What is folic acid?
Folic acid is a water-soluble vitamin. It’s a synthetic version of folate, one of the B vitamins.
Because your body can’t make folate, you need to get it from your diet.
Some foods naturally contain folate. Folic acid is added to other foods. You can also get folic acid from dietary supplements.
What’s the difference between folate and folic acid?
Although the terms “folate” and “folic acid” are often used interchangeably, they are actually different forms of the same vitamin: vitamin B9.
Folic acid has a different structure than folate and has slightly different effects in your body. “Folate” is the generic name that encompasses all forms of vitamin B9, including folic acid and 5-MTHF. Folic acid is a specific synthetic form of this vitamin.
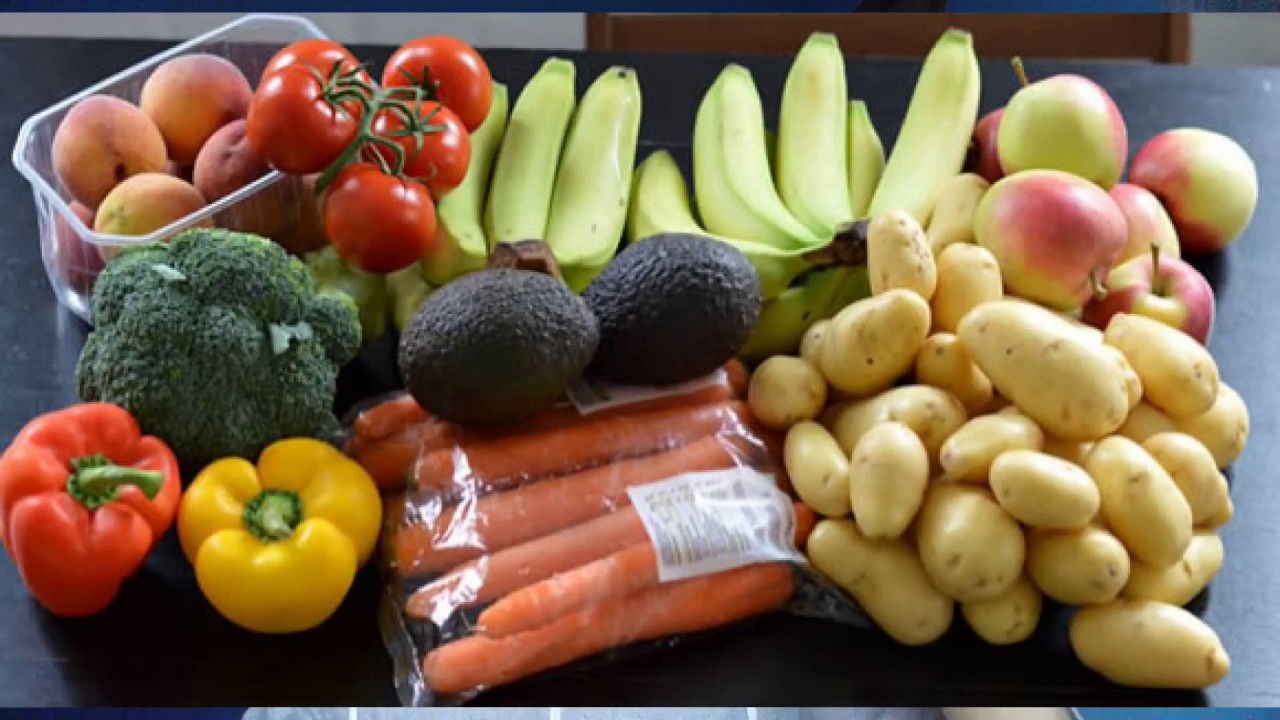
You can find folate in plant and animal foods like these:
- spinach
- kale
- broccoli
- avocado
- citrus fruits
- eggs
- beef liver
Folic acid is added to foods such as flour, ready-to-eat breakfast cereals, and breads.
It’s also in dietary supplements, such as multivitamins.
What does the body use folate for?
Your body uses folate to:
- make and repair DNA
- help cells grow, divide, and work properly
- produce certain proteins
- help red blood cells mature
Folate deficiency can lead to many health problems, including
- anemia
- an increased risk of heart disease and certain cancers
- developmental irregularities in infants if pregnant people don’t get enough folate
Many countries, including the United States, require certain grain products to be fortified with folic acid. Folic acid fortification helps prevent neural tube irregularities in infants.