Ready to leave?
Oops ! Condition name you have entered is invalid.
You are now leaving Aposbook.com and going to an external site managed by another organization.
Please confirm your email address and try to login again.
This account has been deleted. do you want to restore it?

Validate your email
A verification link will be sent to within the next 2 minutes. Please click it to validate your e mail.
*If you didn't get the link, please check your spam folder
Welcome to Aposbook,
As a registered user, you can benefit from the various free tools and services that we provide.
All you need to do is log in to start discussing with others, interacting, asking questions, and sharing your point of view about the various topics.
You can also write reviews and testimonials about any natural solution you have tried and share your experience. Your feedback can be very helpful.
If you are a health expert, you can add information about any topic or suggest text edit. You can also publish content, including articles and videos, about any topic from the related library section.
Together we can help.
The Aposbook Team
Forgot Password?
A validation link will be sent to you by email. Please confirm your address to log in
*If you didn't get the link, please check your spam folder
Please log in to use this feature
Your account has been suspended because you have violated our code of conduct. If you think this was a mistake, you can contact us by email at: support@aposbook.com "Contact us" form.
Success! Thank you for your feedback. Your contribution can make a difference. Together we can help each other.


Health and wellness
Longevity (Live Longer)
Living Longer: Causes, Prevention, and Natural Solutions
Complete Guide to Longevity (Live Longer)
Longevity and Biological Age: Living Longer and Healthier
Longevity refers to living a long life, often surpassing the average lifespan. It is influenced by a variety of factors, including genetics, lifestyle, environment, and advances in healthcare. In recent years, people have become more interested in extending their lifespan and improving the quality of their lives as they age.
One important concept in the study of longevity is biological age. While a person’s chronological age is simply the number of years ...
Longevity and Biological Age: Living Longer and Healthier
Longevity refers to living a long life, often surpassing the average lifespan. It is influenced by a variety of factors, including genetics, lifestyle, environment, and advances in healthcare. In recent years, people have become more interested in extending their lifespan and improving the quality of their lives as they age.
One important concept in the study of longevity is biological age. While a person’s chronological age is simply the number of years they’ve lived, biological age reflects how well their body is functioning based on the health of their cells, tissues, and organs. For example, a person may be 30 years old chronologically, but due to factors such as poor diet, lack of exercise, chronic stress, or smoking, their biological age could be closer to 50. This means their body is aging faster than it should, which could lead to earlier onset of age-related diseases and a shorter lifespan. Conversely, someone who takes care of their health might have a biological age younger than their actual years.
Biological age is influenced by many factors, such as genetics, lifestyle habits, and environmental exposure. Scientists measure biological age through various markers, such as telomere length (the protective caps on chromosomes that shorten with age) and epigenetic changes, which are modifications in gene expression caused by lifestyle and environmental factors.
Advances in science and healthcare are making it possible not just to extend life, but to improve the quality of those extra years. Some researchers believe that with breakthroughs in cellular therapy, genetics, and anti-aging treatments, humans could potentially live to 120 or even 150 years. The focus isn’t solely on living longer but on achieving a healthier, more vital old age—delaying the onset of diseases and maintaining mental and physical well-being throughout life.
Key Causes of Longevity: What Contributes to a Longer, Healthier Life
Several factors affect longevity, ranging from genetics to lifestyle choices. Here are the primary causes that influence longevity and living a healthier life:
- Genetics: Some individuals inherit genes that favor longevity. Variants in genes related to DNA repair, inflammation, and metabolism can contribute to a longer lifespan.
- Lifestyle: Healthy lifestyle choices, such as abstaining from smoking, limiting alcohol consumption, and engaging in regular physical activity, are direct contributors to ...
Key Causes of Longevity: What Contributes to a Longer, Healthier Life
Several factors affect longevity, ranging from genetics to lifestyle choices. Here are the primary causes that influence longevity and living a healthier life:
- Genetics: Some individuals inherit genes that favor longevity. Variants in genes related to DNA repair, inflammation, and metabolism can contribute to a longer lifespan.
- Lifestyle: Healthy lifestyle choices, such as abstaining from smoking, limiting alcohol consumption, and engaging in regular physical activity, are direct contributors to a longer life. People who follow these habits are less likely to suffer from chronic diseases and age-related issues.
- Diet: Consuming a nutrient-rich diet, particularly one high in antioxidants, healthy fats, and plant-based foods, supports longevity. Diets like the Mediterranean diet, rich in fruits, vegetables, nuts, and whole grains, are associated with reduced aging-related diseases.
- Exercise: Regular physical activity enhances cardiovascular health, reduces inflammation, and promotes healthy cellular function. Exercise also helps maintain muscle mass and bone density, which are critical as we age.
- Mental health and stress management: Reducing chronic stress and maintaining mental well-being have direct effects on lifespan. Practices like mindfulness, meditation, and adequate sleep support brain health and emotional balance.
- Social connections: Strong social networks and meaningful relationships contribute to both emotional health and longevity. Studies show that those with strong social ties tend to live longer.
- Avoiding harmful behaviors: Abstaining from smoking, excessive alcohol consumption, and drug use helps to avoid premature aging and reduces the risk of life-threatening diseases like cancer and heart disease.
Major Risk Factors Impacting Longevity: What to Avoid for a Longer Life
While some factors enhance longevity, there are several risk factors that can shorten lifespan and reduce quality of life. Understanding and mitigating these risks can help promote healthier aging:
- Chronic diseases: Conditions like heart disease, diabetes, cancer, and Alzheimer's are major contributors to early mortality. Managing these conditions early on, or preventing them through lifestyle changes, is key to longevity.
- Obesity: Excess weight puts stress on the body ...
Major Risk Factors Impacting Longevity: What to Avoid for a Longer Life
While some factors enhance longevity, there are several risk factors that can shorten lifespan and reduce quality of life. Understanding and mitigating these risks can help promote healthier aging:
- Chronic diseases: Conditions like heart disease, diabetes, cancer, and Alzheimer's are major contributors to early mortality. Managing these conditions early on, or preventing them through lifestyle changes, is key to longevity.
- Obesity: Excess weight puts stress on the body and increases the risk of developing chronic conditions, such as heart disease and diabetes, which negatively impact lifespan.
- Sedentary lifestyle: Lack of physical activity leads to a host of health problems, including obesity, reduced muscle strength, and poor cardiovascular health, all of which can reduce longevity.
- Social isolation: A lack of meaningful social connections is associated with higher mortality rates and poor mental health outcomes. Loneliness has been compared to smoking 15 cigarettes a day in terms of its impact on health.
- Chronic stress: Prolonged exposure to stress hormones can weaken the immune system, promote inflammation, and accelerate aging. Stress management techniques are vital for reducing this risk.
- Environmental factors: Exposure to pollution, toxins, and chemicals can damage cells and increase the risk of diseases that shorten lifespan.
Signs of Longevity: Symptoms That Suggest a Longer, Healthier Life
Identifying symptoms associated with longevity can provide insights into healthy aging and overall well-being. These indicators often reflect a body functioning optimally and suggest that an individual is likely to enjoy a longer, healthier life. Key symptoms of longevity include:
- Physical Vitality: High levels of energy and endurance, allowing individuals to engage in daily activities and exercise with ease.
- Cognitive Sharpness: Clear thinking, good memory retention, and effective problem-solving abilities ...
Signs of Longevity: Symptoms That Suggest a Longer, Healthier Life
Identifying symptoms associated with longevity can provide insights into healthy aging and overall well-being. These indicators often reflect a body functioning optimally and suggest that an individual is likely to enjoy a longer, healthier life. Key symptoms of longevity include:
- Physical Vitality: High levels of energy and endurance, allowing individuals to engage in daily activities and exercise with ease.
- Cognitive Sharpness: Clear thinking, good memory retention, and effective problem-solving abilities.
- Stable Weight: Maintenance of a healthy weight through balanced nutrition and regular physical activity.
- Robust Immunity: Rare occurrences of illness and quick recovery from infections, indicating a strong immune system.
- Good Mobility: Flexibility, strength, and balance that support active living and independence.
- Positive Mental Health: Resilience, emotional stability, and effective stress management.
- Healthy Skin and Hair: Resilient, elastic skin and strong hair, which are signs of good overall health and effective self-care.
Diagnostic Tools and Methods for Evaluating Longevity
Diagnosing longevity involves evaluating various aspects of biological aging to understand how well an individual is aging compared to their chronological age. Here are the key diagnostic tests and tools associated with modern research in longevity:
- Epigenetic Age Testing: Epigenetic age testing analyzes DNA methylation patterns to estimate biological age. DNA methylation changes with age and can provide a comprehensive measure of biological age based on these molecular changes. This test reflects ...
Diagnostic Tools and Methods for Evaluating Longevity
Diagnosing longevity involves evaluating various aspects of biological aging to understand how well an individual is aging compared to their chronological age. Here are the key diagnostic tests and tools associated with modern research in longevity:
- Epigenetic Age Testing: Epigenetic age testing analyzes DNA methylation patterns to estimate biological age. DNA methylation changes with age and can provide a comprehensive measure of biological age based on these molecular changes. This test reflects various biological processes and is considered one of the most accurate methods for assessing biological age.
- Telomere Length Measurement: Telomere length measurement evaluates the length of telomeres, the protective caps on chromosomes that shorten with age. While it is a specific indicator of cellular aging, telomere length provides useful information about the rate of cellular aging and overall cellular health.
- Sirtuin Activity: Sirtuins are proteins involved in regulating cellular processes related to aging and metabolism. Testing sirtuin activity or the expression of sirtuin-related genes provides insights into how well these proteins are functioning and their potential impact on aging and health.
- Cellular Senescence Markers: Tests that detect markers of cellular senescence, such as the presence of senescence-associated beta-galactosidase (SA-β-gal), provide information on the extent of cellular aging. Cellular senescence is linked to aging and various age-related diseases.
- Oxidative Stress Markers: Advanced tests measure markers of oxidative stress, which can indicate how well your body is handling the biochemical processes associated with aging. High levels of oxidative stress are linked to accelerated aging and age-related conditions.
- Biomarker Panels for Aging: Comprehensive biomarker panels include a range of specific biomarkers related to aging, such as inflammatory markers, hormone levels, and metabolic indicators. These panels offer a detailed picture of an individual's aging process and overall health.
Natural Solutions for Longevity
There are several natural remedies that can be used to promote longevity and living healthier. Click on natural treatments for longevity to find a detailed list of all the natural solutions to prolong life and prevent premature aging, including various natural therapies, diet programs, alternative medicine, vitamins, supplements, herbal medicine, and home remedies. You can also go to www.aposbook.com to find all natural treatments for any medical condition IN ONE CLICK.
Meanwhile, some ...
Natural Solutions for Longevity
There are several natural remedies that can be used to promote longevity and living healthier. Click on natural treatments for longevity to find a detailed list of all the natural solutions to prolong life and prevent premature aging, including various natural therapies, diet programs, alternative medicine, vitamins, supplements, herbal medicine, and home remedies. You can also go to www.aposbook.com to find all natural treatments for any medical condition IN ONE CLICK.
Meanwhile, some of the most common natural solutions that can be used for longevity include.
Diet Programs
- Intermittent Fasting: Intermittent fasting involves cycles of eating and fasting. This diet can promote longevity by triggering cellular repair processes like autophagy, which removes damaged cells and supports cellular rejuvenation. It can also reduce oxidative stress and inflammation, which are linked to aging.
- Collagen Diet: Consuming collagen, particularly hydrolyzed collagen, may support cellular health by providing amino acids essential for maintaining the structural integrity of cells and tissues. Collagen supports skin elasticity and joint health, which can indirectly influence overall cellular function and aging.
- Caloric Restriction: Caloric restriction reduces calorie intake without malnutrition. It has been shown to extend lifespan in various organisms by enhancing cellular repair mechanisms, reducing oxidative stress, and improving metabolic function.
Vitamins and Supplements
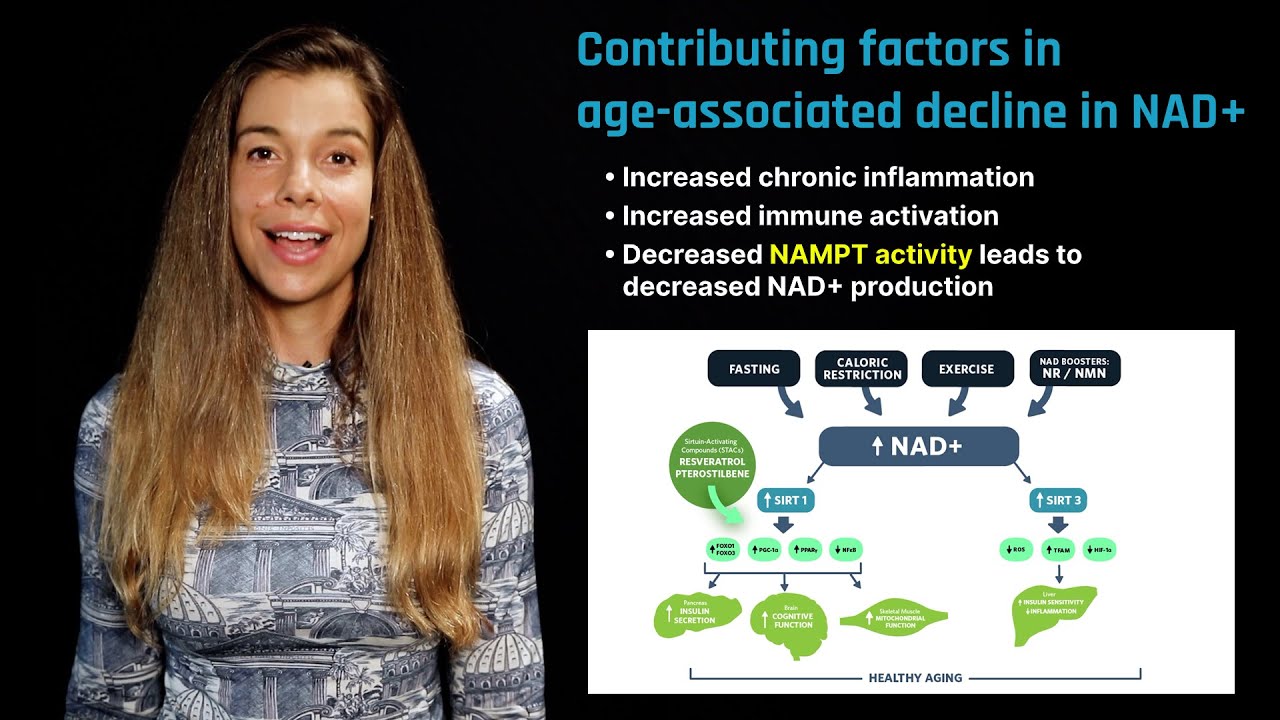
- NAD+ Precursors (e.g., NMN, NR): NAD+ (nicotinamide adenine dinucleotide) is crucial for cellular metabolism and repair. Precursors like NMN (Nicotinamide Mononucleotide) and NR (Nicotinamide Riboside) aim to boost NAD+ levels, supporting cellular energy production and mitigating age-related decline in cellular function.
- Glutathione: Known as a major antioxidant, glutathione helps protect cells from oxidative damage and supports cellular detoxification processes. High levels of glutathione can help maintain cellular health and potentially extend lifespan.
- Resveratrol: This compound, found in red wine and grapes, activates sirtuins, which are proteins involved in regulating cellular aging and metabolism. Resveratrol may mimic some effects of caloric restriction, promoting cellular repair and longevity.
- Alpha-Lipoic Acid: This antioxidant helps regenerate other antioxidants like vitamin C and E. It supports mitochondrial function and reduces oxidative stress, which may contribute to improved cellular health and longevity.
- N-Acetylcysteine (NAC): NAC is a precursor to glutathione and helps in its production. It also has antioxidant properties that support cellular health and protect against oxidative damage.
Herbal Medicine
- Astragalus: Contains compounds that may support telomere length and enhance cellular repair, potentially influencing lifespan. Research is ongoing, but it has been traditionally used to support overall vitality.
- Ginseng: Some studies suggest it may impact cellular aging processes and improve vitality by enhancing cellular energy and stress resilience.
Medical Treatment for Longevity
There are several medical treatments and interventions that are being explored or used to potentially extend lifespan and improve healthspan. These treatments include:
- Senolytics: Senolytics are drugs designed to target and remove senescent cells, which accumulate with age and contribute to age-related diseases. These treatments aim to reduce inflammation and improve overall health by clearing these dysfunctional cells.
- Metformin: Metformin is an established medication for type 2 diabetes that is being investigated for its potential ...
Medical Treatment for Longevity
There are several medical treatments and interventions that are being explored or used to potentially extend lifespan and improve healthspan. These treatments include:
- Senolytics: Senolytics are drugs designed to target and remove senescent cells, which accumulate with age and contribute to age-related diseases. These treatments aim to reduce inflammation and improve overall health by clearing these dysfunctional cells.
- Metformin: Metformin is an established medication for type 2 diabetes that is being investigated for its potential anti-aging effects. It works by improving insulin sensitivity and has been shown to affect various biological pathways associated with aging.
- Rapamycin: Originally used as an immunosuppressant, rapamycin is being studied for its potential to extend lifespan. It influences cellular growth, metabolism, and autophagy (the body's process of cleaning out damaged cells), which may contribute to slowing down the aging process.
- Growth Hormone Therapy: Human Growth Hormone (HGH) therapy is used to address deficiencies and is explored for its potential to improve physical function and reduce age-related decline. It aims to enhance muscle mass, bone density, and overall vitality.
- Testosterone Replacement Therapy (TRT): For individuals with low testosterone levels, testosterone replacement therapy is used to improve symptoms such as decreased muscle mass, fatigue, and diminished libido. It may help maintain physical function and overall youth and well-being.
- Gene Therapy and Genetic Interventions:
- Gene Editing: Techniques such as CRISPR are being explored to correct genetic mutations associated with aging and age-related diseases. The goal is to enhance cellular function and extend lifespan.
- Gene Therapy: Research is ongoing into modifying genes to improve cellular repair mechanisms and potentially slow the aging process.
- Stem Cell Therapy: Stem cell therapy aims to regenerate damaged tissues and organs. By using stem cells to repair or replace aged or damaged cells, these treatments seek to restore function and promote longevity.
- Cell Reprogramming: Cell reprogramming involves converting adult cells into a more youthful state, potentially reversing some aspects of cellular aging. This approach aims to rejuvenate tissues and extend healthspan.
- Anti-Aging Vaccines: Research is underway to develop vaccines targeting age-related diseases. These vaccines aim to prevent or mitigate conditions that typically arise with aging, potentially contributing to longer and healthier life.
Frequently Asked Questions About Longevity
What is longevity?
Longevity refers to the length of an individual's life, particularly when it is extended beyond the average lifespan. It often focuses on not just living longer, but also maintaining health and vitality throughout those additional years.
What factors influence longevity?
Key factors influencing longevity include:
- Genetics: Inherited traits can play a significant role in lifespan and health.
- Lifestyle: Diet, exercise, and daily habits can impact overall health and longevity.
- Environment: Living conditions ...
Frequently Asked Questions About Longevity
What is longevity?
Longevity refers to the length of an individual's life, particularly when it is extended beyond the average lifespan. It often focuses on not just living longer, but also maintaining health and vitality throughout those additional years.
What factors influence longevity?
Key factors influencing longevity include:
- Genetics: Inherited traits can play a significant role in lifespan and health.
- Lifestyle: Diet, exercise, and daily habits can impact overall health and longevity.
- Environment: Living conditions, pollution levels, and access to healthcare affect longevity.
- Medical Care: Quality of healthcare, including preventive measures and treatment for illnesses, influences lifespan.
How can I increase my longevity?
Here are key strategies to increase longevity with brief explanations:
- NAD+ Boosting: Enhancing NAD+ levels through exercise, dietary supplements like niacin, and caloric restriction can support cellular health and energy metabolism, potentially slowing aging processes.
- Intermittent Fasting (IF): Alternating between eating and fasting periods promotes cellular repair through autophagy, improves insulin sensitivity, and may enhance metabolic health.
- Ketogenic Diet (Keto): A high-fat, low-carb diet shifts metabolism to ketones, which may reduce inflammation, improve metabolic health, and offer neuroprotective benefits.
- Glutathione: As a potent antioxidant, glutathione helps reduce oxidative stress, supports detoxification, and enhances immune function, potentially contributing to longer, healthier life.
- Regular Exercise: Engage in physical activities, including aerobic and strength-training exercises.
- Adequate Sleep: Ensure you get 7-9 hours of quality sleep each night.
- Avoid Harmful Habits: Refrain from smoking, limit alcohol consumption, and avoid excessive drug use.
What are some dietary recommendations for longevity?
Dietary recommendations for longevity include:
- Whole Foods: Focus on consuming whole, unprocessed foods rich in nutrients.
- Healthy Fats: Include sources of healthy fats such as avocados, nuts, and olive oil.
- Lean Proteins: Incorporate lean protein sources like fish, poultry, and legumes.
- Antioxidant-Rich Foods: Eat foods high in antioxidants, such as berries, leafy greens, and nuts, to combat oxidative stress.
How does exercise impact longevity?
Regular exercise contributes to longevity by:
- Improving Cardiovascular Health: Enhances heart and lung function, reducing the risk of heart disease.
- Maintaining Healthy Weight: Helps manage body weight and reduces the risk of obesity-related conditions.
- Boosting Mood and Mental Health: Exercise releases endorphins, which can improve mood and reduce stress.
- Enhancing Muscle and Bone Strength: Prevents muscle loss and supports bone health, reducing the risk of fractures and falls.
What role does sleep play in longevity?
Adequate sleep is crucial for longevity because:
- Restores Body Functions: Allows for cellular repair and maintenance of bodily functions.
- Regulates Metabolism: Helps balance hormones that regulate appetite and metabolism.
- Supports Cognitive Health: Improves memory and cognitive function, reducing the risk of neurodegenerative diseases.
- Enhances Immune Function: Boosts the immune system, aiding in the prevention of illnesses.
How can stress affect longevity?
Chronic stress negatively impacts longevity by:
- Increasing Risk of Chronic Diseases: Can lead to conditions such as heart disease, diabetes, and hypertension.
- Accelerating Aging: Chronic stress can accelerate cellular aging and reduce overall health.
- Compromising Immune System: Weakens the immune system, making the body more susceptible to infections and illnesses.
- Affecting Mental Health: Contributes to anxiety, depression, and cognitive decline.
What are some common myths about longevity?
Common myths about longevity include:
- Myth: Longevity is solely determined by genetics.
Fact: While genetics play a role, lifestyle choices and environmental factors also significantly impact longevity.
- Myth: Only extreme measures can extend lifespan.
Fact: Simple, consistent healthy habits can contribute to a longer, healthier life.
- Myth: Longevity means living a long life in poor health.
Fact: Longevity often focuses on not just extending life but also maintaining good health and quality of life.
Can supplements improve longevity?
- NAD+ Supplements: NAD+ (Nicotinamide Adenine Dinucleotide) is essential for cellular energy production and repair. Supplements like nicotinamide riboside (NR) or nicotinamide mononucleotide (NMN) may boost NAD+ levels, potentially supporting cellular health and slowing the aging process.
- Glutathione: This powerful antioxidant helps combat oxidative stress and supports detoxification processes. Supplementing with glutathione or its precursors (like N-acetylcysteine) may enhance the body’s ability to neutralize free radicals and support overall health.
- Resveratrol: Found in red wine and certain plants, resveratrol is known for its antioxidant properties. It may mimic the effects of caloric restriction by activating sirtuins, which are proteins linked to longevity and cellular repair.
- Coenzyme Q10 (CoQ10): CoQ10 is involved in energy production and acts as an antioxidant. Supplementing with CoQ10 can support cellular energy and protect against oxidative damage, potentially promoting healthy aging.
- Omega-3 Fatty Acids: These essential fats, found in fish oil, have anti-inflammatory properties and support heart and brain health. Omega-3s may contribute to a longer, healthier life by reducing inflammation and supporting cardiovascular function.
- Vitamin D: Adequate levels of vitamin D are crucial for bone health, immune function, and inflammation reduction. Supplementing with vitamin D can help maintain overall health and potentially support longevity.
These supplements, combined with a balanced diet and healthy lifestyle, can contribute to overall well-being and may play a role in extending lifespan and enhancing quality of life.
When should I consult a healthcare provider about longevity?
Consult a healthcare provider if you have concerns about your health, chronic conditions, or lifestyle factors that may impact your longevity. They can offer personalized advice, conduct screenings, and help you develop a plan to improve your overall health and lifespan.
Explore other Health and wellness
Natural Treatments for Longevity (Live Longer)
Longevity (Live Longer) Dos and Don'ts
Eating less can help you live longer and healthier. Research has shown that cutting just 300 to 500 calories a day from your diet could help slowing the signs of aging and
Physical training is very important for anti aging. Doing HIIT (High intensity interval training) is recommended and try to get your heart rate up to 85%.
Eat more nuts because they are rich in protein, fiber, and antioxidants. They also represent a great source of vitamins and minerals, such as copper, magnesium, potassium,
It is recommended to sleep between 7 and 9 hours per night. Sleeping less than 7 hours or more than 9 hours might decrease your lifespan by 38%. Longevity is also linked to
Avoid sun exposure because it can cause DNA damage. Make sure you always put sunscreen or sit in the shade.
Avoid X ray because it can cause DNA damage and prevents cell from reproducing. It can also damage critical cellular systems.
Extreme temperatures, whether from cold or heat stress, can have profound effects on cellular health and longevity. The body’s response to these environmental stresses
Smoking has a profound impact on cellular health and longevity. The toxins in cigarette smoke cause oxidative stress and inflammation, leading to extensive damage to cellular
Excessive alcohol consumption has similarly detrimental effects on cellular health and longevity. Alcohol metabolism generates acetaldehyde, a toxic compound that contributes to
Chronic stress has a significant impact on cellular health and longevity, influencing both the rate of cellular aging and the development of age-related diseases. When the body is
Dos and Don'ts
Library center Longevity (Live Longer)
Success storiess

NMN Trial 1 Year Result | My Physical Changes

NMN Resveratrol Trial 1 Year Result | NMN Reversed My Wife's Menopause??

Results/Problems With NMN Human Trial













































[0]