatment.
- Difficulty Falling Asleep: Taking more than 30 minutes to drift off, even when feeling tired.
- Waking Up During the Night: Frequently waking up and struggling to get back to sleep.
- Waking Up Too Early: Rising hours before the intended wake-up time and unable to return to sleep.
- Daytime Fatigue ...
Insomnia Symptoms
Insomnia manifests in several ways, and its symptoms can vary depending on the severity and duration of the disorder. Recognizing these symptoms early is important for diagnosis and treatment.
- Difficulty Falling Asleep: Taking more than 30 minutes to drift off, even when feeling tired.
- Waking Up During the Night: Frequently waking up and struggling to get back to sleep.
- Waking Up Too Early: Rising hours before the intended wake-up time and unable to return to sleep.
- Daytime Fatigue: Feeling excessively tired during the day despite having spent enough time in bed.
- Mood Changes: Irritability, anxiety, or depression resulting from poor sleep.
- Decreased Performance: Difficulty concentrating, reduced productivity, and memory problems.
- Worrying About Sleep: Increased anxiety about sleep, often leading to a vicious cycle of insomnia.
Insomnia Diagnosis
Diagnosing insomnia typically involves a thorough evaluation of an individual's sleep patterns, medical history, and any underlying conditions. This helps healthcare providers determine the appropriate treatment approach.
- Sleep History: A detailed account of sleep patterns, bedtime routines, and any disruptions throughout the night.
- Physical Exam: A general health check to rule out medical conditions that could be causing insomnia, such as respiratory issues or chronic pain.
- Sleep Diary: Individuals may be asked to keep a log of their ...
Insomnia Diagnosis
Diagnosing insomnia typically involves a thorough evaluation of an individual's sleep patterns, medical history, and any underlying conditions. This helps healthcare providers determine the appropriate treatment approach.
- Sleep History: A detailed account of sleep patterns, bedtime routines, and any disruptions throughout the night.
- Physical Exam: A general health check to rule out medical conditions that could be causing insomnia, such as respiratory issues or chronic pain.
- Sleep Diary: Individuals may be asked to keep a log of their sleep habits, including the time they go to bed, wake up, and any nighttime awakenings.
- Sleep Study (Polysomnography): In more complex cases, a sleep study may be conducted to monitor brain waves, heart rate, breathing, and oxygen levels while the individual sleeps.
- Mental Health Screening: A psychological evaluation to assess any underlying mental health conditions that might contribute to insomnia, such as anxiety or depression.
Natural Treatments for Insomnia
There are several remedies that can be used to treat and prevent insomnia. Click on natural treatments for insomnia to find a detailed list of all the natural solutions to treat insomnia and improve sleep, including various natural therapies, diet programs, alternative medicine, vitamins, supplements, herbal medicine, and home remedies. You can also go to www.aposbook.com to find all the natural treatments for any medical condition IN ONE CLICK.
Meanwhile, some of the main ...
Natural Treatments for Insomnia
There are several remedies that can be used to treat and prevent insomnia. Click on natural treatments for insomnia to find a detailed list of all the natural solutions to treat insomnia and improve sleep, including various natural therapies, diet programs, alternative medicine, vitamins, supplements, herbal medicine, and home remedies. You can also go to www.aposbook.com to find all the natural treatments for any medical condition IN ONE CLICK.
Meanwhile, some of the main natural solutions used for insomnia include:
Diet Programs for Insomnia
Diet plays a significant role in sleep quality. Certain foods and nutrients can help promote relaxation and better sleep patterns.
- Anti-Inflammatory Diet: Reducing inflammation in the body can improve sleep. A diet rich in fruits, vegetables, whole grains, and omega-3 fatty acids from fish can help reduce inflammation and improve sleep.
- Collagen Diet: Collagen plays an important role in supporting overall health, including joint, skin, and muscle function. It may also support better sleep by reducing inflammation and promoting relaxation. A collagen-boosting diet includes foods rich in glycine (like bone broth, chicken skin, and fish) and vitamin C (such as citrus fruits, strawberries, and broccoli). Glycine is an amino acid known for its calming properties and can aid in improving sleep quality.
Herbal Medicine for Insomnia
Several herbs are known for their calming and sedative effects, helping to naturally improve sleep quality.
- Valerian Root: A popular herbal remedy that promotes relaxation and reduces the time it takes to fall asleep.
- Chamomile: Known for its mild sedative properties, chamomile tea can help induce sleep by calming the nervous system.
- Passionflower: This herb is often used to treat anxiety and insomnia by increasing levels of gamma-aminobutyric acid (GABA), which reduces brain activity and promotes sleep.
- Lavender: The scent of lavender has been shown to help improve sleep quality. Lavender essential oil can be used in a diffuser or applied topically.
Vitamins and Supplements for Insomnia
Certain vitamins and supplements can support healthy sleep patterns by addressing underlying deficiencies or promoting relaxation.
- Melatonin: A hormone that regulates sleep-wake cycles. Taking melatonin supplements can help individuals who struggle to fall asleep, especially those with jet lag or irregular sleep schedules.
- Magnesium: Magnesium supplements can help relax the muscles and nervous system, making it easier to fall asleep.
- L-theanine: An amino acid found in tea leaves, L-theanine promotes relaxation without causing drowsiness. It can help reduce anxiety and promote better sleep.
Alternative Medicine for Insomnia
In addition to herbal remedies and supplements, other natural treatments focus on relaxation techniques and lifestyle changes that can improve sleep quality.
- Cognitive Behavioral Therapy for Insomnia (CBT-I): This therapy naturally helps address insomnia by altering thought patterns and behaviors that interfere with sleep. It includes techniques like stimulus control, sleep restriction, and relaxation training.
- Hypnotherapy: Hypnotherapy uses guided relaxation and focused attention to help individuals achieve a calm state of mind, making it easier to fall asleep and stay asleep.
- Acupuncture: This traditional Chinese medicine practice involves inserting thin needles into specific points on the body to help balance energy and promote relaxation, which can improve sleep.
By incorporating these natural treatments, individuals can create a holistic approach to managing insomnia, addressing both the physical and mental aspects that affect sleep.
Medical Treatments for Insomnia
Medical treatments for insomnia are typically recommended when lifestyle changes and natural remedies are not enough to improve sleep. These treatments aim to address both the underlying cause of insomnia and the symptoms, providing relief and improving sleep quality. Medical treatment include the following prescription Medications
- Benzodiazepines: These are sedative medications like temazepam or lorazepam, commonly prescribed for short-term treatment of insomnia. They help promote sleep by slowing down the brain's activity.
- Non-Benzodiazepine Hypnotics: Medications such ...
Medical Treatments for Insomnia
Medical treatments for insomnia are typically recommended when lifestyle changes and natural remedies are not enough to improve sleep. These treatments aim to address both the underlying cause of insomnia and the symptoms, providing relief and improving sleep quality. Medical treatment include the following prescription Medications
- Benzodiazepines: These are sedative medications like temazepam or lorazepam, commonly prescribed for short-term treatment of insomnia. They help promote sleep by slowing down the brain's activity.
- Non-Benzodiazepine Hypnotics: Medications such as zolpidem (Ambien), eszopiclone (Lunesta), and zaleplon (Sonata) are often prescribed because they have fewer side effects and lower risk of dependency compared to benzodiazepines.
- Melatonin Receptor Agonists: Ramelteon (Rozerem) mimics the effects of the hormone melatonin, which regulates the sleep-wake cycle. It’s particularly useful for those who have trouble falling asleep.
- Antidepressants: Some antidepressants, such as trazodone or amitriptyline, have sedative effects and are prescribed for patients with insomnia linked to depression or anxiety.
- Orexin Receptor Antagonists: Suvorexant (Belsomra) helps regulate wakefulness by blocking orexin, a neurotransmitter that promotes wakefulness.
Frequently Asked Questions About Insomnia
What is insomnia?
Insomnia is a sleep disorder characterized by difficulty falling asleep, staying asleep, or waking up too early and not being able to return to sleep. It can be short-term (acute) or long-term (chronic), and it affects the quality of life by causing fatigue, irritability, and impaired concentration.
How many hours of sleep is considered insomnia?
While individual sleep needs can vary, most adults need about 7-9 hours of sleep per night. Insomnia ...
Frequently Asked Questions About Insomnia
What is insomnia?
Insomnia is a sleep disorder characterized by difficulty falling asleep, staying asleep, or waking up too early and not being able to return to sleep. It can be short-term (acute) or long-term (chronic), and it affects the quality of life by causing fatigue, irritability, and impaired concentration.
How many hours of sleep is considered insomnia?
While individual sleep needs can vary, most adults need about 7-9 hours of sleep per night. Insomnia is typically diagnosed when someone consistently struggles to sleep for at least 30 minutes or more, or sleeps fewer than 6 hours per night despite having the opportunity to sleep.
What are the natural treatments for insomnia?
Natural treatments include lifestyle changes such as maintaining a regular sleep schedule, dietary adjustments (like the collagen-boosting or anti-inflammatory diet), herbal remedies like valerian root and chamomile, and techniques like meditation and cognitive behavioral therapy for insomnia (CBT-I).
Can a collagen-boosting diet help with insomnia?
Yes, a collagen-boosting diet can help with insomnia. Foods rich in glycine, such as bone broth, chicken skin, and fish, can promote relaxation and improve sleep quality by supporting the nervous system.
5. What herbs are effective for treating insomnia?
Several herbs are known to promote sleep, including valerian root, chamomile, passionflower, and lavender. These herbs can naturally calm the mind, reduce anxiety, and encourage restful sleep.
Is melatonin a good natural remedy for insomnia?
Yes, melatonin is a widely used natural supplement to regulate the body's sleep-wake cycle. It’s especially useful for those with jet lag or irregular sleep schedules, helping to improve both the onset and duration of sleep.
How can cognitive behavioral therapy (CBT-I) treat insomnia naturally?
CBT-I helps address the thought patterns and behaviors that contribute to insomnia. By teaching relaxation techniques, sleep restriction, and positive associations with sleep, CBT-I helps naturally improve sleep quality without medication.
How does meditation help with insomnia?
Meditation promotes relaxation and reduces stress, both of which are key contributors to insomnia. Regular mindfulness meditation can help the mind and body relax, making it easier to fall asleep and stay asleep.
What role does acupuncture play in treating insomnia?
Acupuncture, a traditional Chinese medicine practice, involves inserting fine needles into specific points on the body to balance energy flow. It promotes relaxation and can help alleviate insomnia by reducing anxiety and stress.
How do anti-inflammatory diets help with insomnia?
An anti-inflammatory diet, which includes foods like fruits, vegetables, whole grains, and omega-3-rich fish, helps reduce inflammation in the body. Lower inflammation levels are linked to improved sleep quality, as chronic inflammation can interfere with restful sleep.
Natural Treatments for Insomnia
Dos and Don'ts
Library center Insomnia
Success storiess
Reduce stress, improve sleep with acupuncture

Benefits of Ashwagandha: Hormones, Stress, and Sleep

Anti-aging and longevity with NAD therapy.
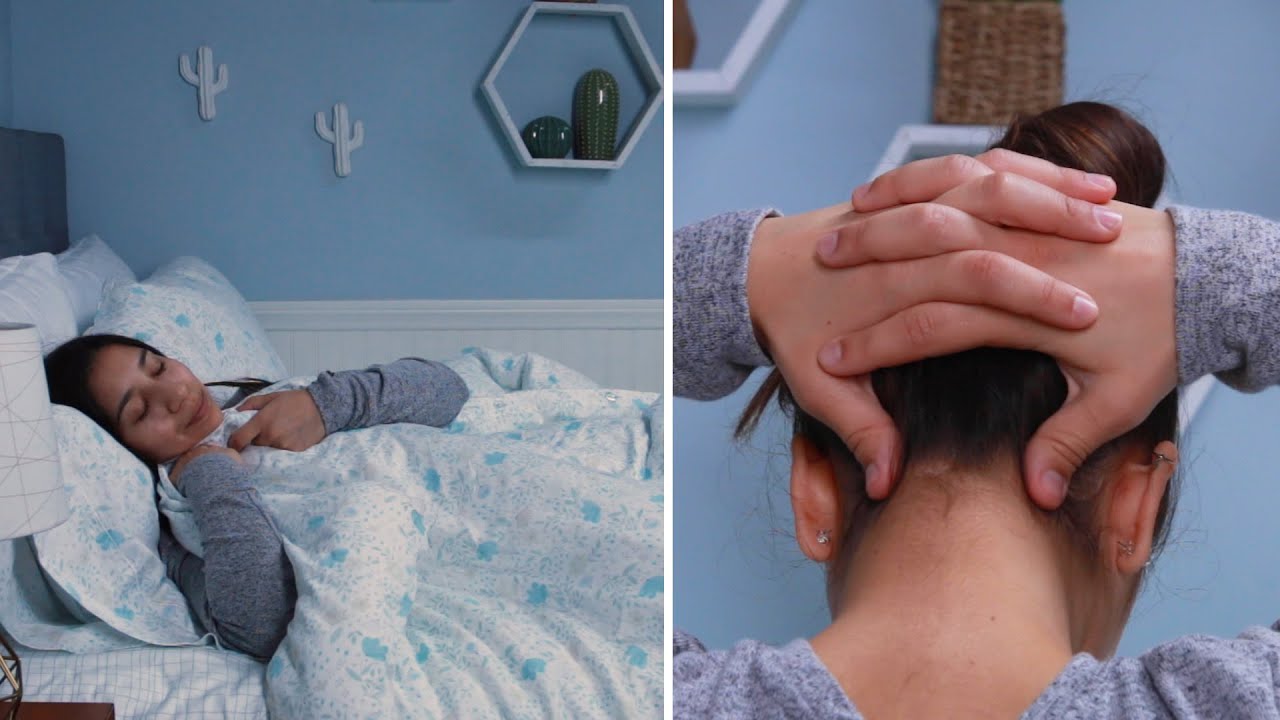








































[0]