Ready to leave?
Oops ! Condition name you have entered is invalid.
You are now leaving Aposbook.com and going to an external site managed by another organization.
Please confirm your email address and try to login again.
This account has been deleted. do you want to restore it?

Validate your email
A verification link will be sent to within the next 2 minutes. Please click it to validate your e mail.
*If you didn't get the link, please check your spam folder
Welcome to Aposbook,
As a registered user, you can benefit from the various free tools and services that we provide.
All you need to do is log in to start discussing with others, interacting, asking questions, and sharing your point of view about the various topics.
You can also write reviews and testimonials about any natural solution you have tried and share your experience. Your feedback can be very helpful.
If you are a health expert, you can add information about any topic or suggest text edit. You can also publish content, including articles and videos, about any topic from the related library section.
Together we can help.
The Aposbook Team
Forgot Password?
A validation link will be sent to you by email. Please confirm your address to log in
*If you didn't get the link, please check your spam folder
Please log in to use this feature
Your account has been suspended because you have violated our code of conduct. If you think this was a mistake, you can contact us by email at: support@aposbook.com "Contact us" form.
Success! Thank you for your feedback. Your contribution can make a difference. Together we can help each other.


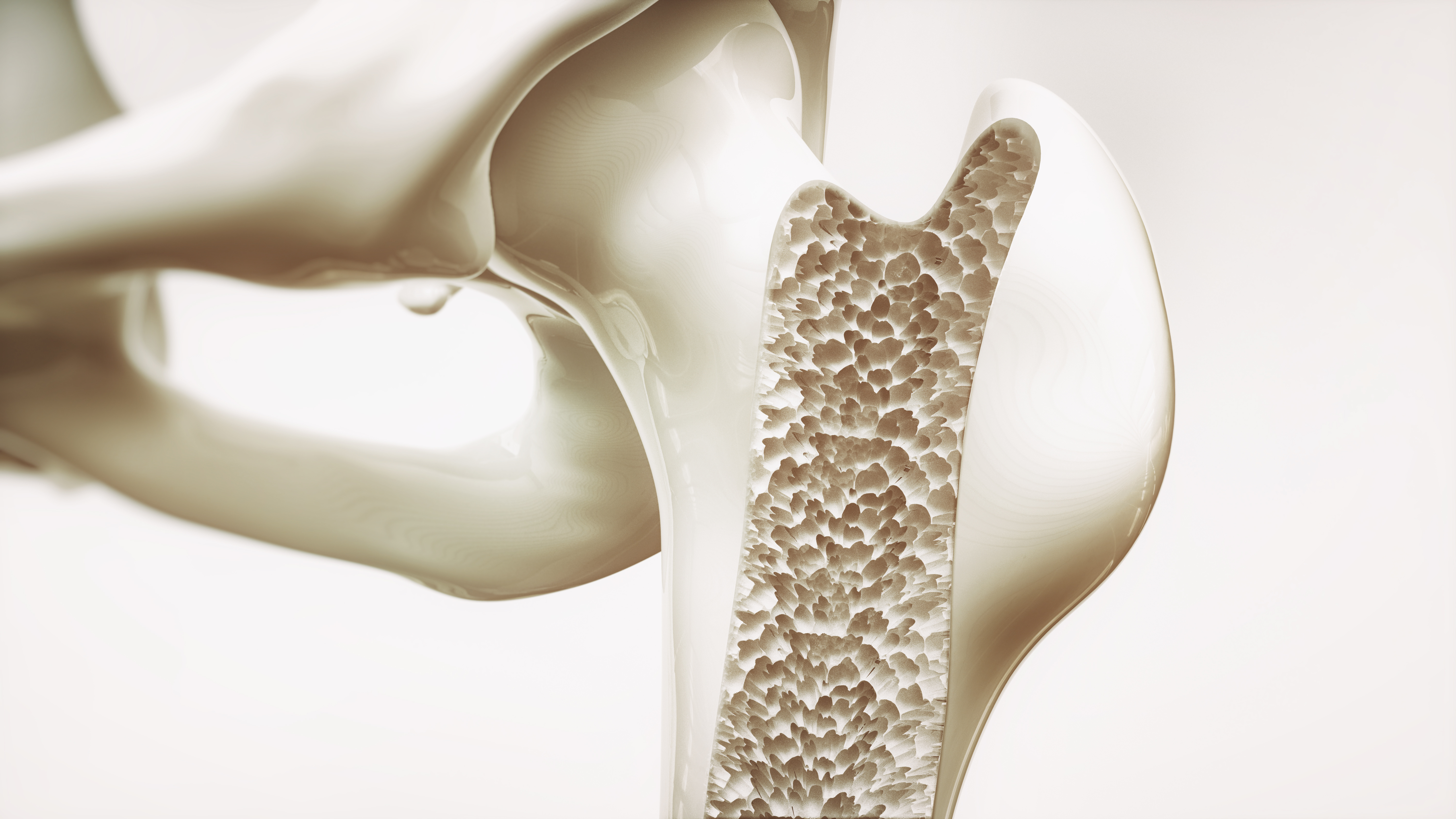
Can Magnesium Help for Osteoporosis?
Complete Guide to Magnesium For Osteoporosis
Causes of Osteoporosis Addressed by Magnesium
Osteoporosis is a bone condition characterized by decreased bone density and increased fragility, leading to a higher risk of fractures. The condition is often linked to various general causes, including aging, hormonal changes, nutritional deficiencies, and lack of physical activity. Meanwhile, the specific causes of osteoporosis that can be addressed by magnesium include:
- Magnesium Deficiency: Low levels of magnesium can impair the body's ability to absorb calcium, leading to decreased bone mineral density ...
Causes of Osteoporosis Addressed by Magnesium
Osteoporosis is a bone condition characterized by decreased bone density and increased fragility, leading to a higher risk of fractures. The condition is often linked to various general causes, including aging, hormonal changes, nutritional deficiencies, and lack of physical activity. Meanwhile, the specific causes of osteoporosis that can be addressed by magnesium include:
- Magnesium Deficiency: Low levels of magnesium can impair the body's ability to absorb calcium, leading to decreased bone mineral density.
- Hormonal Changes: Decreased estrogen levels in postmenopausal women can accelerate bone loss, and magnesium plays a role in hormone regulation and bone health.
- Chronic Inflammation: Inflammation can disrupt bone remodeling processes by increasing the activity of osteoclasts, the cells responsible for bone resorption. This imbalance can lead to accelerated bone loss and reduced bone density.
Learn everything about osteoporosis and find all the natural solutions for osteoporosis, including various natural therapies, diet programs, alternative medicine, vitamins, supplements, herbal medicine, and home remedies. Visit www.aposbook.com to find all the natural treatments for any medical condition IN ONE CLICK.
Why Magnesium Helps for Osteoporosis
Magnesium is essential for maintaining bone health and density. Its role in calcium metabolism and its effect on hormonal regulation make it a valuable component in addressing osteoporosis.
- Restore Magnesium Levels: Supplementing magnesium can restore adequate levels, improving calcium absorption and bone health.
- Regulate Hormones: Magnesium supports the regulation of hormones that influence bone density, helping mitigate bone loss associated with hormonal changes.
- Anti-Inflammatory Properties: Magnesium's anti-inflammatory effects can help reduce the inflammation that adversely ...
Why Magnesium Helps for Osteoporosis
Magnesium is essential for maintaining bone health and density. Its role in calcium metabolism and its effect on hormonal regulation make it a valuable component in addressing osteoporosis.
- Restore Magnesium Levels: Supplementing magnesium can restore adequate levels, improving calcium absorption and bone health.
- Regulate Hormones: Magnesium supports the regulation of hormones that influence bone density, helping mitigate bone loss associated with hormonal changes.
- Anti-Inflammatory Properties: Magnesium's anti-inflammatory effects can help reduce the inflammation that adversely affects bone health, promoting better bone remodeling and density.
Magnesium serves as a supportive solution for osteoporosis, often used in conjunction with other treatments such as calcium supplementation and lifestyle modifications.
How Magnesium Works for Osteoporosis
Understanding how magnesium works in the body is essential for grasping its role in supporting bone health. Magnesium participates in various biochemical processes that influence bone density and remodeling. It contributes to the regulation of calcium, the formation of bone structure, and the modulation of inflammatory responses, all of which are critical for maintaining healthy bones. Here are the specific mechanisms through which magnesium exerts its beneficial effects:
- Regulate Calcium Levels: Magnesium helps maintain optimal ...
How Magnesium Works for Osteoporosis
Understanding how magnesium works in the body is essential for grasping its role in supporting bone health. Magnesium participates in various biochemical processes that influence bone density and remodeling. It contributes to the regulation of calcium, the formation of bone structure, and the modulation of inflammatory responses, all of which are critical for maintaining healthy bones. Here are the specific mechanisms through which magnesium exerts its beneficial effects:
- Regulate Calcium Levels: Magnesium helps maintain optimal calcium levels in the body by influencing the absorption of calcium in the intestines and its reabsorption in the kidneys. This balance ensures that sufficient calcium is available for bone mineralization, which is essential for maintaining bone density.
- Support Bone Density: Magnesium is involved in the synthesis of bone matrix proteins, such as osteocalcin, which are critical for bone formation. By facilitating the proper formation of these proteins, magnesium contributes to the structural integrity and strength of bones.
- Stabilize Hormones: Magnesium plays a crucial role in regulating hormones like parathyroid hormone (PTH) and calcitonin. PTH is essential for mobilizing calcium from bones into the bloodstream, while calcitonin helps lower blood calcium levels. By maintaining the balance of these hormones, magnesium supports healthy calcium metabolism and bone health.
- Mitigate Chronic Inflammation: Magnesium reduces the production of pro-inflammatory cytokines, which can disrupt the normal bone remodeling process. By inhibiting these inflammatory markers, magnesium helps maintain the delicate balance between bone resorption and formation, thus preventing excessive bone loss associated with chronic inflammation.
Dose and Forms of Magnesium for Osteoporosis
There is no universally agreed-upon dose of magnesium specifically for osteoporosis. For addressing osteoporosis, dosages may vary based on individual needs and specific product formulations, with common supplementation doses typically ranging from 200 to 400 mg per day. Consulting with a healthcare provider for personalized dosing is recommended. The recommended dietary allowance (RDA) for magnesium varies by age and gender, generally ranging from 310 to 420 mg per day.
Best Types of Magnesium ...
Dose and Forms of Magnesium for Osteoporosis
There is no universally agreed-upon dose of magnesium specifically for osteoporosis. For addressing osteoporosis, dosages may vary based on individual needs and specific product formulations, with common supplementation doses typically ranging from 200 to 400 mg per day. Consulting with a healthcare provider for personalized dosing is recommended. The recommended dietary allowance (RDA) for magnesium varies by age and gender, generally ranging from 310 to 420 mg per day.
Best Types of Magnesium for Osteoporosis
- Magnesium Citrate: Known for its high bioavailability, magnesium citrate is effective in increasing magnesium levels and is often recommended for bone health.
- Magnesium Glycinate: This form is well-absorbed and less likely to cause gastrointestinal side effects, making it suitable for long-term use.
- Magnesium Malate: This type may help with muscle fatigue and is often used for its potential benefits in energy production.
- Magnesium Threonate: While more research is needed, this form has shown promise in supporting cognitive health, which can indirectly benefit individuals concerned about overall well-being in osteoporosis.
In conclusion, magnesium citrate and magnesium glycinate are among the best types for addressing osteoporosis due to their high bioavailability and effectiveness in improving magnesium levels. For individuals seeking convenience, capsules or liquid forms may be preferable.
Available Forms of Magnesium for Osteoporosis
Magnesium supplements are available in various forms, including:
- Capsules: Easy to swallow and convenient for on-the-go supplementation.
- Tablets: Commonly available, though they may be larger and harder to swallow.
- Powder: Can be mixed with liquids, providing flexibility in dosage.
- Liquid: Often more easily absorbed and suitable for those who have difficulty swallowing pills.
Magnesium for Osteoporosis: Precautions
When considering magnesium supplementation for osteoporosis, it is essential to take the following precautions to ensure safety and effectiveness:
- Consult a Healthcare Provider: Before starting magnesium supplements, it is crucial to consult with a healthcare professional, especially for individuals with underlying health conditions. A healthcare provider can assess the individual's overall health, determine if magnesium supplementation is necessary, and recommend appropriate dosages based on individual needs.
- Monitor Kidney Function: Magnesium is primarily excreted through the kidneys ...
Magnesium for Osteoporosis: Precautions
When considering magnesium supplementation for osteoporosis, it is essential to take the following precautions to ensure safety and effectiveness:
- Consult a Healthcare Provider: Before starting magnesium supplements, it is crucial to consult with a healthcare professional, especially for individuals with underlying health conditions. A healthcare provider can assess the individual's overall health, determine if magnesium supplementation is necessary, and recommend appropriate dosages based on individual needs.
- Monitor Kidney Function: Magnesium is primarily excreted through the kidneys. Individuals with impaired kidney function may struggle to eliminate excess magnesium, leading to toxicity. Regular monitoring of kidney function through blood tests is advised, especially for those with pre-existing kidney issues or conditions that may affect renal health.
- Be Aware of Drug Interactions: Magnesium can interact with various medications, potentially altering their effectiveness or increasing the risk of side effects. It is advisable to discuss any current medications with a healthcare provider to ensure there are no significant interactions with magnesium supplements.
- Gradual Dosage Increase: If starting supplementation, it may be beneficial to begin with a lower dose and gradually increase it. This approach can help the body adjust and minimize gastrointestinal side effects, such as diarrhea or nausea.
- Dietary Considerations: While supplementation can help, obtaining magnesium through diet is also essential. Foods rich in magnesium, such as leafy greens, nuts, seeds, and whole grains, should be incorporated into the diet. This balanced approach helps maintain optimal magnesium levels and overall bone health.
- Stay Informed on Recommended Dosages: Follow the recommended dietary allowance (RDA) guidelines for magnesium and adjust based on individual health status and needs. Excessive magnesium intake can lead to serious health issues, so staying within recommended limits is vital for safety.
By adhering to these precautions, individuals can safely incorporate magnesium supplementation into their osteoporosis management plan, supporting their bone health while minimizing potential risks.
Magnesium for Osteoporosis: Side Effects
Possible side effects of magnesium supplementation for osteoporosis may include:
- Diarrhea: Excessive magnesium intake can lead to gastrointestinal upset.
- Nausea: Some individuals may experience nausea, especially with high doses.
- Abdominal cramping: High doses may cause discomfort in the digestive tract.
- Fatigue: In rare cases, excessive magnesium can lead to lethargy or weakness.
- Heart rhythm disturbances: Very high doses can potentially impact heart rhythms, particularly in individuals with pre-existing conditions.
It's essential to adhere to recommended ...
Magnesium for Osteoporosis: Side Effects
Possible side effects of magnesium supplementation for osteoporosis may include:
- Diarrhea: Excessive magnesium intake can lead to gastrointestinal upset.
- Nausea: Some individuals may experience nausea, especially with high doses.
- Abdominal cramping: High doses may cause discomfort in the digestive tract.
- Fatigue: In rare cases, excessive magnesium can lead to lethargy or weakness.
- Heart rhythm disturbances: Very high doses can potentially impact heart rhythms, particularly in individuals with pre-existing conditions.
It's essential to adhere to recommended dosages to minimize the risk of these side effects.
FAQ About Magnesium for Osteoporosis
How does magnesium help with osteoporosis?
Magnesium plays a crucial role in bone health by aiding calcium absorption, regulating bone remodeling, and supporting overall skeletal structure.
What is the recommended dosage of magnesium for osteoporosis?
While there is no universally agreed-upon dosage, general guidelines suggest that adults typically require between 310 to 420 mg of magnesium per day, depending on age and gender. Specific supplementation for osteoporosis may vary, often ranging from 200 to 400 ...
FAQ About Magnesium for Osteoporosis
How does magnesium help with osteoporosis?
Magnesium plays a crucial role in bone health by aiding calcium absorption, regulating bone remodeling, and supporting overall skeletal structure.
What is the recommended dosage of magnesium for osteoporosis?
While there is no universally agreed-upon dosage, general guidelines suggest that adults typically require between 310 to 420 mg of magnesium per day, depending on age and gender. Specific supplementation for osteoporosis may vary, often ranging from 200 to 400 mg per day.
What are the best forms of magnesium for osteoporosis?
Some effective forms of magnesium for bone health include magnesium citrate, magnesium malate, and magnesium glycinate, as they are easily absorbed by the body.
Can I get enough magnesium from my diet to support bone health?
Yes, many foods are rich in magnesium, including leafy green vegetables, nuts, seeds, whole grains, and legumes. A balanced diet can help meet magnesium needs for bone health.
Are there any side effects of magnesium supplements?
Common side effects may include gastrointestinal issues like diarrhea, nausea, and stomach cramps, particularly when taken in high doses. It's essential to follow recommended dosages.
Is magnesium supplementation safe for everyone?
While magnesium is generally safe for most people, those with kidney issues or certain health conditions should consult a healthcare provider before taking supplements.
Can magnesium interact with medications?
Yes, magnesium can interact with various medications, such as certain antibiotics and blood pressure medications, potentially affecting their efficacy. Consulting a healthcare provider is recommended.
How long does it take to see results from magnesium supplementation for osteoporosis?
The timeline for seeing improvements can vary based on individual health status, but it may take several weeks to months of consistent supplementation to notice changes in bone density or overall health.
Can I take magnesium supplements with calcium?
Yes, magnesium can be taken with calcium, as both minerals work together to support bone health. However, it’s essential to maintain a balanced ratio between the two.
What should I do if I experience side effects from magnesium supplements?
If you experience side effects, such as gastrointestinal discomfort, it is advisable to reduce the dosage or try a different form of magnesium. Consult a healthcare provider if symptoms persist.
Disclaimer: The published information is based on research and published medical sources. It is provided for educational purposes only and is not intended to replace professional medical advice. Always consult with your doctor or healthcare provider regarding any questions you may have about your health. We are not responsible for any actions taken based on this information, nor for any errors, omissions, or inaccuracies in the content. Medical research is constantly evolving, and the information presented may not reflect the most current medical standards.
October 2024
AposBook
Reviews & Testimonials
-
Overall rating
-
Success Rate
-
Effectiveness
-
Accessiblity
-
Safety
-
Fast result
-
Ease of use
Add review
Was solution successfull?
Overall rating score
Rate each parameters
Effective
Accessible
Safe
Fast results
Easy to apply
Review title
Add images to support your review(if any)
Support images
You can review a solution if you have used it personally. Please remain objective and genuine. Your input can help others.
You have already reviewed this
Please rate all parameters.
Success! Thank you for your feedback. Your contribution can make a difference. Together we can help each other.
What science says about Magnesium For Osteoporosis
Library center Magnesium For Osteoporosis
Additional benefits of Magnesium





 Buy now
Buy now
























[0]