Ready to leave?
Oops ! Condition name you have entered is invalid.
You are now leaving Aposbook.com and going to an external site managed by another organization.
Please confirm your email address and try to login again.
This account has been deleted. do you want to restore it?

Validate your email
A verification link will be sent to within the next 2 minutes. Please click it to validate your e mail.
*If you didn't get the link, please check your spam folder
Welcome to Aposbook,
As a registered user, you can benefit from the various free tools and services that we provide.
All you need to do is log in to start discussing with others, interacting, asking questions, and sharing your point of view about the various topics.
You can also write reviews and testimonials about any natural solution you have tried and share your experience. Your feedback can be very helpful.
If you are a health expert, you can add information about any topic or suggest text edit. You can also publish content, including articles and videos, about any topic from the related library section.
Together we can help.
The Aposbook Team
Forgot Password?
A validation link will be sent to you by email. Please confirm your address to log in
*If you didn't get the link, please check your spam folder
Please log in to use this feature
Your account has been suspended because you have violated our code of conduct. If you think this was a mistake, you can contact us by email at: support@aposbook.com "Contact us" form.
Success! Thank you for your feedback. Your contribution can make a difference. Together we can help each other.


Diseases and conditions
Bronchitis
Bronchitis: Causes, Prevention, and Natural Treatments
Complete Guide to Bronchitis
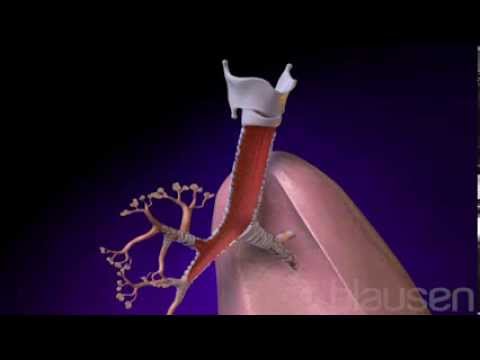
What is Bronchitis
Bronchitis is a respiratory condition that causes inflammation in the bronchial tubes, which are responsible for carrying air to and from the lungs. It often leads to persistent coughing and difficulty breathing. There are two main types of bronchitis: acute bronchitis and chronic bronchitis.
- Acute bronchitis is typically short-term and usually develops from a cold or respiratory infection. It lasts for a few weeks and is most common during the winter months.
- Chronic bronchitis is a more ...
What is Bronchitis
Bronchitis is a respiratory condition that causes inflammation in the bronchial tubes, which are responsible for carrying air to and from the lungs. It often leads to persistent coughing and difficulty breathing. There are two main types of bronchitis: acute bronchitis and chronic bronchitis.
- Acute bronchitis is typically short-term and usually develops from a cold or respiratory infection. It lasts for a few weeks and is most common during the winter months.
- Chronic bronchitis is a more serious, long-term condition. It involves ongoing inflammation of the bronchial tubes and is often associated with smoking. People with chronic bronchitis experience frequent bouts of coughing that last for several months or even years.
Bronchitis can develop in stages, starting with a mild cough, sore throat, and congestion, progressing to more severe coughing, chest discomfort, and mucus production. Early identification and treatment of bronchitis, whether acute or chronic, can prevent further complications such as pneumonia or chronic obstructive pulmonary disease (COPD).
Bronchitis Causes
Bronchitis is primarily caused by the inflammation of the bronchial tubes due to infections or irritants. The specific cause depends on the type of bronchitis (acute or chronic).
- Viral infections: The most common cause of acute bronchitis, usually resulting from viruses like the common cold or influenza.
- Bacterial infections: In some cases, bronchitis can result from bacterial infections, though this is less common than viral causes.
- Airborne irritants: Exposure to smoke, dust, or toxic chemicals can irritate the ...
Bronchitis Causes
Bronchitis is primarily caused by the inflammation of the bronchial tubes due to infections or irritants. The specific cause depends on the type of bronchitis (acute or chronic).
- Viral infections: The most common cause of acute bronchitis, usually resulting from viruses like the common cold or influenza.
- Bacterial infections: In some cases, bronchitis can result from bacterial infections, though this is less common than viral causes.
- Airborne irritants: Exposure to smoke, dust, or toxic chemicals can irritate the bronchial tubes, leading to inflammation.
- Allergens: Pollen, mold, and other allergens can cause inflammation, especially in people with allergic bronchitis.
- Chronic smoking: Smoking irritates and damages the bronchial tubes over time, leading to chronic bronchitis.
Bronchitis Risk Factors
Risk factors increase the likelihood of developing bronchitis but do not directly cause the condition.
- Smoking or secondhand smoke exposure: Smokers and those regularly exposed to secondhand smoke have a higher risk of developing both acute and chronic bronchitis.
- Weakened immune system: Individuals with weakened immune systems, such as the elderly, children, or those with chronic illnesses, are more susceptible to infections leading to bronchitis.
- Occupational exposure: Workers exposed to dust, chemical fumes, or other lung irritants ...
Bronchitis Risk Factors
Risk factors increase the likelihood of developing bronchitis but do not directly cause the condition.
- Smoking or secondhand smoke exposure: Smokers and those regularly exposed to secondhand smoke have a higher risk of developing both acute and chronic bronchitis.
- Weakened immune system: Individuals with weakened immune systems, such as the elderly, children, or those with chronic illnesses, are more susceptible to infections leading to bronchitis.
- Occupational exposure: Workers exposed to dust, chemical fumes, or other lung irritants are at higher risk of chronic bronchitis.
- Frequent respiratory infections: People who often experience colds, flu, or sinus infections have a higher chance of developing acute bronchitis.
- Gastroesophageal reflux disease (GERD): Those with GERD may have frequent acid reflux, which can irritate the bronchial tubes, increasing the risk of bronchitis.
Bronchitis Symptoms
The symptoms of bronchitis can vary depending on whether it is acute or chronic, but there are common signs to watch for in both types.
- Persistent cough: A frequent, heavy cough is a hallmark symptom of bronchitis.
- Production of mucus: Coughing up clear, white, yellow, or greenish mucus (phlegm) is common.
- Chest discomfort: Individuals may feel tightness or pain in the chest, especially when coughing.
- Fatigue: The body's effort to fight off inflammation can lead to feelings of ...
Bronchitis Symptoms
The symptoms of bronchitis can vary depending on whether it is acute or chronic, but there are common signs to watch for in both types.
- Persistent cough: A frequent, heavy cough is a hallmark symptom of bronchitis.
- Production of mucus: Coughing up clear, white, yellow, or greenish mucus (phlegm) is common.
- Chest discomfort: Individuals may feel tightness or pain in the chest, especially when coughing.
- Fatigue: The body's effort to fight off inflammation can lead to feelings of exhaustion and fatigue.
- Shortness of breath: Difficulty breathing or wheezing may occur, especially after physical activity.
- Sore throat: Bronchitis can start with a scratchy or sore throat, which may worsen as the condition progresses.
Bronchitis Diagnosis
Diagnosing bronchitis involves a combination of medical history, physical exams, and specific tests to determine the underlying cause.
- Physical examination: A doctor will listen to your lungs with a stethoscope to detect any wheezing or abnormal sounds.
- Chest X-ray: An X-ray can help rule out pneumonia or other lung conditions that may mimic bronchitis symptoms.
- Sputum test: Testing mucus that you cough up can identify infections, such as bacterial bronchitis or a possible allergic response.
- Pulmonary function test ...
Bronchitis Diagnosis
Diagnosing bronchitis involves a combination of medical history, physical exams, and specific tests to determine the underlying cause.
- Physical examination: A doctor will listen to your lungs with a stethoscope to detect any wheezing or abnormal sounds.
- Chest X-ray: An X-ray can help rule out pneumonia or other lung conditions that may mimic bronchitis symptoms.
- Sputum test: Testing mucus that you cough up can identify infections, such as bacterial bronchitis or a possible allergic response.
- Pulmonary function test: This test measures lung capacity and how well air flows into the lungs, which can help detect chronic bronchitis or other lung diseases like COPD.
- Blood tests: Blood tests may be used to check for infections or other health conditions that may be contributing to your symptoms.
Natural Treatments for Bronchitis
There are several natural remedies that can help relieve bronchitis symptoms by supporting the healing process and strengthening the respiratory system. Click on natural treatments for bronchitis to find a detailed list of all the natural solutions to treat and prevent bronchitis, including various natural therapies, diet programs, alternative medicine, vitamins, supplements, herbal medicine, and home remedies. You can also go to www.aposbook.com to find all the natural treatments for any medical condition IN ONE ...
Natural Treatments for Bronchitis
There are several natural remedies that can help relieve bronchitis symptoms by supporting the healing process and strengthening the respiratory system. Click on natural treatments for bronchitis to find a detailed list of all the natural solutions to treat and prevent bronchitis, including various natural therapies, diet programs, alternative medicine, vitamins, supplements, herbal medicine, and home remedies. You can also go to www.aposbook.com to find all the natural treatments for any medical condition IN ONE CLICK.
Some of the most common natural solutions for bronchitis include:
Diet Programs
Certain diet adjustments can help manage bronchitis by boosting the immune system and reducing inflammation.
- Anti-inflammatory diet: Focus on foods rich in antioxidants and anti-inflammatory properties such as berries, leafy greens, nuts, and fatty fish.
Herbal Medicine
Several herbs are known for their expectorant and anti-inflammatory properties, which can be beneficial for bronchitis.
- Echinacea: Helps reduce respiratory infections and supports immune function.
- Thyme: Acts as a natural expectorant and soothes coughs.
- Licorice root: Eases inflammation in the bronchial tubes and helps expel mucus.
- Ginger: Known for its anti-inflammatory properties, it can reduce airway inflammation and alleviate symptoms.
Vitamins and Supplements
Supporting the immune system and respiratory health with vitamins and supplements can aid in recovery from bronchitis.
- Vitamin C: Strengthens the immune system and helps the body fight infections more effectively.
- Zinc: Helps the body resist infection and can shorten the duration of bronchitis symptoms.
Alternative Medicine
Several alternative therapies can provide relief for bronchitis symptoms and help speed up recovery.
- Steam inhalation: Inhaling steam from a bowl of hot water can help clear mucus from the lungs and ease breathing.
- Acupuncture: This ancient Chinese practice may help relieve chest tightness, reduce coughing, and strengthen lung function.
- Chest physiotherapy: Techniques like chest percussion can help loosen mucus and make it easier to expel.
Before starting any natural treatments, including diet changes, herbal remedies, or supplements, it’s important to consult with a healthcare professional to ensure they are safe and appropriate for your specific condition and treatment plan.
Medical Treatment for Bronchitis
In cases where natural solutions are not sufficient, medical treatment may be necessary to address bronchitis symptoms, especially chronic cases.
- Bronchodilators: These medications help relax the muscles around the airways and make breathing easier, often prescribed for chronic bronchitis.
- Corticosteroids: Inhaled or oral corticosteroids can reduce inflammation in the bronchial tubes, helping to alleviate chronic bronchitis symptoms.
- Antibiotics: If bronchitis is caused by a bacterial infection, antibiotics may be prescribed.
- Cough suppressants: In some cases, especially ...
Medical Treatment for Bronchitis
In cases where natural solutions are not sufficient, medical treatment may be necessary to address bronchitis symptoms, especially chronic cases.
- Bronchodilators: These medications help relax the muscles around the airways and make breathing easier, often prescribed for chronic bronchitis.
- Corticosteroids: Inhaled or oral corticosteroids can reduce inflammation in the bronchial tubes, helping to alleviate chronic bronchitis symptoms.
- Antibiotics: If bronchitis is caused by a bacterial infection, antibiotics may be prescribed.
- Cough suppressants: In some cases, especially when coughing is severe, cough suppressants may be recommended to provide relief.
- Oxygen therapy: For those with severe chronic bronchitis, oxygen therapy can help improve breathing by increasing oxygen intake.
Before starting any medical treatment, it is important to consult with a healthcare professional to ensure that the prescribed medications and therapies are suitable for your individual health needs and medical conditions.
Frequently Asked Questions About Bronchitis
What is bronchitis?
Bronchitis is a condition where the bronchial tubes, responsible for carrying air to and from the lungs, become inflamed. This inflammation leads to coughing, mucus production, and difficulty breathing. It can be acute (short-term) or chronic (long-term).
What causes bronchitis?
Bronchitis has various causes depending on the type. Acute bronchitis is typically caused by viral infections, while chronic bronchitis often results from long-term exposure to irritants like smoking. Other causes include bacterial ...
Frequently Asked Questions About Bronchitis
What is bronchitis?
Bronchitis is a condition where the bronchial tubes, responsible for carrying air to and from the lungs, become inflamed. This inflammation leads to coughing, mucus production, and difficulty breathing. It can be acute (short-term) or chronic (long-term).
What causes bronchitis?
Bronchitis has various causes depending on the type. Acute bronchitis is typically caused by viral infections, while chronic bronchitis often results from long-term exposure to irritants like smoking. Other causes include bacterial infections, airborne irritants, and allergens.
How is acute bronchitis different from chronic bronchitis?
Acute bronchitis lasts for a few weeks and is often triggered by viral infections, similar to the common cold or flu. Chronic bronchitis, on the other hand, is a long-term condition that results from ongoing irritation of the bronchial tubes, usually due to smoking or exposure to pollutants.
Is bronchitis contagious?
If bronchitis is caused by a viral or bacterial infection, it can be contagious. This is especially true for acute bronchitis, as it can spread through droplets when an infected person coughs or sneezes. Chronic bronchitis, caused by irritants like smoke, is not contagious.
Who is most at risk of developing bronchitis?
Certain factors increase your risk of developing bronchitis. These include smoking, exposure to secondhand smoke, weakened immunity, frequent respiratory infections, and exposure to chemicals or dust at work. Gastroesophageal reflux disease (GERD) can also raise your risk by causing irritation in the bronchial tubes.
What are the typical symptoms of bronchitis?
The main symptoms include persistent coughing, mucus production (which can be yellow, green, or clear), shortness of breath, chest discomfort, and fatigue. Chronic bronchitis may cause these symptoms to last for months or even longer.
How is bronchitis diagnosed?
To diagnose bronchitis, your doctor will assess your symptoms and may recommend certain tests. These can include a chest X-ray, sputum test, pulmonary function tests, and blood work to rule out other respiratory issues like pneumonia or asthma.
What natural solutions are available for bronchitis?
There are various natural solutions to help manage bronchitis. These include adopting anti-inflammatory diets, using herbal remedies like thyme and eucalyptus, boosting immunity with vitamins C and D, and trying alternative therapies such as steam inhalation or acupuncture. These methods can help alleviate symptoms and support respiratory health.
What medical treatments are commonly prescribed for bronchitis?
If natural remedies are not enough, medical treatments may include bronchodilators to help open airways, corticosteroids to reduce inflammation, and antibiotics if a bacterial infection is present. For chronic bronchitis, oxygen therapy may be necessary to help with breathing.
Can I exercise if I have bronchitis?
While mild exercise can help clear mucus from the lungs and improve breathing, it’s important not to overexert yourself, especially if your symptoms are severe. Always check with your doctor before starting any exercise routine while dealing with bronchitis.
Explore other Diseases and conditions
Natural Treatments for Bronchitis
Bronchitis Dos and Don'ts
A viral infection can decrease the lung capacity and affect its function. Some special breathing exercises can be applied to help improve lung capacity and function, which reduces
Drinking fluids, such as water and hot soups, helps prevent dehydration and thins the mucus in your lungs, making it easier to cough up.
Getting enough sleep helps fight the infection and assists recovery from bronchitis because sleeping soothes breathing and clears mucus from the chest.
Using a breathing steam from a vaporizer or a bowl of hot water or taking a hot shower can help to loosen phlegm.
Avoid cigarette smoke because it causes inflammation that makes bronchitis get worst, and can destroy lung tissue over time. Quitting smoking and eliminating exposure to
Stay away from irritants or try to reduce your time around them as they do irritate your airway (nose, throat, and lungs). Irritants can include dust, mold, air pollution, smoke,
Avoid drinking cold water because it can irritate your airway (nose, throat, and lungs).
Avoid dairy products, such as milk, cheese, and ice cream, because they can increase the amount of mucus your body makes.
Dos and Don'ts

How To Cure Bronchitis In 1 Minute

Bronchitis: Prevention
Library center Bronchitis
Success storiess

Initial Cold & Flu Symptoms: Tai Yin Yang Ming - Acupuncture 123 - The Academy of


























[0]